学习Python中A*算法实现的详细步骤
- PHPz转载
- 2024-01-23 22:51:05767浏览
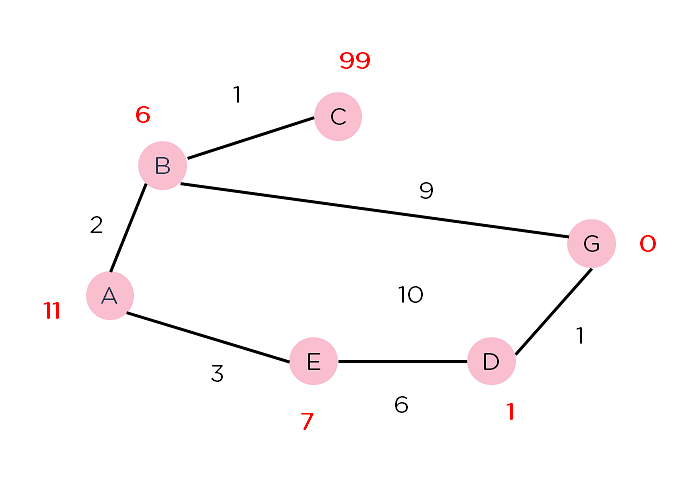
以此加权图为例,用Python实现A*算法。加权图中的节点用粉红色圆圈表示,并且给出了沿节点的路径的权重。节点上方的数字代表节点的启发式值。
首先为算法创建类。一个用于存储与起始节点的距离,另一个用于存储父节点。并将它们初始化为0,以及起始节点。
def aStarAlgo(start_node,stop_node):
open_set=set(start_node)
closed_set=set()
g={}
parents={}
g[start_node]=0
parents[start_node]=start_node找到具有最低f(n)值的相邻节点,针对到达目标节点的条件进行编码。如果不是这种情况,则将当前节点放入打开列表中,并设置其父节点。
While len(open_set)>0: n=None for v in open_set: if n==None or g[v]+heuristic(v)<g[n]+heuristic(n): n=v if n==stop_node or Graph_nodes[n]==None: pass else: for(m,weight)in get_neighbors(n): if m not in open_set and m not in closed_set: open_set.add(m) parents[m]=n g[m]=g[n]+weight
如果相邻的g值低于当前节点并且在封闭列表中,则将其替换为这个新节点作为父节点。
else: if g[m]>g[n]+weight: g[m]=g[n]+weight parents[m]=n if m in closed_set: closed_set.remove(m) open_set.add(m)
如果当前g低于前一个g,并且其相邻在open list中,则将其替换为较低的g值,并将相邻的parent更改为当前节点。
如果不在两个列表中,则将其添加到打开列表并设置其g值。
if n==None:
print('Path does not exist!')
return None
if n==stop_node:
path=[]
while parents[n]!=n:
path.append(n)
n=parents[n]
path.append(start_node)
path.reverse()
print('Path found:{}'.format(path))
return path
open_set.remove(n)
closed_set.add(n)
print('Path does not exist!')
return None现在,定义一个函数来返回相邻节点及其距离。
def get_neighbors(v): if v in Graph_nodes: return Graph_nodes[v] else: return None
此外,创建一个函数来检查启发式值。
def heuristic(n):
H_dist={
'A':11,
'B':6,
'C':99,
'D':1,
'E':7,
'G':0,
}
return H_dist[n]描述一下图表并调用A*函数。
Graph_nodes={
'A':[('B',2),('E',3)],
'B':[('C',1),('G',9)],
'C':Node,
'E':[('D',6)],
'D':[('G',1)],
}
aStarAlgo('A','G')算法遍历图,找到代价最小的路径。
这是通过E => D => G。
以上是学习Python中A*算法实现的详细步骤的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
声明:
本文转载于:163.com。如有侵权,请联系admin@php.cn删除

