在准确率-召回率曲线上,同样的点是用不同的坐标轴绘制的。警告:左边的第一个红点(0%召回率,100%精度)对应于0条规则。左边的第二个点是第一个规则,等等。
Skope-rules使用树模型生成规则候选项。首先建立一些决策树,并将从根节点到内部节点或叶子节点的路径视为规则候选项。然后通过一些预定义的标准(如精确度和召回率)对这些候选规则进行过滤。只有那些精确度和召回率高于其阈值的才会被保留。最后,应用相似性过滤来选择具有足够多样性的规则。一般情况下,应用Skope-rules来学习每个根本原因的潜在规则。
项目地址:https://github.com/scikit-learn-contrib/skope-rules
- Skope-rules是一个建立在scikit-learn之上的Python机器学习模块,在3条款BSD许可下发布。
- Skope-rules旨在学习逻辑的、可解释的规则,用于 "界定 "目标类别,即高精度地检测该类别的实例。
- Skope-rules是决策树的可解释性和随机森林的建模能力之间的一种权衡。
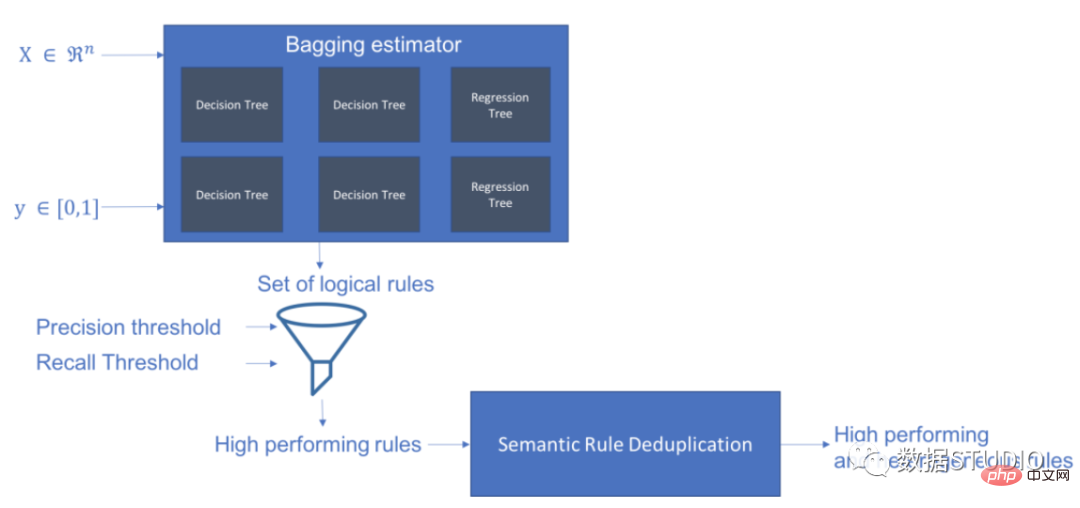
schema
安装
可以使用 pip 获取最新资源:
pip install skope-rules
快速开始
SkopeRules 可用于描述具有逻辑规则的类:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from skrules import SkopeRules
dataset = load_iris()
feature_names = ['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width']
clf = SkopeRules(max_depth_duplicatinotallow=2,
n_estimators=30,
precision_min=0.3,
recall_min=0.1,
feature_names=feature_names)
for idx, species in enumerate(dataset.target_names):
X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target
clf.fit(X, y == idx)
rules = clf.rules_[0:3]
print("Rules for iris", species)
for rule in rules:
print(rule)
print()
print(20*'=')
print()

注意:
如果出现如下错误:

解决方案:
关于 Python 导入错误 : cannot import name 'six' from 'sklearn.externals' ,云朵君在Stack Overflow上找到一个类似的问题:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61867945/
解决方案如下
import six
import sys
sys.modules['sklearn.externals.six'] = six
import mlrose
亲测有效!
如果使用“score_top_rules”方法,SkopeRules 也可以用作预测器:
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skrules import SkopeRules
dataset = load_boston()
clf = SkopeRules(max_depth_duplicatinotallow=None,
n_estimators=30,
precision_min=0.2,
recall_min=0.01,
feature_names=dataset.feature_names)
X, y = dataset.data, dataset.target > 25
X_train, y_train = X[:len(y)//2], y[:len(y)//2]
X_test, y_test = X[len(y)//2:], y[len(y)//2:]
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
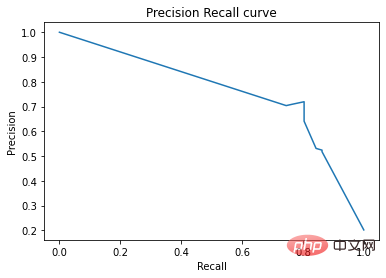
y_score = clf.score_top_rules(X_test) # Get a risk score for each test example
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(y_test, y_score)
plt.plot(recall, precision)
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.title('Precision Recall curve')
plt.show()
实战案例
本案例展示了在著名的泰坦尼克号数据集上使用skope-rules。
skope-rules适用情况:
- 解决二分类问题
- 提取可解释的决策规则
本案例分为5个部分
- 导入相关库
- 数据准备
- 模型训练(使用ScopeRules().score_top_rules()方法)
- 解释 "生存规则"(使用SkopeRules().rules_属性)。
- 性能分析(使用SkopeRules.predict_top_rules()方法)。
导入相关库
# Import skope-rules
from skrules import SkopeRules
# Import librairies
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier, RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, precision_recall_curve
from matplotlib import cm
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from IPython.display import display
# Import Titanic data
data = pd.read_csv('../data/titanic-train.csv')
数据准备
# 删除年龄缺失的行
data = data.query('Age == Age')
# 为变量Sex创建编码值
data['isFemale'] = (data['Sex'] == 'female') * 1
# 未变量Embarked创建编码值
data = pd.concat(
[data,
pd.get_dummies(data.loc[:,'Embarked'],
dummy_na=False,
prefix='Embarked',
prefix_sep='_')],
axis=1
)
# 删除没有使用的变量
data = data.drop(['Name', 'Ticket', 'Cabin',
'PassengerId', 'Sex', 'Embarked'],
axis = 1)
# 创建训练及测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
data.drop(['Survived'], axis=1),
data['Survived'],
test_size=0.25, random_state=42)
feature_names = X_train.columns
print('Column names are: ' + ' '.join(feature_names.tolist())+'.')
print('Shape of training set is: ' + str(X_train.shape) + '.')
Column names are: Pclass Age SibSp Parch Fare
isFemale Embarked_C Embarked_Q Embarked_S.
Shape of training set is: (535, 9).
模型训练
# 训练一个梯度提升分类器,用于基准测试
gradient_boost_clf = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=42, n_estimators=30, max_depth = 5)
gradient_boost_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 训练一个随机森林分类器,用于基准测试
random_forest_clf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42, n_estimators=30, max_depth = 5)
random_forest_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 训练一个决策树分类器,用于基准测试
decision_tree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42, max_depth = 5)
decision_tree_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 训练一个 skope-rules-boosting 分类器
skope_rules_clf = SkopeRules(feature_names=feature_names, random_state=42, n_estimators=30,
recall_min=0.05, precision_min=0.9,
max_samples=0.7,
max_depth_duplicatinotallow= 4, max_depth = 5)
skope_rules_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 计算预测分数
gradient_boost_scoring = gradient_boost_clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
random_forest_scoring = random_forest_clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
decision_tree_scoring = decision_tree_clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
skope_rules_scoring = skope_rules_clf.score_top_rules(X_test)
"生存规则" 的提取
# 获得创建的生存规则的数量
print("用SkopeRules建立了" + str(len(skope_rules_clf.rules_)) + "条规则n")
# 打印这些规则
rules_explanations = [
"3岁以下和37岁以下,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。"
"3岁以上乘坐头等舱或二等舱,支付超过26欧元的女性。"
"坐一等舱或二等舱,支付超过29欧元的女性。"
"年龄在39岁以上,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。"
]
print('其中表现最好的4条 "泰坦尼克号生存规则" 如下所示:/n')
for i_rule, rule in enumerate(skope_rules_clf.rules_[:4])
print(rule[0])
print('->'+rules_explanations[i_rule]+ 'n')
用SkopeRules建立了9条规则。
其中表现最好的4条 "泰坦尼克号生存规则" 如下所示:
Age <= 37.0 and Age > 2.5
and Pclass <= 2.5 and isFemale > 0.5
-> 3岁以下和37岁以下,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。
Age > 2.5 and Fare > 26.125
and Pclass <= 2.5 and isFemale > 0.5
-> 3岁以上乘坐头等舱或二等舱,支付超过26欧元的女性。
Fare > 29.356250762939453
and Pclass <= 2.5 and isFemale > 0.5
-> 坐一等舱或二等舱,支付超过29欧元的女性。
Age > 38.5 and Pclass <= 2.5
and isFemale > 0.5
-> 年龄在39岁以上,在头等舱或二等舱的女性。
def compute_y_pred_from_query(X, rule):
score = np.zeros(X.shape[0])
X = X.reset_index(drop=True)
score[list(X.query(rule).index)] = 1
return(score)
def compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_true, y_pred, index_name='default_index'):
df = pd.DataFrame(data=
{
'precision':[sum(y_true * y_pred)/sum(y_pred)],
'recall':[sum(y_true * y_pred)/sum(y_true)]
},
index=[index_name],
columns=['precision', 'recall']
)
return(df)
def compute_train_test_query_performances(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, rule):
y_train_pred = compute_y_pred_from_query(X_train, rule)
y_test_pred = compute_y_pred_from_query(X_test, rule)
performances = None
performances = pd.concat([
performances,
compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_train, y_train_pred, 'train_set')],
axis=0)
performances = pd.concat([
performances,
compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_test, y_test_pred, 'test_set')],
axis=0)
return(performances)
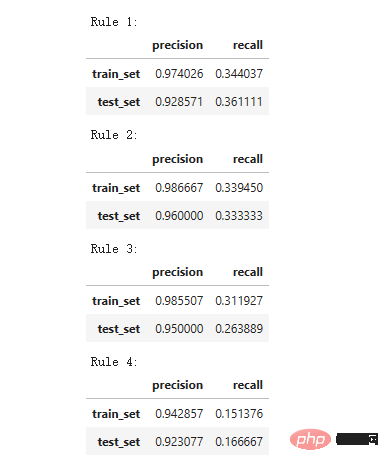
print('Precision = 0.96 表示规则确定的96%的人是幸存者。')
print('Recall = 0.12 表示规则识别的幸存者占幸存者总数的12%n')
for i in range(4):
print('Rule '+str(i+1)+':')
display(compute_train_test_query_performances(X_train, y_train,
X_test, y_test,
skope_rules_clf.rules_[i][0])
)
Precision = 0.96 表示规则确定的96%的人是幸存者。
Recall = 0.12 表示规则识别的幸存者占幸存者总数的12%。
模型性能检测
def plot_titanic_scores(y_true, scores_with_line=[], scores_with_points=[],
labels_with_line=['Gradient Boosting', 'Random Forest', 'Decision Tree'],
labels_with_points=['skope-rules']):
gradient = np.linspace(0, 1, 10)
color_list = [ cm.tab10(x) for x in gradient ]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5),
sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax = axes[0]
n_line = 0
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_line):
n_line = n_line + 1
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_true, score)
ax.plot(fpr, tpr, linestyle='-.', c=color_list[i_score], lw=1, label=labels_with_line[i_score])
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_points):
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_true, score)
ax.scatter(fpr[:-1], tpr[:-1], c=color_list[n_line + i_score], s=10, label=labels_with_points[i_score])
ax.set_title("ROC", fnotallow=20)
ax.set_xlabel('False Positive Rate', fnotallow=18)
ax.set_ylabel('True Positive Rate (Recall)', fnotallow=18)
ax.legend(loc='lower center', fnotallow=8)
ax = axes[1]
n_line = 0
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_line):
n_line = n_line + 1
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(y_true, score)
ax.step(recall, precision, linestyle='-.', c=color_list[i_score], lw=1, where='post', label=labels_with_line[i_score])
for i_score, score in enumerate(scores_with_points):
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(y_true, score)
ax.scatter(recall, precision, c=color_list[n_line + i_score], s=10, label=labels_with_points[i_score])
ax.set_title("Precision-Recall", fnotallow=20)
ax.set_xlabel('Recall (True Positive Rate)', fnotallow=18)
ax.set_ylabel('Precision', fnotallow=18)
ax.legend(loc='lower center', fnotallow=8)
plt.show()
plot_titanic_scores(y_test,
scores_with_line=[gradient_boost_scoring, random_forest_scoring, decision_tree_scoring],
scores_with_points=[skope_rules_scoring]
)
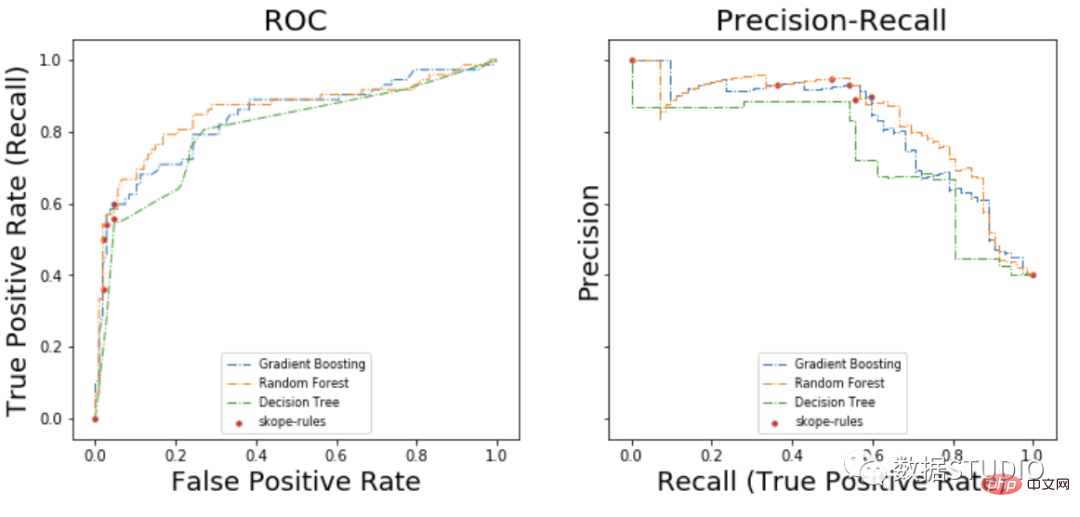
在ROC曲线上,每个红点对应于激活的规则(来自skope-rules)的数量。例如,最低点是1个规则(最好的)的结果点。第二低点是2条规则结果点,等等。
在准确率-召回率曲线上,同样的点是用不同的坐标轴绘制的。警告:左边的第一个红点(0%召回率,100%精度)对应于0条规则。左边的第二个点是第一个规则,等等。
从这个例子可以得出一些结论。
- skope-rules的表现比决策树好。
- skope-rules的性能与随机森林/梯度提升相似(在这个例子中)。
- 使用4个规则可以获得很好的性能(61%的召回率,94%的精确度)(在这个例子中)。
n_rule_chosen = 4
y_pred = skope_rules_clf.predict_top_rules(X_test, n_rule_chosen)
print('The performances reached with '+str(n_rule_chosen)+' discovered rules are the following:')
compute_performances_from_y_pred(y_test, y_pred, 'test_set')
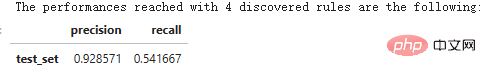
predict_top_rules(new_data, n_r)方法用来计算对new_data的预测,其中有前n_r条skope-rules规则。
以上是涨知识!用逻辑规则进行机器学习的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 软AI的兴起及其对当今企业的意义Apr 15, 2025 am 11:36 AM
软AI的兴起及其对当今企业的意义Apr 15, 2025 am 11:36 AM软AI(被定义为AI系统,旨在使用近似推理,模式识别和灵活的决策执行特定的狭窄任务 - 试图通过拥抱歧义来模仿类似人类的思维。 但是这对业务意味着什么
 为AI前沿的不断发展的安全框架Apr 15, 2025 am 11:34 AM
为AI前沿的不断发展的安全框架Apr 15, 2025 am 11:34 AM答案很明确 - 只是云计算需要向云本地安全工具转变,AI需要专门为AI独特需求而设计的新型安全解决方案。 云计算和安全课程的兴起 在
 生成AI的3种方法放大了企业家:当心平均值!Apr 15, 2025 am 11:33 AM
生成AI的3种方法放大了企业家:当心平均值!Apr 15, 2025 am 11:33 AM企业家,并使用AI和Generative AI来改善其业务。同时,重要的是要记住生成的AI,就像所有技术一样,都是一个放大器 - 使得伟大和平庸,更糟。严格的2024研究O
 Andrew Ng的新简短课程Apr 15, 2025 am 11:32 AM
Andrew Ng的新简短课程Apr 15, 2025 am 11:32 AM解锁嵌入模型的力量:深入研究安德鲁·NG的新课程 想象一个未来,机器可以完全准确地理解和回答您的问题。 这不是科幻小说;多亏了AI的进步,它已成为R
 大语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉是不可避免的吗?Apr 15, 2025 am 11:31 AM
大语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉是不可避免的吗?Apr 15, 2025 am 11:31 AM大型语言模型(LLM)和不可避免的幻觉问题 您可能使用了诸如Chatgpt,Claude和Gemini之类的AI模型。 这些都是大型语言模型(LLM)的示例,在大规模文本数据集上训练的功能强大的AI系统
 60%的问题 - AI搜索如何消耗您的流量Apr 15, 2025 am 11:28 AM
60%的问题 - AI搜索如何消耗您的流量Apr 15, 2025 am 11:28 AM最近的研究表明,根据行业和搜索类型,AI概述可能导致有机交通下降15-64%。这种根本性的变化导致营销人员重新考虑其在数字可见性方面的整个策略。 新的
 麻省理工学院媒体实验室将人类蓬勃发展成为AI R&D的核心Apr 15, 2025 am 11:26 AM
麻省理工学院媒体实验室将人类蓬勃发展成为AI R&D的核心Apr 15, 2025 am 11:26 AM埃隆大学(Elon University)想象的数字未来中心的最新报告对近300名全球技术专家进行了调查。由此产生的报告“ 2035年成为人类”,得出的结论是,大多数人担心AI系统加深的采用


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器







