一文聊聊Node中的fs文件模块和path路径模块(案例分析)
- 青灯夜游转载
- 2022-11-18 20:36:171913浏览
本篇文章通过读写文件和处理路径的案例,来一起学习下Node中的fs文件模块和path路径模块,希望对大家有所帮助!

一、fs 文件系统模块
fs 模块 是 Node.js 官方提供的、用来 操作文件 的模块。它提供了一系列的方法和属性,用来满足用户对文件的操作要求。【相关教程推荐:nodejs视频教程】
1、读取指定文件
fs.readFile():读取指定文件中的内容
参数 1:必选参数,字符串,表示文件的路径
参数 2:可选参数,表示以什么编码格式来读取文件
参数 3:必选参数,文件读取完成后,通过回调函数拿到读取的结果
fs.readFile(path, [options], callback)
示例1:读取 demo.txt 文件
demo.txt 文件
'前端杂货铺'
app.js 文件
// 导入 fs 文件系统模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 读取文件 utf-8 为中文编码格式
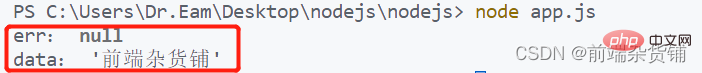
fs.readFile('../files/demo.txt', 'utf-8', function (err, data) {
console.log('err:', err)
console.log('data:', data)
})
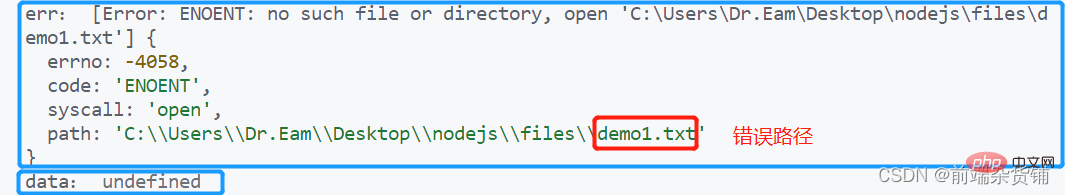
备注:若写错路径,即文件读取失败,打印内容如下【err为错误对象,data为undefined】
示例2:判断读取 demo.txt 文件是否成功
app.js 文件
- 故意写错路径,读取失败
- 失败的结果如下
// 导入 fs 模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 读取文件
fs.readFile('../files/demo1.txt', 'utf-8', function (err, data) {
if(err) {
return console.log('读取文件失败', err.message)
}
console.log('data:', data)
})
2、写入指定文件
fs.writeFile():向指定的文件中写入内容
参数 1:必选参数,需要指定一个文件路径的字符串,表示文件的存放路径
参数 2:必选参数,表示要写入的内容
参数 3:可选参数,表示以什么格式写入文件内容,默认 utf-8
参数 4:必选参数,文件写入完成后的回调函数
fs.writeFile(file, data, [options], callback)
示例1:写入 demo.txt 文件

demo.txt 文件
// 该文件内容为空
app.js 文件
// 导入 fs 文件系统模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 写入文件内容
fs.writeFile('../files/demo.txt', '这里是前端杂货铺', function(err, data) {
if (err) {
return console.log('写入文件失败', err.message)
}
console.log('文件写入成功')
})
备注:若写入不存在的盘中,即文件写入失败,打印内容如下

3、整理成绩案例
示例:成绩的格式转换
转换前的成绩格式
转换后的成绩格式

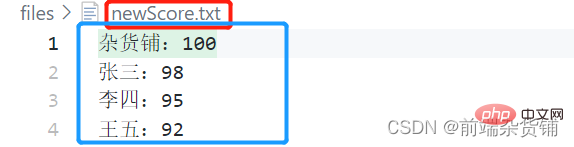
文件格式如下

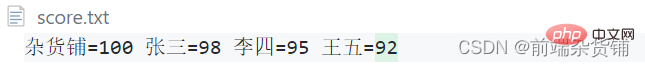
score.txt 文件
- 写入成绩内容
杂货铺=100 张三=98 李四=95 王五=92
app.js 文件
- 导入需要的 fs 文件模块
- 使用 fs.readFile() 方法,读取素材目录下的 score.txt 文件
- 判断文件是否读取失败
- 文件读取成功后,处理成绩数据
- 将处理完成的成绩数据,调用 fs.writeFile() 方法,写入到新文件 newScore.txt 中
// 导入 fs 文件系统模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 写入文件内容
fs.readFile('../files/score.txt', 'utf-8', function (err, data) {
// 判断是否读取成功
if (err) {
return console.log('读取文件失败' + err.message)
}
// 把成绩按空格进行分割
const arrOld = data.split(' ')
// 新数组的存放
const arrNew = []
// 循环分割后的数组 对每一项数据 进行字符串的替换操作
arrOld.forEach(item => {
arrNew.push(item.replace('=', ':'))
})
// 把新数组中的每一项合并 得到新的字符串
const newStr = arrNew.join('\r\n')
// 写入新数据
fs.writeFile('../files/newScore.txt', newStr, function (err) {
if (err) {
return console.log('写入成绩失败' + err.message)
}
console.log('成绩写入成功')
})
})
4、处理路径
__dirname:表示当前文件所处的目录
示例:写相对路径
const fs = require('fs')
fs.readFile('../files/score.txt', 'utf-8', function(err, data) {
if (err) {
return console.log('文件读取失败' + err.message)
}
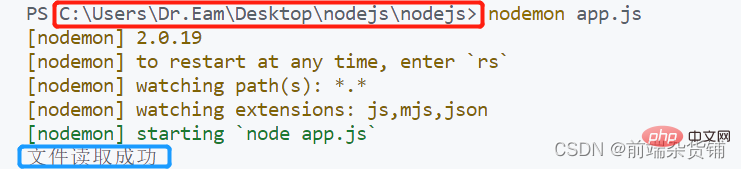
console.log('文件读取成功')
})
示例:使用 __dirname
const fs = require('fs')
// 读取文件
fs.readFile(__dirname + '/files/score.txt', 'utf-8', function(err, data) {
if (err) {
return console.log('文件读取失败' + err.message)
}
console.log('文件读取成功')
})
二、path 路径模块
path 模块是 Node.js 官方提供的、用来处理路径的模块
1、path.join() 路径拼接
path.join():用来将多个路径判断拼接成一个完整的路径字符串
参数:…paths
<string></string>路径片段的序列
返回值:返回值<string></string>
path.join([...paths])
示例:路径拼接
// 导入 path 模块 const path = require('path') // ../ 会抵消前面的路径 const pathStr = path.join('/a','/b/c', '../', './d', 'e') console.log(pathStr)

备注:涉及到路径拼接的操作,都要使用 path.join() 方法进行处理。不要直接用 + 进行字符串拼接
示例:使用 path 进行路径拼接
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
// 文件读取
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, '/files/score.txt'), 'utf-8', function(err, data) {
if (err) {
return console.log('文件读取失败', err.message)
}
console.log('文件读取成功')
})
2、path.basename() 解析文件名
path.basename():用来从路径字符串中,将文件名解析出来
参数 1:path 必选参数,表示一个路径的字符串
参数 2:ext 可选参数,表达文件扩展名
返回值:返回 表示路径中的最后一部分
path.basename(path, [ext])
示例:解析路径,去除扩展名
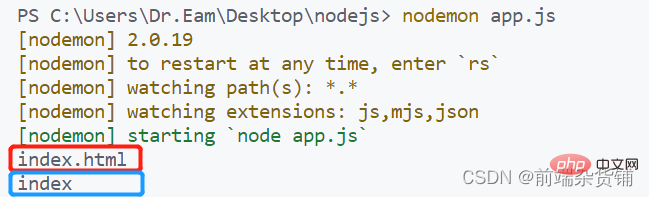
// 导入 path 模块 const path = require('path') // 文件的存放路径 const fpath = '/a/b/c/index.html' // 将文件名解析出来 const fullName = path.basename(fpath) console.log(fullName) // 输出 index.html // 去除扩展名 const nameWithoutExt = path.basename(fpath, '.html') console.log(nameWithoutExt) // 输出 index
3、path.extname() 获取扩展名
path.extname():可以获取路径中的扩展名部分
参数:
path <string></string>必选参数,表示一个路径的字符串
返回值:返回<string></string>返回得到的扩展名字符串
path.extname(path)
示例:获取扩展名
// 导入 path 模块
const path = require('path')
// 文件的存放路径
const fpath = '/a/b/c/index.html'
// 获取扩展名
const fext = path.extname(fpath)
console.log(fext) // .html

更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
以上是一文聊聊Node中的fs文件模块和path路径模块(案例分析)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

