如何基于moment实现日期可左右滑动的日历?
- 不言原创
- 2018-09-15 16:44:453718浏览
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于如何基于moment实现日期可左右滑动的日历?有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
效果如图(日期可左右滑动)
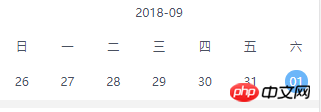
思路:
1、先得到相邻三个周的数据,初始化的时候讲容器向左移动一个视口的距离,确保中间周在可视范围(在可是范围的所用为1)
2、触摸移动阶段,比如向左移动,相当于改变可是范围的索引,也就是2,即向左移动过两个视口的范围
3、移动结束,这时右边已经没有待显示的数据,需要重组数据,再向后加一周,使当前显示的周在中间,同时需要改变显示的索引为1
1、用moment处理日期数据
在当前视口内显示本周的7天,由于需要滑动,所以事先还需要把今天以前的一周和以后的一周准备好
let today = moment().format('YYYY-MM-DD') // 当前日期:"2018-09-14"
moment(today).subtract(7, 'd').format('YYYY-MM-DD') // 上一周的今天:"2018-09-07"
moment(today).add(7, 'd').format('YYYY-MM-DD') // 下一周的今天:"2018-09-21"
得到数组: dates
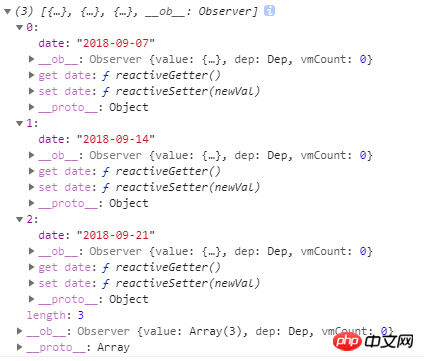
由此数据可以生成三个模板,分别表示上周,本周和下周,再根据此数据,计算上周,本周和下周的详情。
getDays: function (day) {
let arr = []
/* 计算传进来的日期为星期几 */
let weekOfDate = Number(moment(day).format('E'))
// 提前定义好的: this.week = ['一', '二', '三', '四', '五', '六', '日']
for (let i = 0; i < this.week.length; i++) {
arr.push(
{
date: moment(day).subtract(weekOfDate - i - 1, 'd').format('YYYY-MM-DD'),
week: this.week[i]
}
)
}
return arr
}遍历数组dates。分别传进getDays可的到三周的详情

然后遍历数组进行页面渲染
<template v-for="(item, index) in dates">
<p class="slider">
<p class="day" v-for="(day, dayIndex) in getDays(item.date)">
<p :class="{today: day.date === defaultDate}">{{day.date.split('-')[2]}}</p>
</p>
</p>
</template>
这里,静态显示已经完成
为组件添加滑动功能
改写上方的页面渲染代码
<p class="week-slider">
<p
class="sliders"
ref="sliders"
@touchstart="touchStart"
@touchmove="touchmove"
// 初始样式,应该向饰扣左方移动一个视口的距离,确保当前周在中间
:style="getTransform"
@touchend="touchend"
@webkit-transition-end="transitionEnd"
@transitionend="transitionEnd">
<template v-for="(item, index) in dates">
<p class="slider">
<p class="day" v-for="(day, dayIndex) in getDays(item.date)">
<p :class="{today: day.date === defaultDate}">{{day.date.split('-')[2]}}</p>
</p>
</p>
</template>
</p>
</p>
// actIndex: 当前活动视图的缩影,初始为1,sliderWidth:视口的宽度, distan: {x:0, y: 0}: 触摸移动的距离
//
getTransform: function () {
this.endx = (-this.actIndex * this.sliderWidth) + this.distan.x
let style = {}
style['transform'] = 'translateX(' + this.endx + 'px)'
// 这一条必须写,因为触摸移动的时候需要过渡动画,但是在动画结束重组数据的时候需要瞬间回到该去的位置,不能要过渡动画
style['transition'] = this.isAnimation ? 'transform .5s ease-out' : 'none'
return style
}
最后触摸时间处理:
touchStart: function (e) {
this.start.x = e.touches[0].pageX
},
touchmove: function (e) {
// 这里需要过渡动画
this.isAnimation = true
this.distan.x = e.touches[0].pageX - this.start.x
// 需要移动的容器
let dom = this.$refs.sliders
// 向左
this.endx = this.endx + this.distan.x
dom.style['transform'] = 'translateX('+ this.endx + 'px)'
},
touchend: function (e) {
this.isAnimation = true
this.distan.x = e.changedTouches[0].pageX - this.start.x
// 向右
if (this.distan.x > 0) {
this.direction = 'right'
this.actIndex = 0
} else if (this.distan.x < 0) {
this.direction = 'left'
this.actIndex = 2
}
this.distan.x = 0
},
过渡结束后重置容器位置
// 过渡结束
transitionEnd: function () {
this.isAnimation = false
if (this.actIndex === 2) {
this.dates.push({
date: moment(this.dates[this.actIndex].date).add(7, 'd').format('YYYY-MM-DD')
})
this.dates.shift()
this.actIndex = 1
}else if (this.actIndex === 0) {
this.dates.unshift({
date: moment(this.dates[this.actIndex].date).subtract(7, 'd').format('YYYY-MM-DD')
})
this.dates.pop()
this.actIndex = 1
}
}
相关推荐:
以上是如何基于moment实现日期可左右滑动的日历?的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
声明:
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系admin@php.cn

