
在建立现实生活项目时,与时代和日期合作是不可避免的,并且有很多用例。值得庆幸的是,Python有几个模块,可以轻松地与不同时区的日期和时代一起工作。
> 可以在github上找到本教程的代码。>。 内容:
时间模块
- time()函数
- gmtime()函数
- localtime()函数
- > ctime()函数
- strftime()函数
- 睡眠()函数
- 在Python中获取当前日期和时间 在python
- 中获取当前日期 dateTime模块类
- 日期类
- 时间类
- dateTime类
- the timedelta class
- python dateTime格式
- 使用Strftime()方法 格式化日期> 使用Strptime()方法
- 格式化日期>
- 与TimeDelta
- 一起工作
- Python提供`dateTime'和`time'模块来处理日期和时间操作,这对于现实生活项目至关重要。 `dateTime`模块都包括``date'',time',`dateTime`,`timeDeTim','timeDelta',`tzinfo'和`timeZone''和`timezone''的类。
`termedelta'类可用于计算日期和时间的差异,允许添加,减法和其他基于时间的计算。
时区处理由`ZoneInfo`模块促进,从而实现了TimeZone Aware Aware Aware DateTime对象的创建。 Python的日期和时间格式遵守ISO 8601标准的方法,但也允许自定义适合区域偏好。- 时间模块 Python时间模块用于执行时间相关的操作。现在,我们将在时间模块中重点介绍一些最常用的功能,其中包括示例。
- time()函数
- time()函数自集合时期作为浮点数以来,返回当前时间。使用的时期从1970年1月1日开始,00:00:00(UTC):
- 这是上述代码的输出:
<span>import time as time_module </span> time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.time() </span><span>print("Time in sceconds from epoch", time_in_seconds)</span>gmtime()函数
gmtime()函数自从时代开始以来,从秒内以秒的时间表示UTC中的struct_time。 struct_time是一种时间值序列,其命名元组接口由GMTime(),Localtime()和Strptime()返回
Time <span>in sceconds from epoch 1680712853.0801558</span>
这是以上代码的输出:
localtime()函数<span>import time as time_module </span> utc_time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.gmtime() </span><span>print("Time struct in UTC", utc_time_in_seconds)</span>localtime()函数自时代开始以来的本地时间内返回struct_time。
这是以上代码的输出:
Time struct <span>in UTC: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=14, tm_min=47, tm_sec=28, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>
> ctime()函数
> ctime()方法将从时期开头的几秒钟转换为字符串格式。如果没有参数传递给该函数,它将在秒内返回当前时间的时间字符串:> <span>import time as time_module </span> local_time <span>= time_module.localtime() </span><span>print("Time struct in local time:", local_time)</span>这是上述代码的输出:
strftime()函数
Time struct <span>in local time: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=15, tm_min=46, tm_sec=15, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>
strftime()方法将struct_time转换为给定格式参数指定的时间字符串:>
这是上述代码的输出:<span>import time as time_module </span> time_in_secs <span>= 1678671984.939945 </span> time_string <span>= time_module.ctime(time_in_secs) </span><span>print("Time string: ",time_string)</span>睡眠()函数
sleep()函数延迟了指定数量的线程的执行
Time string: Thu Apr <span>20 01:46:24 2023</span>
这是上述代码的输出:
>在上面的代码中,数字2作为睡眠()函数的参数传递,这会导致循环在执行前延迟两秒钟。输出的数字验证我们的代码。<span>import time as time_module </span> time_tuple <span>= time_module.gmtime() </span>time_format <span>= "%y/%m/%d %I:%M:%S %p" </span> time_in_string <span>= time_module.strftime(time_format, time_tuple) </span> <span>print("Time expressed as formatted string:", time_in_string)</span>dateTime模块
DateTime模块提供用于操纵日期和时间的类
这些类对于时间间隔,时间和日期的轻松操纵,提取和输出格式至关重要。通常,日期和时间在Python中不被视为数据类型,但它们是DateTime模块类的日期和时间对象。 DateTime类还具有可用于处理日期和时间对象的不同方法。Time expressed as formatted string: <span>23/04/20 04:40:04 PM</span>
在Python中获取当前日期和时间
获得当前日期和时间,请从DateTime模块导入DateTime类。 DateTime类具有一个方法,即现在(),该类返回当前日期和时间:> <span>import time as time_module </span> <span>for i in range(5): </span> local_time <span>= time_module.localtime() </span> seconds <span>= local_time.tm_sec </span> <span>print(seconds) </span> time_module<span>.sleep(2)</span>
这是上述代码的输出:
在python
中获取当前日期获得当前日期,请从DateTime模块导入日期类。日期类有一个方法,今天(),该方法返回当前日期:
>
这是上述代码的输出:
dateTime模块类
> DateTime模块当前有六个类,每个类都有不同的方法来操纵日期和时间对象。这些课程列出如下:<span>49 </span><span>51 </span><span>53 </span><span>55 </span><span>57</span>
- > date
- 时间
- dateTime
- timedelta
- > tzinfo
- 时区
日期类
日期对象在理想化的日历中代表日期(年,月和日) - 当前的Gregorian日历无限期地扩展了两个方向。
>可以将日期对象实例化如下:
<span>import time as time_module </span> time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.time() </span><span>print("Time in sceconds from epoch", time_in_seconds)</span>日期对象构造函数采用三个整数参数,应在指定的范围内:
> - minyear
1
1
在上面的代码中,minyear为1,Maxyear为9999。该值代表了A
或
这是以上代码的输出:
>示例:获取当前日期
Time <span>in sceconds from epoch 1680712853.0801558</span>要获取当前的本地日期,请使用今天的日期类()和ctime()方法:
> today()方法将返回本地日期,而ctime()方法将日期呈现为字符串。 这是以上代码的输出:
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
utc_time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.gmtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in UTC", utc_time_in_seconds)</span>>
>示例:创建来自ISO格式的日期
可以从ISO 8601格式的日期字符串创建日期对象。使用日期类的fromisOformat()方法来执行此操作:
Time struct <span>in UTC: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=14, tm_min=47, tm_sec=28, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>>
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
local_time <span>= time_module.localtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in local time:", local_time)</span>注意:ISO 8601是一种标准化格式,用于呈现日期和时间,而无需在不同区域或时区造成混淆。 ISO 8601采用格式yyyy-mm-dd。
这是以上代码的输出:
>示例:从字符串创建日期对象
Time struct <span>in local time: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=15, tm_min=46, tm_sec=15, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>为创建一个日期对象,将日期字符串和相应格式传递给Strptime()方法。使用返回的dateTime对象的日期()方法提取日期:
这是上述代码的输出:
>要从日期对象提取年,月和一天
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_secs <span>= 1678671984.939945
</span>
time_string <span>= time_module.ctime(time_in_secs)
</span><span>print("Time string: ",time_string)</span>这是以上代码的输出:时间类
一个时间对象代表一天中的(本地)时间,独立于任何特定的一天,并通过tzinfo对象进行调整。
Time string: Thu Apr <span>20 01:46:24 2023</span>
可以将日期对象实例化如下:
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.time()
</span><span>print("Time in sceconds from epoch", time_in_seconds)</span>
可以在没有任何参数的情况下实例化时间对象。所有参数都是可选的,默认值为0,除了tzinfo,这不是。所有参数必须是指定范围内的整数,而tzinfo参数应为tzinfo子类的一个实例:
- 0
- 0
- 0
- 0
>当不超出范围的参数传递给构造函数时,它会提高价值。
>示例:创建一个时间对象
创建一个时间对象,请从DateTime模块导入时间类。通过几个小时,分钟,秒,微秒和tzinfo的争论。请记住,所有参数都是可选的,因此,当没有参数传递给构造函数时,时间对象返回00:00:00:
Time <span>in sceconds from epoch 1680712853.0801558</span>
这是上述代码的输出:
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
utc_time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.gmtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in UTC", utc_time_in_seconds)</span>>示例:从ISO格式创建时间可以从ISO 8601格式中的时间字符串创建时间对象。使用时间类的fromisoformat()方法来执行此操作:
>
Time struct <span>in UTC: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=14, tm_min=47, tm_sec=28, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>这是上述代码的输出:
>示例:从字符串
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
local_time <span>= time_module.localtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in local time:", local_time)</span>创建时间对象
创建一个时间对象,将日期字符串和相应格式传递给Strptime()方法。使用返回的DateTime对象的time()方法提取时间:
这是上述代码的输出:
Time struct <span>in local time: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=15, tm_min=46, tm_sec=15, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>>示例:从时间对象
获取小时,分钟,秒和微秒
>提取数小时,分钟,秒和微秒的值,使用时间对象的小时,分钟,第二和微秒属性:<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_secs <span>= 1678671984.939945
</span>
time_string <span>= time_module.ctime(time_in_secs)
</span><span>print("Time string: ",time_string)</span>
这是上述代码的输出:
dateTime类
Time string: Thu Apr <span>20 01:46:24 2023</span>
dateTime对象是一个单个对象,其中包含来自日期对象和时间对象的所有信息。
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_tuple <span>= time_module.gmtime()
</span>time_format <span>= "%y/%m/%d %I:%M:%S %p"
</span>
time_in_string <span>= time_module.strftime(time_format, time_tuple)
</span>
<span>print("Time expressed as formatted string:", time_in_string)</span>>
dateTime构造函数需要年度,月和日论点。 tzinfo默认值不或tzinfo子类的实例。时间参数是可选的,但是参数必须是整数,并且在范围内:
minyear 1 Time expressed as formatted string: <span>23/04/20 04:40:04 PM</span>
1 0
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.time()
</span><span>print("Time in sceconds from epoch", time_in_seconds)</span>
>示例:获取当前的本地日期和时间
要获取当前的本地日期和时间,请使用DateTime类的NOW()方法:
Time <span>in sceconds from epoch 1680712853.0801558</span>这是上述代码的输出:
>示例:创建从ISO格式创建日期时间
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
utc_time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.gmtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in UTC", utc_time_in_seconds)</span>
>从ISO 8601格式的日期时间字符串创建DateTime对象,请使用DateTime类的fromisOformat()方法:
>>
Time struct <span>in UTC: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=14, tm_min=47, tm_sec=28, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>>注意:如果将日期字符串参数传递到FromisOformat()方法不是有效的ISO格式字符串中,则提高了ValueError异常。此处的日期输出与从dateTime.now()。
>获得的结果非常相似
这是上述代码的输出:
>示例:从DateTime对象获取日期和时间属性
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
local_time <span>= time_module.localtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in local time:", local_time)</span>> DateTime对象提供以下属性:年,月,每日,小时,分钟,第二,微秒,tzinfo和fold。属性可以访问如下:>
这是上述代码的输出:
Time struct <span>in local time: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=15, tm_min=46, tm_sec=15, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>
注意:tzinfo的默认属性值无了,因为没有传递对象参数,并且fold将默认情况下返回0。有关折叠属性的更多信息(在Python版本3.6中引入),请参见文档。
the timedelta class<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_secs <span>= 1678671984.939945
</span>
time_string <span>= time_module.ctime(time_in_secs)
</span><span>print("Time string: ",time_string)</span>
序列对象代表持续时间,两个日期或时间之间的差异。
参数被转换为如下:
毫秒转换为1000微秒。
一分钟转换为60秒。Time string: Thu Apr <span>20 01:46:24 2023</span>
一个小时转换为3600秒。
一周转换为7天。
- 所有参数均应在文档中指定的以下范围内:
> - 0
- 0 >
- -999999999
>示例:创建一个timedelta对象
- >创建一个timedelta对象,请从datetime模块导入timedelta类。将适当的参数传递给构造函数函数:
- 这是上述代码的输出:
- python dateTime格式
日期和时间格式因地区到国家和国家 /地区而异。这是因为在日期和时间格式方面存在这些差异,因此引入了ISO 8601格式,作为标准化日期和时间的一种方式。 但是,可能需要根据一个国家或地区以特定方式格式化日期和时间。
使用Strftime()方法格式化日期>
可以使用strftime()方法来完成 dateTime格式。 strftime()方法是时间,日期和日期时间类的实例方法,这意味着我们必须创建一个日期,时间或日期对象才能应用该方法。该方法将给定的格式代码作为参数,并以所需格式返回代表时间,日期或日期的字符串。
方法签名看起来像这样:
通常,将字符串格式代码作为参数传递给strftime()方法以格式日期。某些格式代码如下:
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.time()
</span><span>print("Time in sceconds from epoch", time_in_seconds)</span>>
>%a:工作日缩写名称 - 例如太阳,蒙上等
- %b:月份为缩写名称 - 例如1月,2月等
- %y:一年没有世纪作为零填充的十进制数字 - 例如00、01、02等
- 可以在Python文档中找到带有格式代码的更详细的表格。 >示例:dateTime对象中的格式日期和时间
-
>与以前的示例一样,我们可以将所需日期和时间输出格式字符串的参数传递给strftime()方法: >
这是上述代码的输出:
格式化日期> 与Strftime()不同,Strptime()是DateTime类方法,这意味着可以在不创建类的对象的情况下使用它。该方法从给定的日期字符串和格式返回DateTime对象。
方法签名看起来像这样:
Time <span>in sceconds from epoch 1680712853.0801558</span>
将字符串格式代码作为参数传递给strptime()方法以格式日期。
><span>import time as time_module
</span>
utc_time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.gmtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in UTC", utc_time_in_seconds)</span>>示例:dateTime对象的字符串要创建一个DateTime对象,我们将将两个参数传递给Strptime()方法,日期字符串和相应的格式。当日期字符串与提供的格式不匹配时,会提高value error:
>
这是上述代码的输出:
Time struct <span>in UTC: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=14, tm_min=47, tm_sec=28, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>与TimeDelta
一起工作
> python中的时间介绍类用于计算日期之间的差异,计算特定日期之间的时间差,并使用特定的时间单位(例如周或小时)进行其他计算。>示例:计算将来的日期
>
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
local_time <span>= time_module.localtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in local time:", local_time)</span>这是上述代码的输出:在上面的示例中,我们首先获得当前的本地日期和时间,以及7天的时间码对象。由于TimeDERTA支持诸如添加之类的操作,因此我们添加了DateTime对象和TimeDelta对象,以在7天内获得未来的一天。如果我们的当前日期是2023-04-20,则日期将在2023-04-27之内。
Time struct <span>in local time: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=15, tm_min=46, tm_sec=15, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>>示例:计算两个序列对象之间的差异
>
这是上述代码的输出:
使用时区
>示例:将DateTime对象从一个时区转换为另一个时区
结论 >
可以在github >。
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.time()
</span><span>print("Time in sceconds from epoch", time_in_seconds)</span>
在上面的代码段中,我们创建了两个TimeDelta对象,即time_delta1和time_delta2,并计算了它们之间的差异。
Time <span>in sceconds from epoch 1680712853.0801558</span>
这是上述代码的输出:<span>import time as time_module
</span>
utc_time_in_seconds <span>= time_module.gmtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in UTC", utc_time_in_seconds)</span>>
ZoneInfo是一个内置的Python模块,用于使用时区。 这是以上代码的输出:
Time struct <span>in UTC: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=14, tm_min=47, tm_sec=28, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>
首先,我们从DateTime模块和Zoneinfo模块中导入DateTime类。我们创建一个ZoneInfo对象,然后创建一个DateTime对象,但是这次我们将TimeZone对象TZ传递给NOW()方法。 <span>import time as time_module
</span>
local_time <span>= time_module.localtime()
</span><span>print("Time struct in local time:", local_time)</span>>
>要在时区之间转换,我们使用DateTime对象的AstimeZone()方法,以新的时区对象传递。 AstimeZone()返回一个带有更新的时区信息的新的DateTime对象。 Time struct <span>in local time: time.struct_time(tm_year=2023, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=15, tm_min=46, tm_sec=15, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=75, tm_isdst=0)</span>
<span>import time as time_module
</span>
time_in_secs <span>= 1678671984.939945
</span>
time_string <span>= time_module.ctime(time_in_secs)
</span><span>print("Time string: ",time_string)</span>跟踪时间是我们日常生活的重要方面,这也转化为编程。当我们构建现实世界项目时,总是需要保留登录和登录等用户活动的时间日志,以及其他用例。在在线生成的内容上放置时间戳并根据用户的区域或时区显示时间和日期也很重要。
经常询问有关Python日期和时间的问题(常见问题解答)
>如何将字符串转换为python中的日期?>在Python中,您可以使用DateTime模块的Strptime()函数将字符串转换为日期。此功能需要两个参数:要转换的字符串和与字符串的日期格式匹配的格式代码。例如,如果您的格式“ yyyy-mm-dd”中有一个日期字符串“ 2022-03-01”,则可以将其转换为这样的日期:datetime import import import
date_object = dateTime.strptime(date_string,“%y-%m-%d”)
>
我如何获得python的当前日期和时间?从dateTime import import dateTime
>我如何在python中格式化一个日期? fort_date_date = currated_date = current_dateTime。 strftime(“%y-%m-%d”)
print(formatted_date)
>我如何从python的日期中添加或减去天数? TIMEDERTA类,您可以用来添加或减去日期的一定天数。以下是您可以使用它的方法:
>来自dateTime import dateTime,timeDELTA
current_date = dateTime.now() print> print(new_date)
如何比较python中的两个日期?以下是一个示例:
>来自dateTime import import dateTime
dateTime(2022,3,1)
>我如何在Python中获得一周的一天?作为整数的一周(周一为0,星期日为6)。以下是您可以使用它的方法:
>来自dateTime import dateTime
current_date = dateTime.now()
current_date = dateTime.now()
timestamp = current_date.timestamp()
>如何从Python中的字符串中解析一个日期?以下是您可以使用它的方法:
从dateutil import import parser
date_string =“ 2022-03-01”
date_object = parser.parser.parse.parse(date_string)(date_string)
print(date_object)
>如何在Python中获得当前时间?如果您只需要时间,则可以使用Time()函数这样:
>如何将时间戳转换为python中的日期?
>在Python中,您可以使用dateTime.fromtimestamp()函数将时间戳转换为日期。这是一个示例:
>来自DateTime Import DateTime
以上是了解python日期和时间,示例的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 定制电信软件的好处May 11, 2025 am 08:28 AM
定制电信软件的好处May 11, 2025 am 08:28 AM定制电信软件开发无疑是一项相当大的投资。然而,从长远来看,您可能会意识到,这样的项目可能更具成本效益,因为它可以像市场上任何现成的解决方案一样提高您的生产力。了解构建定制电信系统的最重要优势。 获取您所需的确切功能 您可以购买的现成电信软件有两个潜在问题。有些缺乏可能显着改善您工作效率的有用功能。有时您可以通过一些外部集成来增强它们,但这并不总是足以使它们变得出色。 其他软件功能过多,使用起来过于复杂。您可能不会使用其中的一些(永远不会!)。大量的功能通常还会增加价格。 基于您的需求
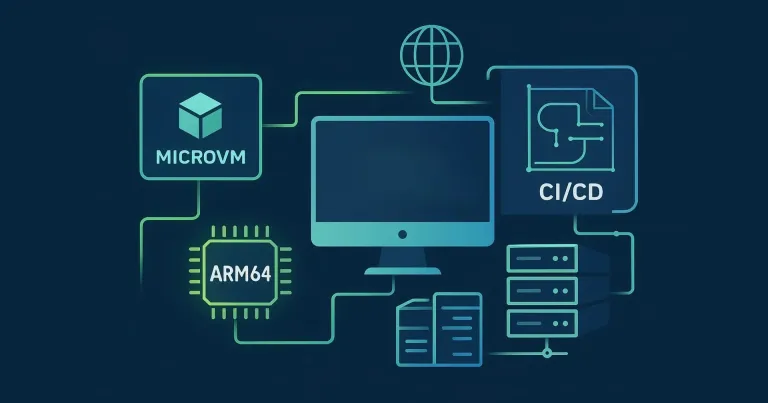 CNCF触发了ARM64和X86的平台平等突破May 11, 2025 am 08:27 AM
CNCF触发了ARM64和X86的平台平等突破May 11, 2025 am 08:27 AMArm64 架构开源软件的 CI/CD 难题与解决方案 在 Arm64 架构上部署开源软件需要一个强大的 CI/CD 环境。然而,Arm64 和传统 x86 处理器架构的支持水平之间存在差异,Arm64 通常处于劣势。面向多种架构的基础设施组件开发人员对工作环境有一定的期望: 一致性:跨平台使用的工具和方法保持一致,避免因采用不太流行的平台而需要改变开发流程。 性能:平台和支持机制具有良好的性能,确保在支持多个平台时部署方案不会因速度不足而受影响。 测试覆盖率:对所有平台同时进行效率、合规性和
 21个开发人员新闻通讯将在2025年订阅Apr 24, 2025 am 08:28 AM
21个开发人员新闻通讯将在2025年订阅Apr 24, 2025 am 08:28 AM与这些顶级开发人员新闻通讯有关最新技术趋势的了解! 这个精选的清单为每个人提供了一些东西,从AI爱好者到经验丰富的后端和前端开发人员。 选择您的收藏夹并节省时间搜索REL
 使用AWS ECS和LAMBDA的无服务器图像处理管道Apr 18, 2025 am 08:28 AM
使用AWS ECS和LAMBDA的无服务器图像处理管道Apr 18, 2025 am 08:28 AM该教程通过使用AWS服务来指导您通过构建无服务器图像处理管道。 我们将创建一个部署在ECS Fargate群集上的next.js前端,与API网关,Lambda函数,S3桶和DynamoDB进行交互。 Th
 CNCF ARM64飞行员:影响和见解Apr 15, 2025 am 08:27 AM
CNCF ARM64飞行员:影响和见解Apr 15, 2025 am 08:27 AM该试点程序是CNCF(云本机计算基础),安培计算,Equinix金属和驱动的合作,简化了CNCF GitHub项目的ARM64 CI/CD。 该计划解决了安全问题和绩效


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器






