使用 Javascript 进行算法之旅 - 冒泡排序
- PHPz原创
- 2024-07-29 06:30:53464浏览
什么是冒泡排序?
冒泡排序是计算机科学中最简单的排序算法之一。它以每次迭代时较小的元素“冒泡”到列表顶部的方式命名,是教授排序算法基础知识的绝佳工具。虽然对于大型数据集来说不是最有效的,但它的简单性使其成为理解排序算法如何工作的一个很好的起点。
冒泡排序的工作原理
冒泡排序的工作原理是重复遍历列表,比较相邻元素,如果顺序错误则交换它们。重复此过程,直到不再需要交换为止,表明列表已排序。
这是一步一步的细分:
- 从数组中的第一个元素开始。
- 将其与下一个元素进行比较。
- 如果第一个元素大于第二个元素,则交换它们。
- 移动到下一个元素并重复步骤 2-3,直到到达数组末尾。
- 如果进行了任何交换,请从头开始重复该过程。
- 如果在完整传递中没有进行交换,则数组已排序。
让我们可视化这个过程:
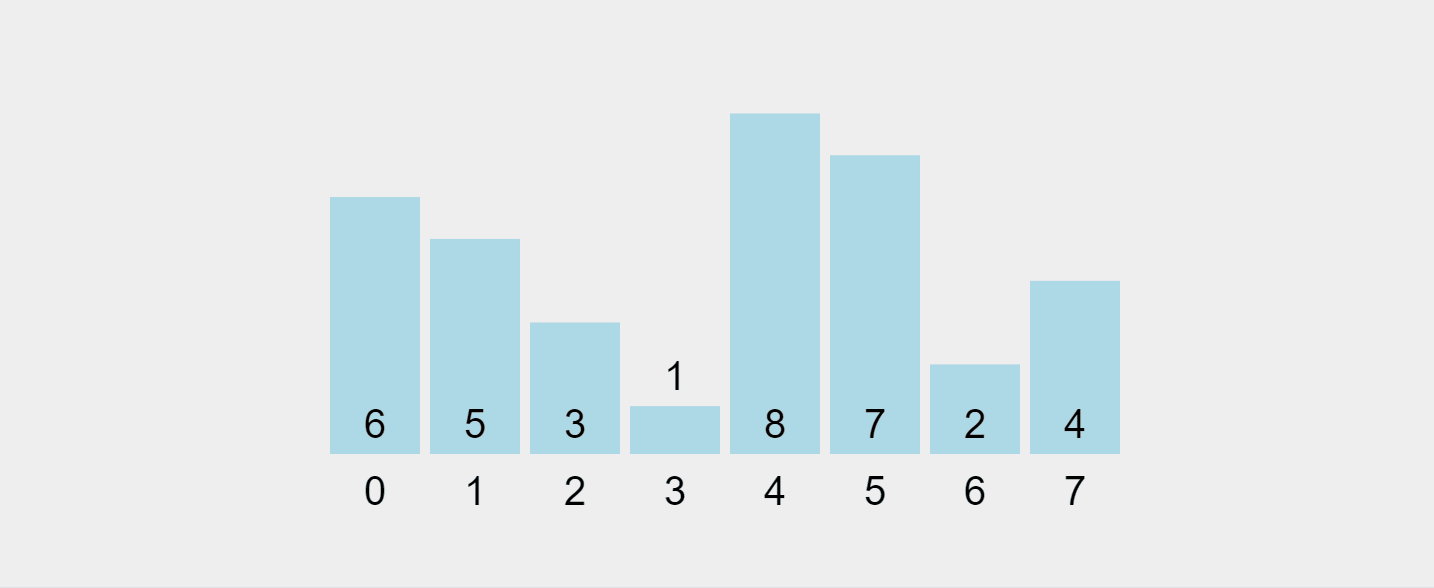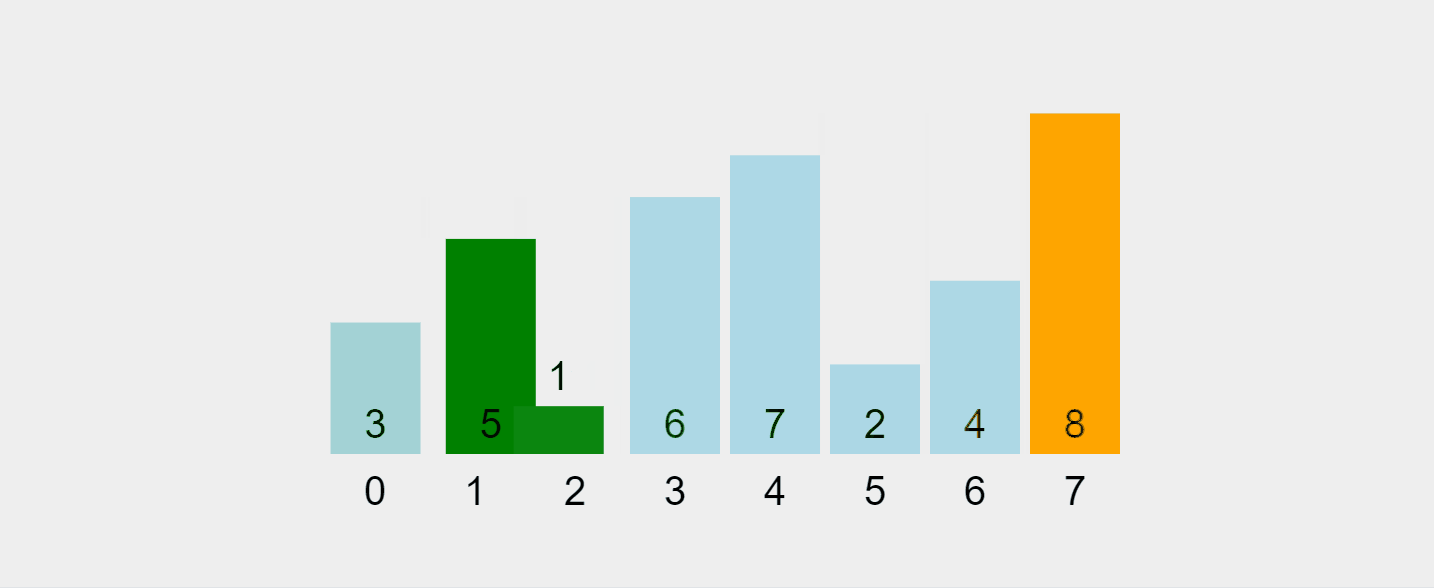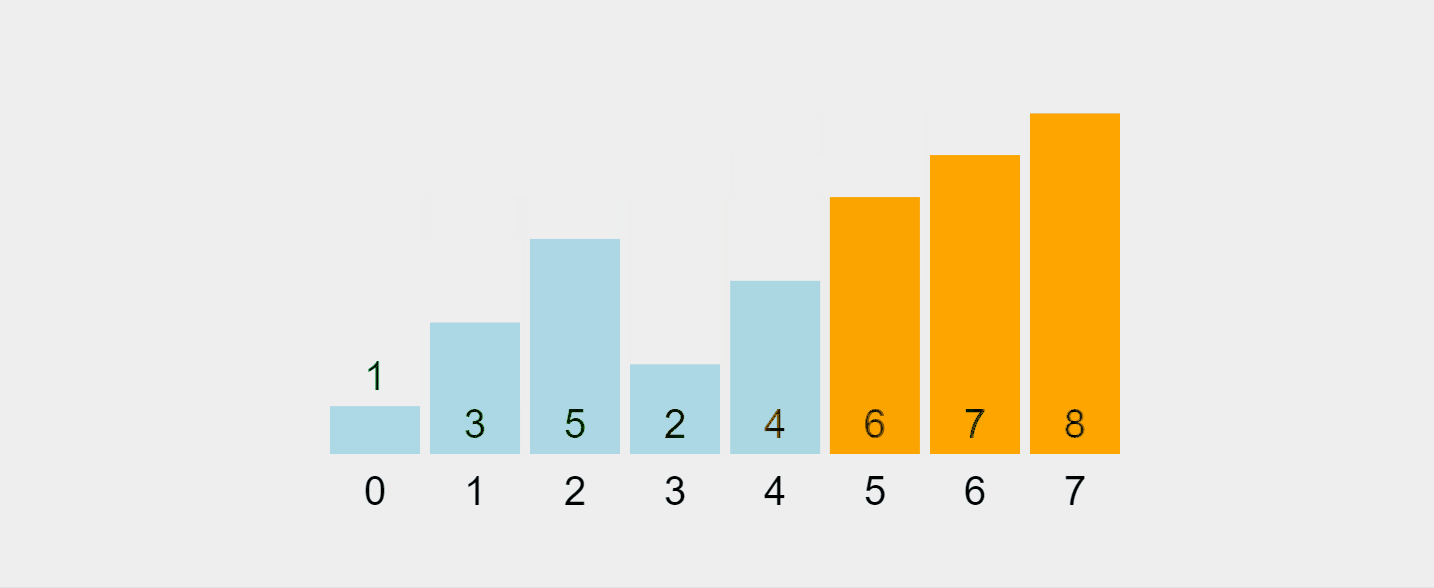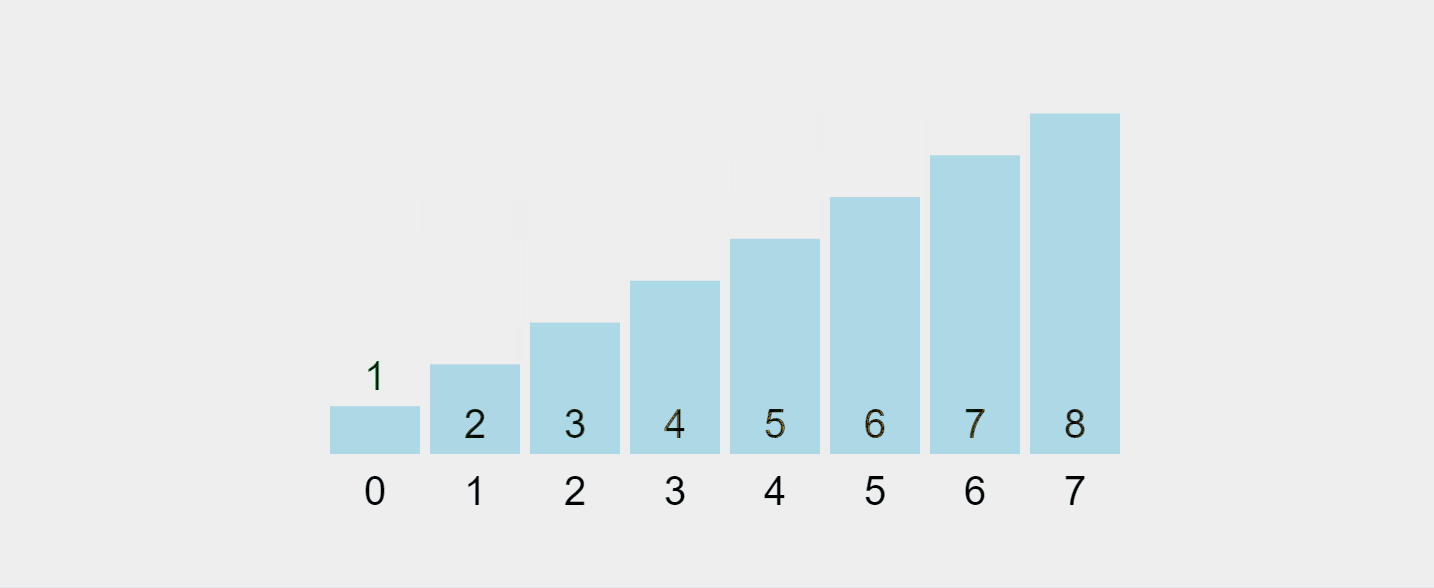
录制的 gif 来自 https://visualgo.net/en/sorting
在 JavaScript 中实现冒泡排序
让我们研究一下 JavaScript 中冒泡排序的三种实现,每种实现的优化级别都在增加。
基本实现 (v1)
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
}
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
这个基本实现使用嵌套循环来比较和交换相邻元素。外循环确保我们对数组进行了足够的遍历,而内循环则执行比较和交换。
优化实施 (v2)
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
此版本引入了交换标志来检查一次传递中是否进行了任何交换。如果没有发生交换,则列表已经排序,我们可以提前跳出循环。
最优化的实施 (v3)
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
// Note: We reduce the upper bound by i in each pass
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1 - i; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
最终的优化在每次传递中将内部循环的范围减少了 i。这是因为每次传递后,最大的未排序元素“冒泡”到数组末尾的正确位置。
时间和空间复杂度分析
冒泡排序的性能特点如下:
-
时间复杂度:
- 最佳情况:O(n) - 当数组已排序时
- 平均情况:O(n^2)
- 最坏情况:O(n^2) - 当数组逆序时
空间复杂度:O(1) - 冒泡排序是一种就地排序算法,仅需要恒定量的额外内存。
与快速排序(平均 O(n log n))或合并排序(O(n log n))等更高级的算法相比,冒泡排序的二次时间复杂度使其对于大型数据集效率低下。
冒泡排序的优点和缺点
优点:
- 易于理解和实施
- 就地排序(O(1) 空间)
- 稳定的排序算法
- 可以检测已经排序的列表
缺点:
- 对于大型数据集效率低下 (O(n^2))
- 在接近排序的数据上表现不佳
- 过多的交换操作
何时使用冒泡排序
- 教育目的:它的简单性使其非常适合教授基本算法概念。
- 小数据集:对于非常小的数组,与复杂算法相比,性能差异可能可以忽略不计。
- 近排序数据:使用优化版本,在近排序列表上可以相当高效。
- 有限的内存环境:它的就地性质在内存极度受限的场景中可能是有利的。
鸡尾酒排序:改进的变体
鸡尾酒排序,也称为鸡尾酒摇排序或双向冒泡排序,是冒泡排序的改进版本。它双向遍历列表,有助于更有效地将元素移动到正确的位置。
How Cocktail Sort Works
- Start with the first element and move towards the end, swapping adjacent elements if they're in the wrong order.
- When you reach the end, start from the second-to-last element and move towards the beginning, again swapping elements as needed.
- Repeat this process, narrowing the range of elements to check with each pass, until no swaps are needed.
Cocktail Sort is particularly useful in cases where the array has elements that are initially large at the beginning and small at the end, as it can reduce the total number of passes needed compared to traditional Bubble Sort.
Here's a visualization of Cocktail Sort:
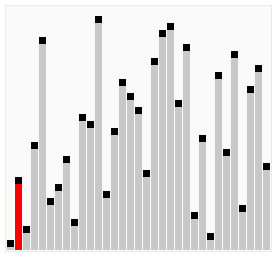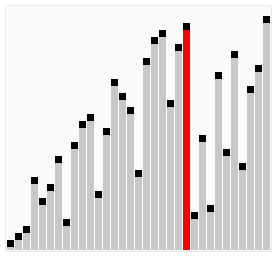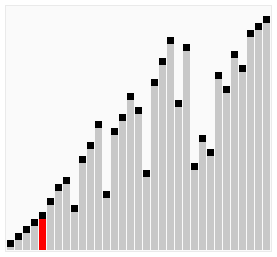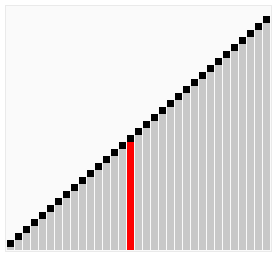
Visual from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cocktail_shaker_sort
Cocktail Sort implementation in Javascript
function cocktailSort(list) {
let swapped;
// The do...while loop ensures the sorting continues until no swaps are needed
do {
// Reset the swapped flag at the beginning of each complete iteration
swapped = false;
// First pass: left to right (like standard bubble sort)
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in the first pass, the array is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the do...while loop early
}
// Reset the swapped flag for the second pass
swapped = false;
// Second pass: right to left (this is what makes it "cocktail" sort)
for (let i = list.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// The loop will continue if any swaps occurred in either pass
} while (swapped);
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
This implementation alternates between forward and backward passes through the list, potentially reducing the number of iterations needed to sort the array.
Practical Applications and Use Cases
While Bubble Sort isn't typically used in production environments for large-scale applications, it can still find use in certain scenarios:
- Educational tools: It's often used to introduce sorting algorithms and algorithm analysis in computer science education.
- Embedded systems: In systems with very limited memory, its in-place sorting can be advantageous.
- Small datasets: For sorting small lists (e.g., less than 50 elements), its simplicity might outweigh the performance benefits of more complex algorithms.
- Nearly sorted data: If data is known to be almost sorted, an optimized Bubble Sort can be reasonably efficient.
- Sorting stability requirement: When a stable sort is needed and simplicity is preferred over efficiency, Bubble Sort can be a straightforward choice.
Conclusion
Bubble Sort, despite its inefficiencies with large datasets, offers valuable insights into the world of sorting algorithms and algorithm analysis. Its straightforward approach makes it an excellent teaching tool for beginners in computer science.
Key takeaways are:
- It's simple to understand and implement.
- It has a time complexity of O(n^2), making it inefficient for large datasets.
- It's an in-place and stable sorting algorithm.
- Optimizations can improve its performance, especially for nearly sorted data.
- It's primarily used for educational purposes and in scenarios with very small datasets or limited memory.
While you're unlikely to use Bubble Sort in production code for large-scale applications, the principles behind it are fundamental to many algorithms. The process of optimizing Bubble Sort teaches valuable lessons about algorithm improvement, serving as a stepping stone to more advanced computational problem-solving.
When it comes to algorithms, there's rarely a one-size-fits-all solution. The best algorithm for a given task depends on the specific requirements, constraints, and characteristics of your data. Bubble Sort, with all its limitations, still has its place in this diverse algorithmic ecosystem.
以上是使用 Javascript 进行算法之旅 - 冒泡排序的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

