AdaBoost - 集成方法,分类:监督机器学习
- 王林原创
- 2024-07-18 21:00:01992浏览
提升
定义和目的
Boosting 是机器学习中用于提高模型准确性的集成学习技术。它结合了多个弱分类器(性能比随机猜测稍好的模型)来创建强分类器。 boosting的主要目的是依次将弱分类器应用到数据上,纠正先前分类器所犯的错误,从而提高整体性能。
主要目标:
- 提高准确率:通过组合多个弱分类器的输出来提高预测准确率。
- 减少偏差和方差:解决偏差和方差问题,以实现模型更好的泛化。
- 处理复杂数据:有效地建模数据中的复杂关系。
AdaBoost(自适应增强)
定义和目的
AdaBoost,Adaptive Boosting 的缩写,是一种流行的 boosting 算法。它调整错误分类实例的权重,以便后续分类器更加关注困难的案例。 AdaBoost 的主要目的是通过在每次迭代中强调难以分类的示例来提高弱分类器的性能。
主要目标:
- 权重调整:增加错误分类实例的权重,以确保下一个分类器重点关注它们。
- 顺序学习:顺序构建分类器,每个新分类器都会纠正其前一个分类器的错误。
- 性能提升:将弱分类器组合起来形成具有更好预测能力的强分类器。
AdaBoost 的工作原理
-
初始化权重:
- 为所有训练实例分配相同的权重。对于包含 n 个实例的数据集,每个实例的权重为 1/n。
-
训练弱分类器:
- 使用加权数据集训练弱分类器。
-
计算分类器错误:
- 计算弱分类器的误差,即错误分类实例的权重之和。
-
计算分类器权重:
- 根据分类器的误差计算其权重。重量由下式给出: 阿尔法 = 0.5 * log((1 - 误差) / 误差)
- 较低的错误导致较高的分类器权重。
-
更新实例的权重:
- 调整实例的权重。增加错误分类实例的权重,减少正确分类实例的权重。
- 实例 i 的更新权重为: 权重[i] = 权重[i] * exp(alpha * (错误分类? 1 : -1))
- 标准化权重以确保它们的总和为 1。
-
组合弱分类器:
- 最终的强分类器是弱分类器的加权和: 最终分类器=符号(sum(alpha *weak_classifier))
- sign 函数根据总和确定类标签。
AdaBoost(二元分类)示例
AdaBoost 是 Adaptive Boosting 的缩写,是一种结合多个弱分类器来创建强分类器的集成技术。此示例演示如何使用合成数据实现 AdaBoost 进行二元分类、评估模型的性能以及可视化决策边界。
Python 代码示例
1。导入库
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
此块导入数据操作、绘图和机器学习所需的库。
2。生成样本数据
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility # Generate synthetic data for 2 classes n_samples = 1000 n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 2 # Class 0: Centered around (-1, -1) X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 + [-1, -1] # Class 1: Centered around (1, 1) X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 + [1, 1] # Combine the data X = np.vstack([X0, X1]) y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class), np.ones(n_samples_per_class)]) # Shuffle the dataset shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples) X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
该块生成具有两个特征的合成数据,其中目标变量 y 是基于类中心定义的,模拟二元分类场景。
3。分割数据集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
此块将数据集拆分为训练集和测试集以进行模型评估。
4。创建并训练 AdaBoost 分类器
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=3, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
此块使用决策树桩作为基本估计器来初始化 AdaBoost 模型,并使用训练数据集对其进行训练。
5。做出预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
此块使用经过训练的模型对测试集进行预测。
6。评估模型
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
输出:
Accuracy: 0.9400
Confusion Matrix:
[[96 8]
[ 4 92]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.96 0.92 0.94 104
1.0 0.92 0.96 0.94 96
accuracy 0.94 200
macro avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
weighted avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
此块计算并打印准确性、混淆矩阵和分类报告,提供对模型性能的深入了解。
7。可视化决策边界
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='RdYlBu')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='RdYlBu', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Binary Classification")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundary created by the AdaBoost model, illustrating how the model separates the two classes in the feature space.
Output:

This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for binary classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities. The visualization of the decision boundary aids in interpreting the model's predictions.
AdaBoost (Multiclass Classification) Example
AdaBoost is an ensemble learning technique that combines multiple weak classifiers to create a strong classifier. This example demonstrates how to implement AdaBoost for multiclass classification using synthetic data, evaluate the model's performance, and visualize the decision boundary for five classes.
Python Code Example
1. Import Libraries
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
This block imports the necessary libraries for data manipulation, plotting, and machine learning.
2. Generate Sample Data with 5 Classes
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility
n_samples = 2500 # Total number of samples
n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 5 # Ensure this is exactly n_samples // 5
# Class 0: Centered around (-2, -2)
X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [-2, -2]
# Class 1: Centered around (0, -2)
X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [0, -2]
# Class 2: Centered around (2, -2)
X2 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [2, -2]
# Class 3: Centered around (-1, 2)
X3 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [-1, 2]
# Class 4: Centered around (1, 2)
X4 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [1, 2]
# Combine the data
X = np.vstack([X0, X1, X2, X3, X4])
y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class),
np.ones(n_samples_per_class),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 2),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 3),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 4)])
# Shuffle the dataset
shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
This block generates synthetic data for five classes located in different regions of the feature space.
3. Split the Dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
This block splits the dataset into training and testing sets for model evaluation.
4. Create and Train the AdaBoost Classifier
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=10, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
This block initializes the AdaBoost classifier with a weak learner (decision stump) and trains it using the training dataset.
5. Make Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
This block uses the trained model to make predictions on the test set.
6. Evaluate the Model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
Output:
Accuracy: 0.9540
Confusion Matrix:
[[ 97 2 0 0 0]
[ 0 92 3 0 0]
[ 0 4 92 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 86 14]
[ 0 0 0 0 110]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 1.00 0.98 0.99 99
1.0 0.94 0.97 0.95 95
2.0 0.97 0.96 0.96 96
3.0 1.00 0.86 0.92 100
4.0 0.89 1.00 0.94 110
accuracy 0.95 500
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
This block calculates and prints the accuracy, confusion matrix, and classification report, providing insights into the model's performance.
7. Visualize the Decision Boundary
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='viridis')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='viridis', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Multiclass Classification (5 Classes)")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundaries created by the AdaBoost classifier, illustrating how the model separates the five classes in the feature space.
Output:
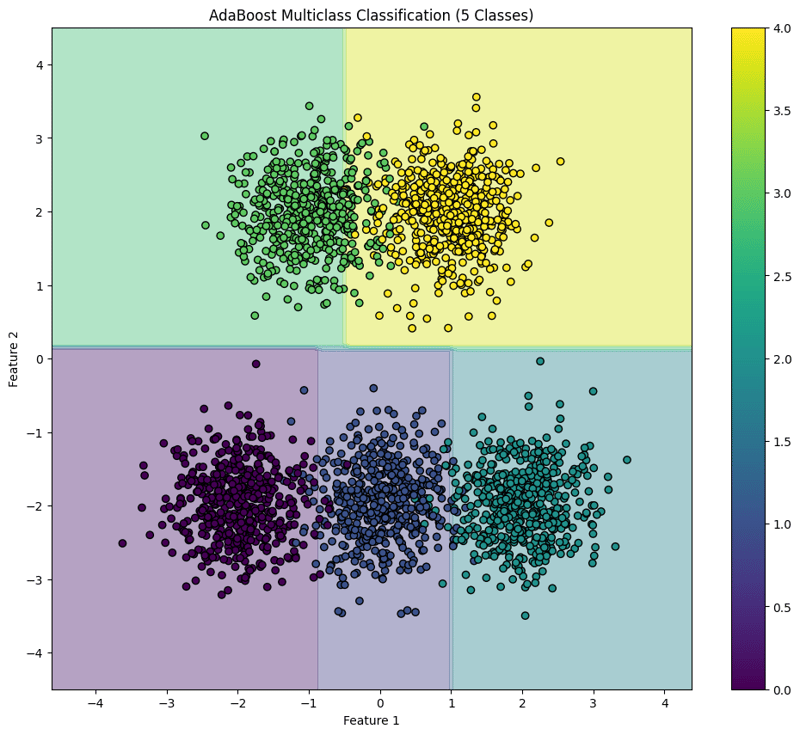
This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for multiclass classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities and the effectiveness of visualizing decision boundaries.
以上是AdaBoost - 集成方法,分类:监督机器学习的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

