分析Java ArrayQueue源碼。
- PHPz轉載
- 2023-05-09 08:10:151330瀏覽
ArrayQueue內部實作
在談ArrayQueue的內部實作之前我們先來看一個ArrayQueue的使用範例:
public void testQueue() {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>(10);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0); // 这个参数只能为0 表示删除队列当中第一个元素,也就是队头元素
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0);
System.out.println(queue);
}
// 输出结果
[1, 2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[3, 4]首先ArrayQueue內部是由循環數組實現的,可能保證增加和刪除資料的時間複雜度都是,不像ArrayList刪除數據的時間複雜度為。在ArrayQueue內部有兩個整數資料head和tail,這兩個的作用主要是指向佇列的頭部和尾部,它的初始狀態在記憶體當中的佈局如下圖所示:

因為是初始狀態head和tail的值都等於0,指向數組當中第一個資料。現在我們向ArrayQueue內部加入5個數據,那麼他的記憶體佈局將如下圖所示:
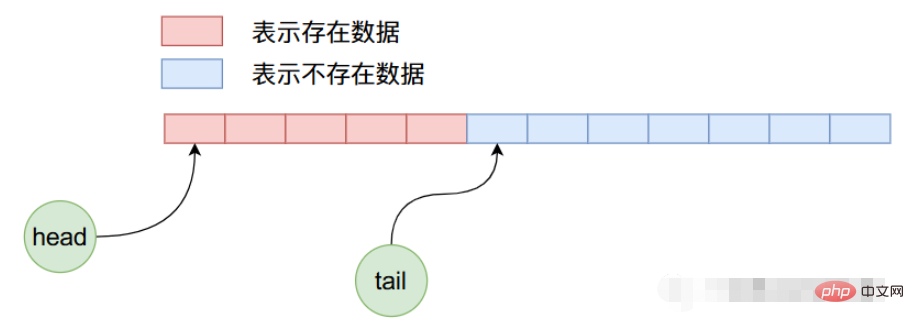
現在我們刪除4個數據,那麼上圖經過4次刪除操作之後,ArrayQueue內部數據佈局如下:

#在上面的狀態下,我們繼續加入8個數據,那麼佈局情況如下:

我們知道上圖在加入資料的時候不僅將陣列後半部的空間使用完了,而且可以繼續使用前半部沒有使用過的空間,也就是說在ArrayQueue內部實作了一個循環使用的過程。
ArrayQueue原始碼剖析
建構子
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity + 1;
this.queue = newArray(capacity + 1);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T[] newArray(int size) {
return (T[]) new Object[size];
}上面的建構子的程式碼比較容易理解,主要就是根據使用者輸入的陣列空間長度去申請數組,不過他具體在申請數組的時候會多申請一個空間。
add函數
public boolean add(T o) {
queue[tail] = o;
// 循环使用数组
int newtail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
if (newtail == head)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue full");
tail = newtail;
return true; // we did add something
}上面的程式碼也相對比較容易看懂,在上文當中我們已經提到了ArrayQueue可以循環將資料加入到數組當中去,這一點在上面的程式碼當中也有所體現。
remove函數
public T remove(int i) {
if (i != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can only remove head of queue");
if (head == tail)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
T removed = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return removed;
}從上面的程式碼當中可以看出,在remove函數當中我們必須傳遞參數0,否則會拋出例外。而在這個函數當中我們只會刪除目前head下標所在位置的數據,然後將head的值進行循環加1操作。
get函數
public T get(int i) {
int size = size();
if (i < 0 || i >= size) {
final String msg = "Index " + i + ", queue size " + size;
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
int index = (head + i) % capacity;
return queue[index];
}get函數的參數表示得到第i個數據,這個第i個數據並不是數組位置的第i個數據,而是距離head位置為i的位置的數據,了解這一點,上面的程式碼很容易理解的。
resize函數
public void resize(int newcapacity) {
int size = size();
if (newcapacity < size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Resizing would lose data");
newcapacity++;
if (newcapacity == this.capacity)
return;
T[] newqueue = newArray(newcapacity);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
newqueue[i] = get(i);
this.capacity = newcapacity;
this.queue = newqueue;
this.head = 0;
this.tail = size;
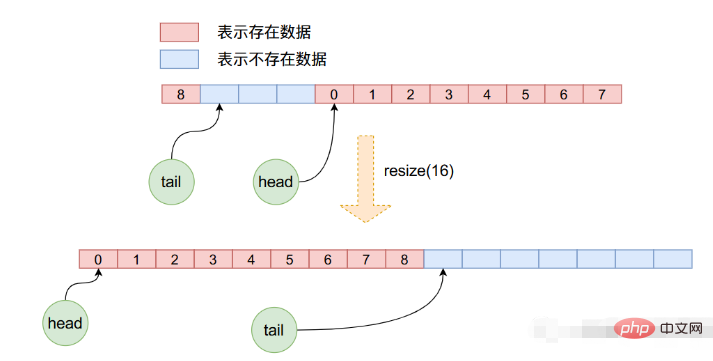
}在resize函數當中先申請新長度的陣列空間,然後將原始陣列的資料一個一個的拷貝到新的陣列當中,注意在這個拷貝的過程當中,重新更新了head與tail,而且並不是簡單的數組拷貝,因為在先前的操作當中head可能已經不是了0,因此新的拷貝需要我們一個一個的從舊數組拿出來,然後放到新數組當中。下圖可以很直覺的看出這個過程:
以上是分析Java ArrayQueue源碼。的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

