如何用Python建立一個文件掃描器?
- 王林轉載
- 2023-04-26 13:10:111853瀏覽
譯者 | 布加迪
審校 | 孫淑娟
您可能想要對文件進行數位化處理,以節省實體空間或建立備份。無論怎樣,編寫一個程式將紙本文件的照片轉換成準格式正是Python所擅長的任務。
結合多個適當的函式庫,您就可以建立一個小型應用程式對文件進行數位化處理。您的程式將以實體文件的影像作為輸入,並運用幾種影像處理技術,即可輸出輸入的掃描版。
1、準備好環境
首先您應該熟悉Python的基礎知識,還需要了解如何使用NumPy Python函式庫。
開啟任何Python IDE,建立兩個Python檔案。將一個命名為main.py,另一個命名為transform.py。然後在終端機上執行以下命令,安裝所需的庫。
pip install OpenCV-Python imutils scikit-image NumPy
您將使用OpenCV-Python獲取影像輸入並進行一些影像處理,使用Imutils來調整輸入和輸出影像的大小,並使用scikit-image對影像施加閾值。 NumPy將幫助您處理陣列。
等待安裝完成,並等待IDE更新專案骨幹內容。骨幹內容更新完成後,您就可以開始程式設計了。完整的原始碼可以在GitHub程式碼庫中找到。
2、導入已安裝的庫
開啟main.py文件,導入所安裝的庫。這將使您能夠在必要時調用和使用它們的函數。
import cv2 import imutils from skimage.filters import threshold_local from transform import perspective_transform
忽略perspective_transform方面拋出的錯誤。您完成處理transform.py檔案的工作後,錯誤會消失。
3、取得並調整輸入的大小
為想要掃描的文件拍攝一張清晰的影像。確保文件的四個角落及其內容都可見。將影像複製到儲存程式檔案的同一個資料夾中。

將輸入影像路徑傳遞給OpenCV。製作原始影像的副本,因為您在透視轉換期間需要它。將原始影像的高度除以您想要調整到的高度。這將保持縱橫比。最後,輸出調整後的影像。
# Passing the image path
original_img = cv2.imread('sample.jpg')
copy = original_img.copy()
# The resized height in hundreds
ratio = original_img.shape[0] / 500.0
img_resize = imutils.resize(original_img, height=500)
# Displaying output
cv2.imshow('Resized image', img_resize)
# Waiting for the user to press any key
cv2.waitKey(0)
上述程式碼的輸出如下:
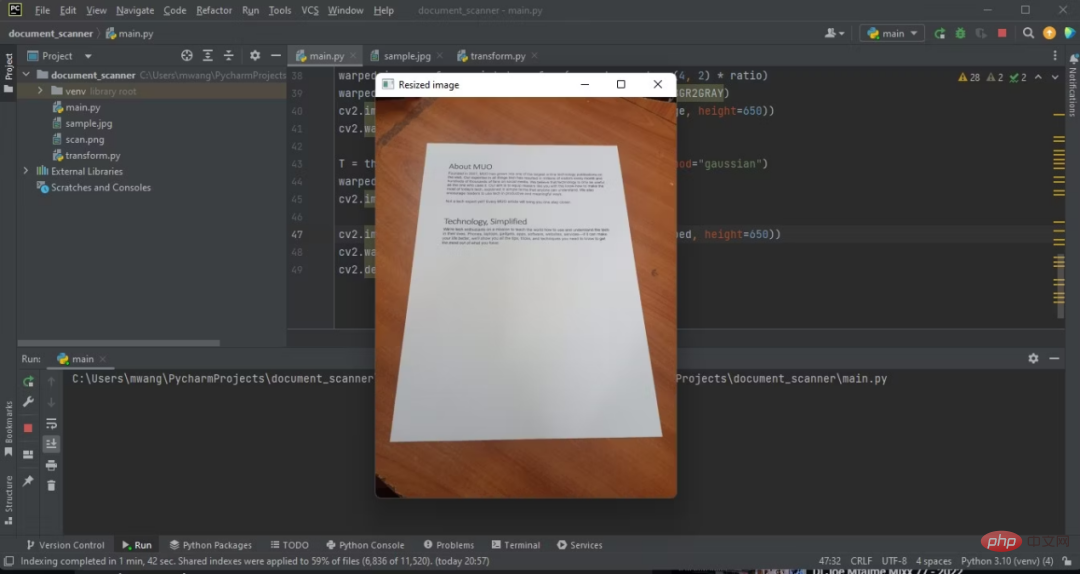
現在您已經將原始影像的高度調整為500像素。
4、將調整後的影像轉換為灰階影像
將調整後的RGB影像轉換為灰階影像。大多數影像處理庫只處理灰階影像,因為它們更容易處理。
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(img_resize, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('Grayed Image', gray_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
注意原始影像和灰階影像之間的差異。
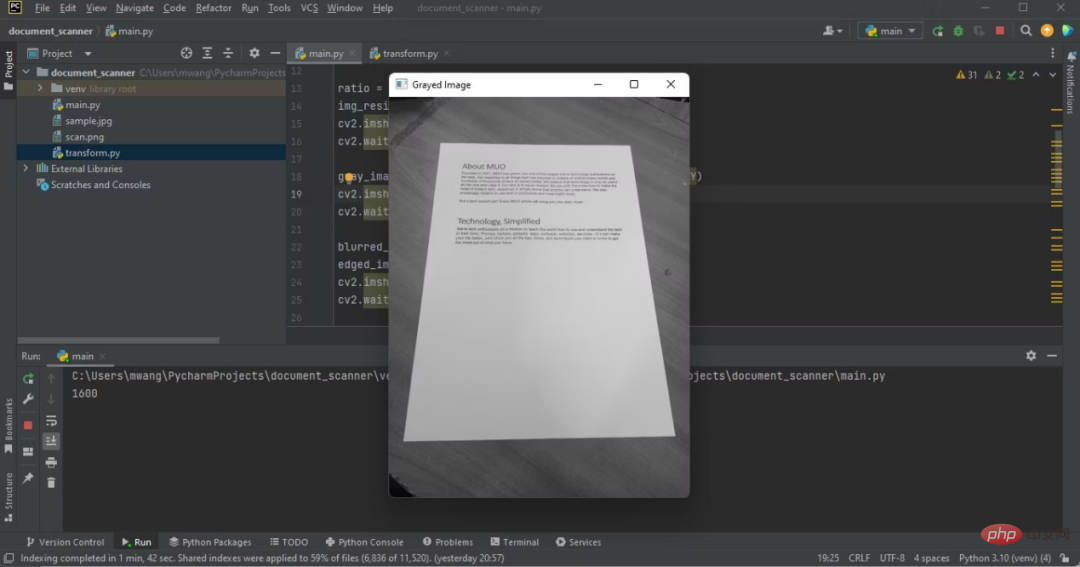
IDE上顯示灰色映像的程式輸出
彩色桌變成了黑白桌。
5、運用邊緣偵測器
對灰階影像運用高斯模糊濾鏡以去除雜訊。然後呼叫OpenCV canny函數來偵測影像中存在的邊緣。
blurred_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_image, (5, 5), 0)
edged_img = cv2.Canny(blurred_image, 75, 200)
cv2.imshow('Image edges', edged_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
邊緣在輸出上是可見的。
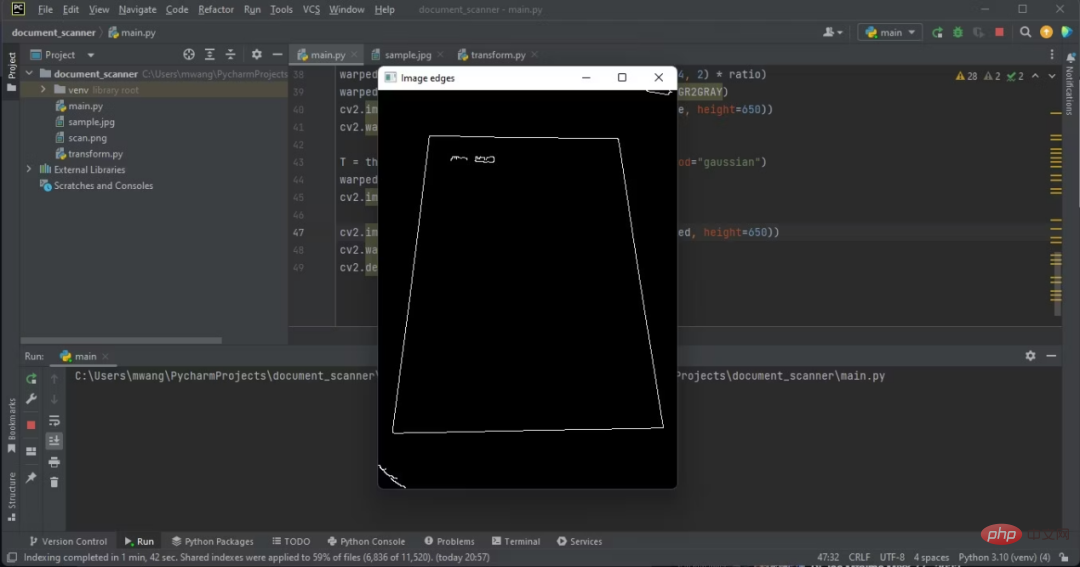
您將處理的邊緣是文件的邊緣。
6、尋找最大的輪廓
#偵測邊緣影像中的輪廓。依降序排序,只保留五個最大的輪廓。透過循環排序後的輪廓,近似獲取最大的四邊輪廓。
cnts, _ = cv2.findContours(edged_img, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[:5] for c in cnts: peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True) approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True) if len(approx) == 4: doc = approx break
有四個邊的輪廓很可能含有文件。
7、圈出文檔輪廓的四個角落
圈出偵測到的文檔輪廓的幾個角落。這將幫助您確定您的程式是否能夠偵測影像中的文件。
p = []
for d in doc:
tuple_point = tuple(d[0])
cv2.circle(img_resize, tuple_point, 3, (0, 0, 255), 4)
p.append(tuple_point)
cv2.imshow('Circled corner points', img_resize)
cv2.waitKey(0)
對調整後的RGB影像圈出幾個角落。
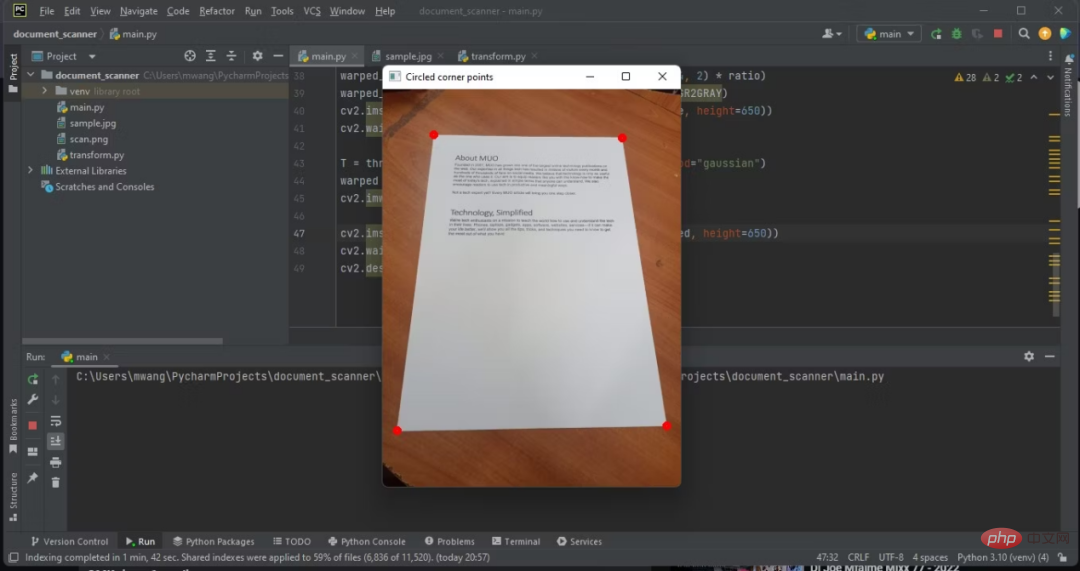
偵測到文件之後,現在需要從映像中提取文件。
8、使用扭曲透視法獲得所需的影像
扭曲透視(warp perspective)是一種電腦視覺技術,用於轉換影像以修正失真。它將圖像轉換成不同的平面,讓您可以從不同的角度查看圖像。
warped_image = perspective_transform(copy, doc.reshape(4, 2) * ratio)
warped_image = cv2.cvtColor(warped_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow("Warped Image", imutils.resize(warped_image, height=650))
cv2.waitKey(0)
為了獲得扭曲後的影像,您需要建立一個簡單的模組來執行透視轉換。
9、轉換模組
该模块将对文档角的点进行排序。它还会将文档图像转换成不同的平面,并将相机角度更改为俯拍。
打开之前创建的那个transform.py文件,导入OpenCV库和NumPy库。
import numpy as np import cv2
这个模块将含有两个函数。创建一个对文档角点的坐标进行排序的函数。第一个坐标将是左上角的坐标,第二个将是右上角的坐标,第三个将是右下角的坐标,第四个将是左下角的坐标。
def order_points(pts): # initializing the list of coordinates to be ordered rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype = "float32") s = pts.sum(axis = 1) # top-left point will have the smallest sum rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)] # bottom-right point will have the largest sum rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)] '''computing the difference between the points, the top-right point will have the smallest difference, whereas the bottom-left will have the largest difference''' diff = np.diff(pts, axis = 1) rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)] rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)] # returns ordered coordinates return rect
创建将计算新图像的角坐标,并获得俯拍的第二个函数。然后,它将计算透视变换矩阵,并返回扭曲的图像。
def perspective_transform(image, pts): # unpack the ordered coordinates individually rect = order_points(pts) (tl, tr, br, bl) = rect '''compute the width of the new image, which will be the maximum distance between bottom-right and bottom-left x-coordinates or the top-right and top-left x-coordinates''' widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2)) maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB)) '''compute the height of the new image, which will be the maximum distance between the top-left and bottom-left y-coordinates''' heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2)) heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB)) '''construct the set of destination points to obtain an overhead shot''' dst = np.array([ [0, 0], [maxWidth - 1, 0], [maxWidth - 1, maxHeight - 1], [0, maxHeight - 1]], dtype = "float32") # compute the perspective transform matrix transform_matrix = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst) # Apply the transform matrix warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, transform_matrix, (maxWidth, maxHeight)) # return the warped image return warped
现在您已创建了转换模块。perspective_transform导入方面的错误现在将消失。
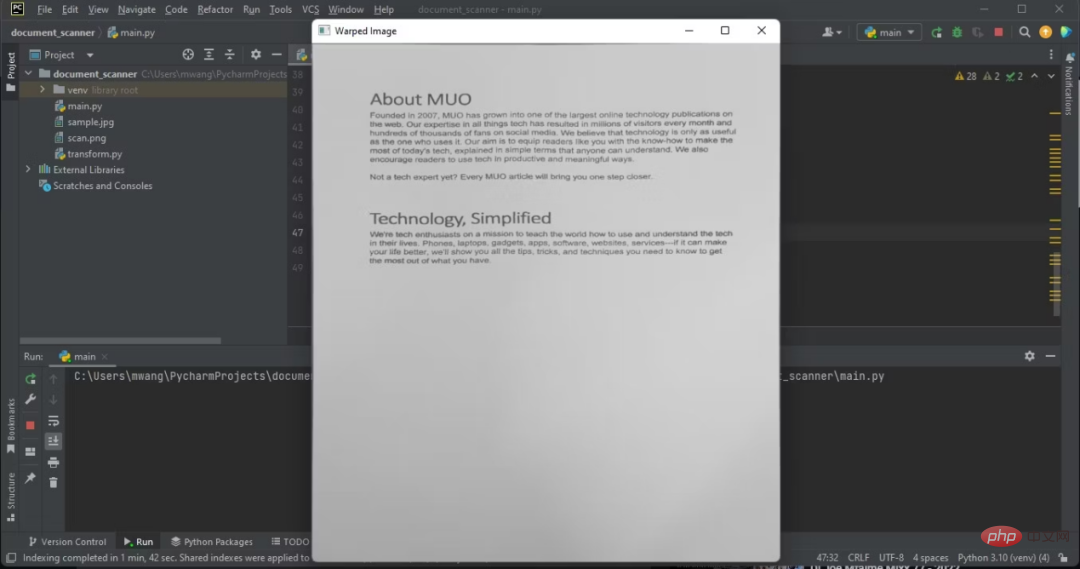
注意,显示的图像有俯拍。
10、运用自适应阈值,保存扫描输出
在main.py文件中,对扭曲的图像运用高斯阈值。这将给扭曲的图像一个扫描后的外观。将扫描后的图像输出保存到含有程序文件的文件夹中。
T = threshold_local(warped_image, 11, offset=10, method="gaussian")
warped = (warped_image > T).astype("uint8") * 255
cv2.imwrite('./'+'scan'+'.png',warped)
以PNG格式保存扫描件可以保持文档质量。
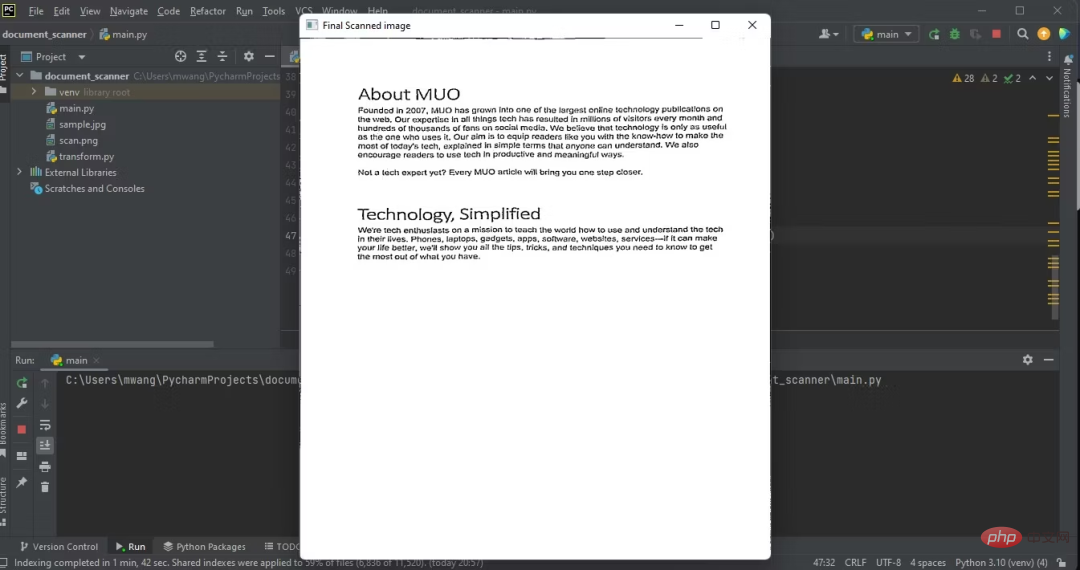
11、显示输出
输出扫描后文档的图像:
cv2.imshow("Final Scanned image", imutils.resize(warped, height=650))
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
下图显示了程序的输出,即扫描后文档的俯拍。
12、计算机视觉在如何进步?
创建文档扫描器涉及计算机视觉的一些核心领域,计算机视觉是一个广泛而复杂的领域。为了在计算机视觉方面取得进步,您应该从事有趣味又有挑战性的项目。
您还应该阅读如何将计算机视觉与当前前技术结合使用方面的更多信息。这让您能了解情况,并为所处理的项目提供新的想法。
原文链接:https://www.makeuseof.com/python-create-document-scanner/
以上是如何用Python建立一個文件掃描器?的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

