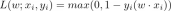目前流行的強化學習演算法包括 Q-learning、SARSA、DDPG、A2C、PPO、DQN 和 TRPO。這些演算法已被用於在遊戲、機器人和決策等各種應用中,而這些流行的演算法仍在不斷發展和改進,本文我們將對其做一個簡單的介紹。
1、Q-learning
Q-learning:Q-learning 是一種無模型、非策略的強化學習演算法。它使用 Bellman 方程式估計最佳動作值函數,該方程式迭代地更新給定狀態動作對的估計值。 Q-learning 以其簡單性和處理大型連續狀態空間的能力而聞名。
以下是使用 Python 實作 Q-learning 的簡單範例:
import numpy as np # Define the Q-table and the learning rate Q = np.zeros((state_space_size, action_space_size)) alpha = 0.1 # Define the exploration rate and discount factor epsilon = 0.1 gamma = 0.99 for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Choose an action using an epsilon-greedy policy if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < epsilon: action = np.random.randint(0, action_space_size) else: action = np.argmax(Q[current_state]) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Update the Q-table using the Bellman equation Q[current_state, action] = Q[current_state, action] + alpha * (reward + gamma * np.max(Q[next_state]) - Q[current_state, action]) current_state = next_state
在上面的範例中,state_space_size 和 action_space_size 分別是環境中的狀態數和動作數。 num_episodes 是要為運行演算法的輪次數。 initial_state 是環境的起始狀態。 take_action(current_state, action) 是一個函數,它將當前狀態和一個動作作為輸入,並傳回下一個狀態、獎勵和一個指示輪次是否完成的布林值。
在 while 迴圈中,使用 epsilon-greedy 策略根據目前狀態選擇一個動作。使用機率 epsilon選擇一個隨機動作,使用機率 1-epsilon選擇對目前狀態具有最高 Q 值的動作。
採取行動後,觀察下一個狀態和獎勵,使用Bellman方程式更新q。並將目前狀態更新為下一個狀態。這只是 Q-learning 的一個簡單範例,並未考慮 Q-table 的初始化和要解決的問題的具體細節。
2、SARSA
SARSA:SARSA 是一種無模型、基於策略的強化學習演算法。它也使用Bellman方程式來估計動作價值函數,但它是基於下一個動作的期望值,而不是像 Q-learning 中的最優動作。 SARSA 以其處理隨機動力學問題的能力而聞名。
import numpy as np # Define the Q-table and the learning rate Q = np.zeros((state_space_size, action_space_size)) alpha = 0.1 # Define the exploration rate and discount factor epsilon = 0.1 gamma = 0.99 for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state action = epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, current_state) while not done: # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Choose next action using epsilon-greedy policy next_action = epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, next_state) # Update the Q-table using the Bellman equation Q[current_state, action] = Q[current_state, action] + alpha * (reward + gamma * Q[next_state, next_action] - Q[current_state, action]) current_state = next_state action = next_action
state_space_size和action_space_size分別是環境中的狀態和動作的數量。 num_episodes是您想要執行SARSA演算法的輪次數。 Initial_state是環境的初始狀態。 take_action(current_state, action)是一個將目前狀態和作為操作輸入的函數,並傳回下一個狀態、獎勵和一個指示情節是否完成的布林值。
在while循環中,使用在單獨的函數epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, current_state)中定義的epsilon-greedy策略來根據當前狀態選擇操作。使用機率 epsilon選擇一個隨機動作,使用機率 1-epsilon對目前狀態具有最高 Q 值的動作。
上面與Q-learning相同,但是採取了一個行動後,在觀察下一個狀態和獎勵時它然後使用貪心策略選擇下一個行動。並使用Bellman方程式更新q表。
3、DDPG
DDPG 是一種用於連續動作空間的無模型、非策略演算法。它是一種actor-critic演算法,其中actor網路用於選擇動作,而critic網路用於評估動作。 DDPG 對於機器人控制和其他連續控制任務特別有用。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam # Define the actor and critic models actor = Sequential() actor.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) actor.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) actor.add(Dense(action_space_size, activation='tanh')) actor.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) critic = Sequential() critic.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) critic.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) critic.add(Dense(1, activation='linear')) critic.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) # Define the replay buffer replay_buffer = [] # Define the exploration noise exploration_noise = OrnsteinUhlenbeckProcess(size=action_space_size, theta=0.15, mu=0, sigma=0.2) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using the actor model and add exploration noise action = actor.predict(current_state)[0] + exploration_noise.sample() action = np.clip(action, -1, 1) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Add the experience to the replay buffer replay_buffer.append((current_state, action, reward, next_state, done)) # Sample a batch of experiences from the replay buffer batch = sample(replay_buffer, batch_size) # Update the critic model states = np.array([x[0] for x in batch]) actions = np.array([x[1] for x in batch]) rewards = np.array([x[2] for x in batch]) next_states = np.array([x[3] for x in batch]) target_q_values = rewards + gamma * critic.predict(next_states) critic.train_on_batch(states, target_q_values) # Update the actor model action_gradients = np.array(critic.get_gradients(states, actions)) actor.train_on_batch(states, action_gradients) current_state = next_state
在本例中,state_space_size和action_space_size分別是環境中的狀態和動作的數量。 num_episodes是輪次數。 Initial_state是環境的初始狀態。 Take_action (current_state, action)是一個函數,它接受目前狀態和動作作為輸入,並傳回下一個動作。
4、A2C
A2C(Advantage Actor-Critic)是一種有策略的actor-critic演算法,它使用Advantage函數來更新策略。此演算法實現簡單,可以處理離散和連續的動作空間。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam from keras.utils import to_categorical # Define the actor and critic models state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) actor = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) actor = Dense(32, activation='relu')(actor) actor = Dense(action_space_size, activation='softmax')(actor) actor_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=actor) actor_model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) critic = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) critic = Dense(32, activation='relu')(critic) critic = Dense(1, activation='linear')(critic) critic_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=critic) critic_model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state done = False while not done: # Select an action using the actor model and add exploration noise action_probs = actor_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0] action = np.random.choice(range(action_space_size), p=action_probs) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Calculate the advantage target_value = critic_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][0] advantage = reward + gamma * target_value - critic_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0][0] # Update the actor model action_one_hot = to_categorical(action, action_space_size) actor_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), advantage * action_one_hot) # Update the critic model critic_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), reward + gamma * target_value) current_state = next_state
在這個例子中,actor模型是一個神經網絡,它有2個隱藏層,每個隱藏層有32個神經元,具有relu激活函數,輸出層具有softmax激活函數。 critic模型也是一個神經網絡,它有2個隱含層,每層32個神經元,具有relu激活函數,輸出層具有線性激活函數。
使用分類交叉熵損失函數訓練actor模型,使用均方誤差損失函數訓練critic模型。動作是根據actor模型預測選擇的,並添加了用於探索的噪音。
5、PPO
PPO(Proximal Policy Optimization)是一種策略演算法,它使用信任域最佳化的方法來更新策略。它在具有高維觀察和連續動作空間的環境中特別有用。 PPO 以其穩定性和高樣品效率而聞名。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam # Define the policy model state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) policy = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) policy = Dense(32, activation='relu')(policy) policy = Dense(action_space_size, activation='softmax')(policy) policy_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=policy) # Define the value model value_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=Dense(1, activation='linear')(policy)) # Define the optimizer optimizer = Adam(lr=0.001) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using the policy model action_probs = policy_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0] action = np.random.choice(range(action_space_size), p=action_probs) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Calculate the advantage target_value = value_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][0] advantage = reward + gamma * target_value - value_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0][0] # Calculate the old and new policy probabilities old_policy_prob = action_probs[action] new_policy_prob = policy_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][action] # Calculate the ratio and the surrogate loss ratio = new_policy_prob / old_policy_prob surrogate_loss = np.minimum(ratio * advantage, np.clip(ratio, 1 - epsilon, 1 + epsilon) * advantage) # Update the policy and value models policy_model.trainable_weights = value_model.trainable_weights policy_model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=-surrogate_loss) policy_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), np.array([action_one_hot])) value_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), reward + gamma * target_value) current_state = next_state
6、DQN
DQN(深度 Q 網路)是一種無模型、非策略演算法,它使用神經網路來逼近 Q 函數。 DQN 特別適用於 Atari 遊戲和其他類似問題,其中狀態空間是高維的,並使用神經網路近似 Q 函數。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam from collections import deque # Define the Q-network model model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(action_space_size, activation='linear')) model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) # Define the replay buffer replay_buffer = deque(maxlen=replay_buffer_size) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using an epsilon-greedy policy if np.random.rand() < epsilon: action = np.random.randint(0, action_space_size) else: action = np.argmax(model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0]) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Add the experience to the replay buffer replay_buffer.append((current_state, action, reward, next_state, done)) # Sample a batch of experiences from the replay buffer batch = random.sample(replay_buffer, batch_size) # Prepare the inputs and targets for the Q-network inputs = np.array([x[0] for x in batch]) targets = model.predict(inputs) for i, (state, action, reward, next_state, done) in enumerate(batch): if done: targets[i, action] = reward else: targets[i, action] = reward + gamma * np.max(model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0]) # Update the Q-network model.train_on_batch(inputs, targets) current_state = next_state
上面的代码,Q-network有2个隐藏层,每个隐藏层有32个神经元,使用relu激活函数。该网络使用均方误差损失函数和Adam优化器进行训练。
7、TRPO
TRPO (Trust Region Policy Optimization)是一种无模型的策略算法,它使用信任域优化方法来更新策略。 它在具有高维观察和连续动作空间的环境中特别有用。
TRPO 是一个复杂的算法,需要多个步骤和组件来实现。TRPO不是用几行代码就能实现的简单算法。
所以我们这里使用实现了TRPO的现有库,例如OpenAI Baselines,它提供了包括TRPO在内的各种预先实现的强化学习算法,。
要在OpenAI Baselines中使用TRPO,我们需要安装:
pip install baselines
然后可以使用baselines库中的trpo_mpi模块在你的环境中训练TRPO代理,这里有一个简单的例子:
import gym
from baselines.common.vec_env.dummy_vec_env import DummyVecEnv
from baselines.trpo_mpi import trpo_mpi
#Initialize the environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
env = DummyVecEnv([lambda: env])
# Define the policy network
policy_fn = mlp_policy
#Train the TRPO model
model = trpo_mpi.learn(env, policy_fn, max_iters=1000)我们使用Gym库初始化环境。然后定义策略网络,并调用TRPO模块中的learn()函数来训练模型。
还有许多其他库也提供了TRPO的实现,例如TensorFlow、PyTorch和RLLib。下面时一个使用TF 2.0实现的样例
import tensorflow as tf
import gym
# Define the policy network
class PolicyNetwork(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(PolicyNetwork, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')
self.dense3 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.dense1(inputs)
x = self.dense2(x)
x = self.dense3(x)
return x
# Initialize the environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
# Initialize the policy network
policy_network = PolicyNetwork()
# Define the optimizer
optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam()
# Define the loss function
loss_fn = tf.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()
# Set the maximum number of iterations
max_iters = 1000
# Start the training loop
for i in range(max_iters):
# Sample an action from the policy network
action = tf.squeeze(tf.random.categorical(policy_network(observation), 1))
# Take a step in the environment
observation, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# Compute the loss
loss = loss_fn(reward, policy_network(observation))
# Compute the gradients
grads = tape.gradient(loss, policy_network.trainable_variables)
# Perform the update step
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, policy_network.trainable_variables))
if done:
# Reset the environment
observation = env.reset()在这个例子中,我们首先使用TensorFlow的Keras API定义一个策略网络。然后使用Gym库和策略网络初始化环境。然后定义用于训练策略网络的优化器和损失函数。
在训练循环中,从策略网络中采样一个动作,在环境中前进一步,然后使用TensorFlow的GradientTape计算损失和梯度。然后我们使用优化器执行更新步骤。
这是一个简单的例子,只展示了如何在TensorFlow 2.0中实现TRPO。TRPO是一个非常复杂的算法,这个例子没有涵盖所有的细节,但它是试验TRPO的一个很好的起点。
总结
以上就是我们总结的7个常用的强化学习算法,这些算法并不相互排斥,通常与其他技术(如值函数逼近、基于模型的方法和集成方法)结合使用,可以获得更好的结果。
以上是七個流行的強化學習演算法及程式碼實現的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!
 優化您的組織與Genai代理商的電子郵件營銷Apr 13, 2025 am 11:44 AM
優化您的組織與Genai代理商的電子郵件營銷Apr 13, 2025 am 11:44 AM介紹 恭喜!您經營一家成功的業務。通過您的網頁,社交媒體活動,網絡研討會,會議,免費資源和其他來源,您每天收集5000個電子郵件ID。下一個明顯的步驟是
 Apache Pinot實時應用程序性能監視Apr 13, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Apache Pinot實時應用程序性能監視Apr 13, 2025 am 11:40 AM介紹 在當今快節奏的軟件開發環境中,確保最佳應用程序性能至關重要。監視實時指標,例如響應時間,錯誤率和資源利用率可以幫助MAIN
 Chatgpt擊中了10億用戶? Openai首席執行官說:'短短幾週內翻了一番Apr 13, 2025 am 11:23 AM
Chatgpt擊中了10億用戶? Openai首席執行官說:'短短幾週內翻了一番Apr 13, 2025 am 11:23 AM“您有幾個用戶?”他扮演。 阿爾特曼回答說:“我認為我們上次說的是每週5億個活躍者,而且它正在迅速增長。” “你告訴我,就像在短短幾週內翻了一番,”安德森繼續說道。 “我說那個私人
 pixtral -12b:Mistral AI&#039;第一個多模型模型 - 分析VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:20 AM
pixtral -12b:Mistral AI&#039;第一個多模型模型 - 分析VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:20 AM介紹 Mistral發布了其第一個多模式模型,即Pixtral-12b-2409。該模型建立在Mistral的120億參數Nemo 12B之上。是什麼設置了該模型?現在可以拍攝圖像和Tex
 生成AI應用的代理框架 - 分析VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:13 AM
生成AI應用的代理框架 - 分析VidhyaApr 13, 2025 am 11:13 AM想像一下,擁有一個由AI驅動的助手,不僅可以響應您的查詢,還可以自主收集信息,執行任務甚至處理多種類型的數據(TEXT,圖像和代碼)。聽起來有未來派?在這個a


熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser是一個安全的瀏覽器環境,安全地進行線上考試。該軟體將任何電腦變成一個安全的工作站。它控制對任何實用工具的訪問,並防止學生使用未經授權的資源。

MantisBT
Mantis是一個易於部署的基於Web的缺陷追蹤工具,用於幫助產品缺陷追蹤。它需要PHP、MySQL和一個Web伺服器。請查看我們的演示和託管服務。

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
將Eclipse與SAP NetWeaver應用伺服器整合。

SublimeText3 英文版
推薦:為Win版本,支援程式碼提示!

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)