技巧
有了上述前置知識,接下來跟著筆者體驗一次如何巧妙運用各種純CSS開發技巧完成一些常見或特殊的佈局排版吧。為了方便瀏覽器自動計算某些樣式,需全域設定box-sizing:border-box,編碼前請引入筆者整理的reset.css。
主體佈局
主體佈局指大部分情況下通用且具備統一特徵的佔位佈局。掌握主體佈局是一個前端必不可少的技能,養成看設計圖就能大概規劃出整體佈局的前提是必須熟悉這些主體佈局的特點與構造。
全螢幕佈局
經典的全螢幕佈局由頂部、底部和主體三部分組成,其特點為三部分左右滿屏拉伸、頂部底部高度固定和主體高度自適應。此佈局很常見,也是大部分Web應用主體的主流佈局。通常使用<header></header>、<footer></footer>和<main></main>三個標籤語義化排版,<main></main>內部也可插入<aside></aside>側欄或其他語意化標籤。

<div class="fullscreen-layout">
<header></header>
<main></main>
<footer></footer>
</div>position left/right/top/bottom
三部分統一宣告left:0和right:0將其左右滿螢幕拉伸;頂部和底部分別聲明top:0和bottom:0將其吸頂和吸底,並宣告兩個高度為固定值;將主體的top和bottom分別宣告為頂部高度和底部高度。透過絕對定位的方式將三部分固定在特定位置,使其互不影響。 .fullscreen-layout {
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
header,
footer,
main {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
}
header {
top: 0;
height: 50px;
background-color: #f66;
}
footer {
bottom: 0;
height: 50px;
background-color: #66f;
}
main {
top: 50px;
bottom: 50px;
background-color: #3c9;
}
}flex
使用flex實作會更簡潔。 display:flex預設會讓子節點橫向排列,需宣告flex-direction:column改變子節點排列方向為縱向排列;頂部和底部高度固定,所以主體需宣告flex:1讓高度自適應。 .fullscreen-layout {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
header {
height: 50px;
background-color: #f66;
}
footer {
height: 50px;
background-color: #66f;
}
main {
flex: 1;
background-color: #3c9;
}
}若<main></main>需表現成可捲動狀態,千萬不要宣告overflow:auto讓容器自適應捲動,這樣做有可能因為其他格式化上下文的影響而導致自適應滾動失效或產生其他未知效果。需在<main></main>內插入一個<div>並宣告如下。 <pre class="brush:css;toolbar:false;">div {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100%;
}</pre><h6 data-id="heading-5"><strong>兩列佈局</strong></h6>
<p>經典的<strong>兩列佈局</strong>由<code>左右兩列組成,其特點為一列寬度固定、另一列寬度自適應和兩列高度固定且相等。以下以左列寬度固定和右列寬度自適應為例,反之同理。

<div class="two-column-layout">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>float margin-left/right
左列宣告float:left與固定寬度,由於float使節點脫流,右列需宣告margin-left為左列寬度,以確保兩列不會重疊。 .two-column-layout {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #f66;
}
.right {
margin-left: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #66f;
}
}overflow float
左列宣告同上,右列宣告overflow:hidden使其形成BFC區域與外界隔離。 .two-column-layout {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #f66;
}
.right {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100%;
background-color: #66f;
}
}flex
使用flex實作會更簡潔。左列宣告固定寬度,右列宣告flex:1自適應寬度。 .two-column-layout {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #f66;
}
.right {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100%;
background-color: #66f;
}
}三列佈局
經典的三列佈局由左中右三列組成,其特點為連續兩列寬度固定、剩餘一列寬度自適應和三列高度固定且相等。以下以左中列寬度固定和右列寬度自適應為例,反之同理。整體的實現原理與上述兩列佈局一致。

<div class="three-column-layout">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="center"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>為了讓右列寬度自適應計算,就不使用float margin-left的方式了,若使用margin-left 還得結合左中列寬度計算。
overflow float
.three-column-layout {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
float: left;
width: 50px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #f66;
}
.center {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #66f;
}
.right {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100%;
background-color: #3c9;
}
}flex
.three-column-layout {
display: flex;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
width: 50px;
background-color: #f66;
}
.center {
width: 100px;
background-color: #66f;
}
.right {
flex: 1;
background-color: #3c9;
}
}圣杯布局/双飞翼布局
经典的圣杯布局和双飞翼布局都是由左中右三列组成,其特点为左右两列宽度固定、中间一列宽度自适应和三列高度固定且相等。其实也是上述两列布局和三列布局的变体,整体的实现原理与上述N列布局一致,可能就是一些细节需注意。
圣杯布局和双飞翼布局在大体相同下也存在一点不同,区别在于双飞翼布局中间列需插入一个子节点。在常规实现方式里也是在这个中间列里做文章,如何使中间列内容不被左右列遮挡。
<li>相同
<li>中间列放首位且声明其宽高占满父节点
<li>被挤出的左右列使用float和margin负值将其拉回与中间列处在同一水平线上
<li>不同
<li>圣杯布局:父节点声明padding为左右列留出空位,将左右列固定在空位上
<li>双飞翼布局:中间列插入子节点并声明margin为左右列让出空位,将左右列固定在空位上

圣杯布局float + margin-left/right + padding-left/right
由于浮动节点在位置上不能高于前面或平级的非浮动节点,否则会导致浮动节点下沉。因此在编写HTML结构时,将中间列节点挪到右列节点后面。 <div class="grail-layout-x">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
<div class="center"></div>
</div>.grail-layout-x {
padding: 0 100px;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
float: left;
margin-left: -100px;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #f66;
}
.right {
float: right;
margin-right: -100px;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #66f;
}
.center {
height: 100%;
background-color: #3c9;
}
}双飞翼布局float + margin-left/right
HTML结构大体同上,只是在中间列里插入一个子节点<div>。根据两者区别,CSS声明会与上述圣杯布局有一点点出入,可观察对比找出不同地方。<pre class="brush:html;toolbar:false;"><div class="grail-layout-y">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
<div class="center">
<div></div>
</div>
</div></pre><pre class="brush:css;toolbar:false;">.grail-layout-y {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #f66;
}
.right {
float: right;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #66f;
}
.center {
margin: 0 100px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #3c9;
}
}</pre><blockquote><p>圣杯布局/双飞翼布局flex</p></blockquote>
<p>使用flex实现<code>圣杯布局/双飞翼布局可忽略上述分析,左右两列宽度固定,中间列宽度自适应。 <div class="grail-layout">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="center"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>.grail-layout {
display: flex;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
.left {
width: 100px;
background-color: #f66;
}
.center {
flex: 1;
background-color: #3c9;
}
.right {
width: 100px;
background-color: #66f;
}
}均分布局
经典的均分布局由多列组成,其特点为每列宽度相等和每列高度固定且相等。总体来说也是最简单的经典布局,由于每列宽度相等,所以很易找到合适的方式处理。

<div class="average-layout">
<div class="one"></div>
<div class="two"></div>
<div class="three"></div>
<div class="four"></div>
</div>.one {
background-color: #f66;
}
.two {
background-color: #66f;
}
.three {
background-color: #f90;
}
.four {
background-color: #09f;
}float + width
每列宽度声明为相等的百分比,若有4列则声明width:25%。N列就用公式100 / n求出最终百分比宽度,记得保留2位小数,懒人还可用width:calc(100% / n)自动计算呢。 .average-layout {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
div {
float: left;
width: 25%;
height: 100%;
}
}flex
使用flex实现会更简洁。节点声明display:flex后,生成的FFC容器里所有子节点的高度都相等,因为容器的align-items默认为stretch,所有子节点将占满整个容器的高度。每列声明flex:1自适应宽度。 .average-layout {
display: flex;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
div {
flex: 1;
}
}居中布局
居中布局由父容器与若干个子容器组成,子容器在父容器中横向排列或竖向排列且呈水平居中或垂直居中。居中布局是一个很经典的问题,相信大家都会经常遇到。

在此直接上一个目前最简单最高效的居中方式。display:flex与margin:auto的强行组合,同学们自行体会。 <div class="center-layout">
<div></div>
</div>.center-layout {
display: flex;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: #f66;
div {
margin: auto;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #66f;
}
}自适布局
自适布局指相对视窗任何尺寸都能占据特定百分比的占位布局。自适布局的容器都是根据视窗尺寸计算,即使父节点或祖先节点的尺寸发生变化也不会影响自适布局的容器尺寸。
搭建自适布局就离不开视窗比例单位。在CSS3里增加了与viewport相关的四个长度单位,随着时间推移,目前大部分浏览器对这四个长度单位都有较好的兼容性,这也是未来最建议在伸缩方案里使用的长度单位。
<li>
1vw表示1%视窗宽度
<li>
1vh表示1%视窗高度
<li>
1vmin表示1%视窗宽度和1%视窗高度里最小者
<li>
1vmax表示1%视窗宽度和1%视窗高度里最大者
视窗宽高在JS里分别对应window.innerWdith和window.innerHeight。若不考虑低版本浏览器兼容性,完全可用一行CSS代码秒杀所有移动端的伸缩方案。 /* 基于UI width=750px DPR=2的网页 */
html {
font-size: calc(100vw / 7.5);
}上述代码使用calc()实现font-size的动态计算。calc()是自适布局里的核心存在,无它就不能愉快地实现自适布局所有动态计算了。
calc()用于动态计算单位,数值、长度、角度、时间和百分比都能作为参数。由于执行数学表达式后返回运算后的计算值,所以可减少大量人工计算甚至无需人工计算。
calc()饥不择食,所有计量单位都能作为参数参加整个动态计算。
calc()虽然好用,但新手难免会遇到一些坑,谨记以下特点,相信就能玩转calc()了。
<li>四则运算:只能使用+、-、*、/作为运算符号
<li>运算顺序:遵循加减乘除运算顺序,可用()提升运算等级
<li>符号连接:每个运算符号必须使用空格间隔起来
<li>混合计算:可混合不同计量单位动态计算
第三点尤为重要,若未能遵守,浏览器直接忽略该属性。
上述font-size:calc(100vw / 7.5)其实就是根据设计图与浏览器视窗的比例动态计算font-size:100/750 = x/100vw。
在SPA里有遇过因为有滚动条或无滚动条而导致页面路由在跳转过程里发生向左或向右的抖动吗?这让强迫症患者很难受,此时可用calc()巧妙解决该问题。 .elem {
padding-right: calc(100vw - 100%);
}不直接声明padding-right为滚动条宽度是因为每个浏览器的默认滚动条宽度都可能不一致。100vw是视窗宽度,100%内容宽度,那么100vw - 100%就是滚动条宽度,声明padding-right用于保留滚动条出现的位置,这样滚动条出不出现都不会让页面抖动了。
有了calc()做保障就可迅速实现一些与视窗尺寸相关的布局了。例如实现一个视窗宽度都为50%的弹窗。

<div class="modal">
<div class="modal-wrapper"></div>
</div>.modal {
display: flex;
position: fixed;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .5);
&-wrapper {
width: 50vw;
height: 200px;
background-color: #f66;
}
}当然使用calc()也不一定结合视窗比例单位计算。例如自适布局已知部分节点高度,不想手动计算最后节点高度但又想其填充布局剩余空间。

<ul class="selfadaption-layout">
<div class="box-1"></div>
<div class="box-2"></div>
<div class="box-3"></div>
</ul>.selfadaption-layout {
width: 200px;
height: 567px;
.box-1 {
height: 123px;
background-color: #f66;
}
.box-2 {
height: 15%;
background-color: #3c9;
}
.box-3 {
height: calc(100% - 123px - 15%);
background-color: #09f;
}
}吸附布局
吸附布局指相对视窗任何滚动都能占据特定位置的占位布局。视窗滚动到特定位置,布局固定在该位置,后续不随视窗滚动而滚动。该布局产生的效果俗称吸附效果,是一种常见网页效果。譬如吸顶效果和吸底效果都是该范畴,经常在跟随导航、移动广告和悬浮提示等应用场景里出现。
在jQuery時代就有很多吸附效果插件,現在三大前端框架也有自身第三方的吸附效果元件。它們都有共通的實作原理:監聽scroll事件,判斷scrollTop和目標節點的位置範圍,符合條件則會目標節點的position宣告為fixed使目標節點相對於視窗定位,讓使用者看起來像是釘在視窗指定位置。
JS實現吸附效果的程式碼在網路上一搜一大堆,更何況筆者喜歡耍CSS,在此就不貼相關的JS程式碼了。在此推薦一個很少見很少用的CSS屬性position:sticky。簡單的兩行核心CSS程式碼就能完成十多行核心JS程式碼的功能,何樂而不為呢。
簡單回顧position屬性值,怎麼用就不說了,大家應該都很熟悉。
| 取值 |
功能 |
|
| #inherit |
繼承 |
2 |
| static |
標準流 |
2 |
| relative |
相對定位 |
2 |
| absolute |
#絕對定位 | ##2 |
| fixed
|
已固定定位 | 2 |
# #sticky | 黏性定位
|
|
#当值为sticky时将节点变成粘性定位。粘性定位是相对定位和固定定位的结合体,节点在特定阈值跨越前为相对定位,跨越后为固定定位。

<div class="adsorption-position">
<ul>
<li>Top 1</li>
<li>Top 2</li>
<li>Normal</li>
<li>Bottom 1</li>
<li>Bottom 2</li>
</ul>
</div>.adsorption-position {
overflow: auto;
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 280px;
outline: 1px solid #3c9;
ul {
padding: 200px 0;
}
li {
position: sticky;
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
&:nth-child(1) {
top: 0;
z-index: 9;
background-color: #f66;
}
&:nth-child(2) {
top: 40px;
z-index: 9;
background-color: #66f;
}
&:nth-child(3) {
background-color: #f90;
}
&:nth-child(4) {
bottom: 0;
z-index: 9;
background-color: #09f;
}
&:nth-child(5) {
bottom: 40px;
z-index: 9;
background-color: #3c9;
}
}
}两行核心CSS代码分别是position:sticky和top/bottom:npx。上述5个节点都声明position:sticky,但由于top/bottom赋值有所不同就产生不同吸附效果。
细心的同学可能发现这些节点在某些滚动时刻处于相对定位,在特定滚动时刻处于固定定位。
<li>第1个<li>:top为0px,滚动到容器顶部就固定
<li>第2个<li>:top为40px,滚动到距离容器顶部40px就固定
<li>第3个<li>:未声明top/bottom,就一直保持相对定位
<li>第4个<li>:bottom为40px,滚动到距离容器底部40px就固定
<li>第5个<li>:bottom为0px,滚动到容器底部就固定
当然,换成left或right也一样能实现横向的吸附效果。
值得注意,粘性定位的参照物并不一定是position:fixed。当目标节点的任意祖先节点都未声明position:relative|absolute|fixed|sticky,才与position:fixed表现一致。当离目标节点最近的祖先节点声明position:relative|absolute|fixed|sticky,目标节点就相对该祖先节点产生粘性定位。简单来说确认参照物的方式与position:absolute一致。
兼容性勉强还行,近2年发版的浏览器都能支持,Safari和Firefox的兼容性还是挺赞的。有吸附效果需求的同学建议一试,要兼容IExplorer就算了。期待该属性有更好的发展,毕竟吸附布局真的是一种常见布局。

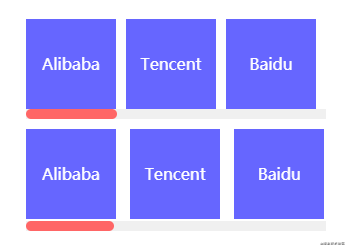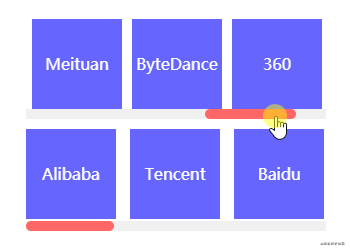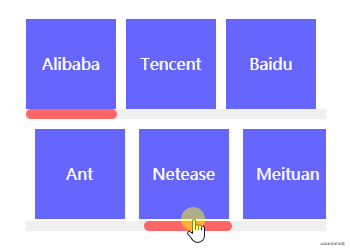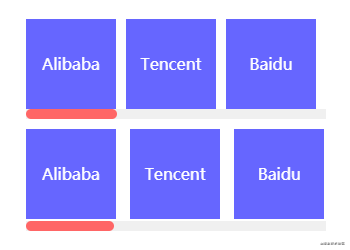
横向布局
横向布局指容器内节点以水平方向排列且溢出部分被隐藏的占位布局。竖向布局很常见,声明overflow:hidden;width:xpx;height:ypx就能实现,但横向布局却不能使用类似方式实现。
为了方便使用多种方式实现横向布局,以下将通用代码拆分出来。

<div class="horizontal-layout">
<ul>
<li>Alibaba</li>
<li>Tencent</li>
<li>Baidu</li>
<li>Jingdong</li>
<li>Ant</li>
<li>Netease</li>
<li>Meituan</li>
<li>ByteDance</li>
<li>360</li>
<li>Sina</li>
</ul>
</div>.horizontal-layout {
overflow: hidden;
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
ul {
overflow-x: auto;
cursor: pointer;
&::-webkit-scrollbar {
height: 10px;
}
&::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}
&::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb {
border-radius: 5px;
background-color: #f66;
}
}
li {
overflow: hidden;
height: 90px;
background-color: #66f;
line-height: 90px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 16px;
color: #fff;
&:not(:first-child) {
margin-left: 10px;
}
}
}有些同学可能会使用行内元素实现横向排版,但必须声明overflow-y:hidden使容器在Y轴方向隐藏溢出部分。由于行内元素在当前行排版产生溢出会自动将其余节点排版到下一行,因此还需声明white-space:nowrap使所有行内元素在一行内排版完毕。若产生滚动条,还需对容器的height做适当的微调。 .horizontal-layout.inline {
height: 102px;
ul {
overflow-y: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
}
li {
display: inline-block;
width: 90px;
}
}上述方式在笔者在开发认知里觉得太繁琐,实质上将所有节点当成文本排列,也是醉了。笔者推荐使用flex布局完成上述布局,flex布局作为目前最常见的布局方式,相信也不用笔者多说。以下实现方式不知大家是否见过呢?在移动端上体验会更棒喔! .horizontal-layout.flex {
ul {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
justify-content: space-between;
}
li {
flex-shrink: 0;
flex-basis: 90px;
}
}凸显布局
凸显布局指容器内节点以同一方向排列且存在一个节点在某个方向上较突出的占位布局。该布局描述起来可能比较拗口,直接看以下效果吧,这是一个横向列表,节点从左往右排列,最右边的节点特别突出。这就是凸显布局的特征,凸显的节点可在凸显布局任意位置,上下左右,左上左下右上右下都行。

这里巧妙运用margin-*:auto实现了凸显布局。相信大家实现水平居中固定宽度的块元素都会使用margin:0 auto。
在此同样原理,当节点声明margin-*:auto时,浏览器会自动计算剩余空间并将该值赋值给该节点。在使用该技巧时必须基于flex布局。




<ul class="highlight-layout">
<li>Alibaba</li>
<li>Tencent</li>
<li>Baidu</li>
<li>Jingdong</li>
<li>Ant</li>
<li>Netease</li>
</ul>.highlight-layout {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
padding: 0 10px;
width: 600px;
height: 60px;
background-color: #3c9;
li {
padding: 0 10px;
height: 40px;
background-color: #3c9;
line-height: 40px;
font-size: 16px;
color: #fff;
}
&.left li {
&:not(:first-child) {
margin-left: 10px;
}
&:last-child {
margin-left: auto;
}
}
&.right li {
&:not(:last-child) {
margin-right: 10px;
}
&:first-child {
margin-right: auto;
}
}
&.top {
flex-direction: column;
width: 120px;
height: 400px;
li {
&:not(:first-child) {
margin-top: 10px;
}
&:last-child {
margin-top: auto;
}
}
}
&.bottom {
flex-direction: column;
width: 120px;
height: 400px;
li {
&:not(:last-child) {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
&:first-child {
margin-bottom: auto;
}
}
}
}在此还有一个小技巧,那就是:not()与:first-child和:last-child的巧妙运用。这样组合让特殊位置的节点直接减少属性覆盖的问题,不仅易读还能装逼。
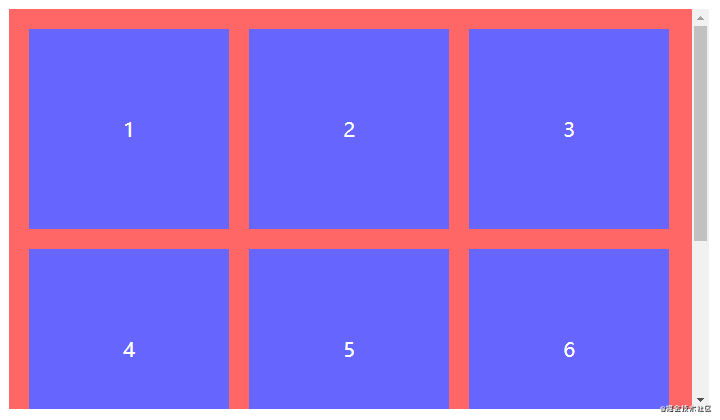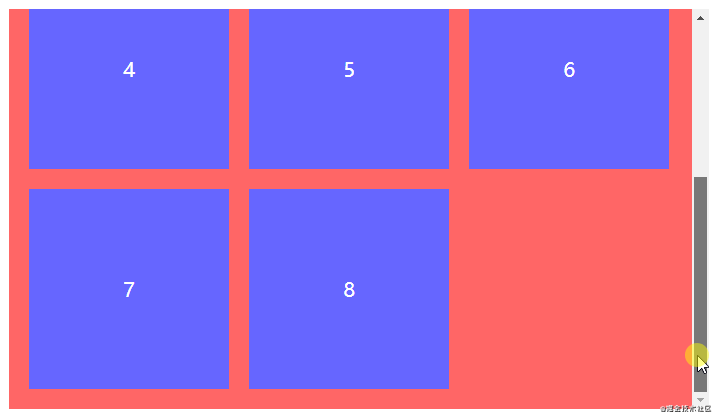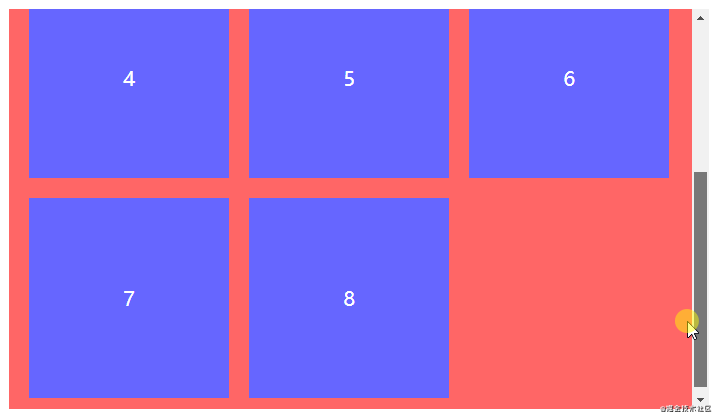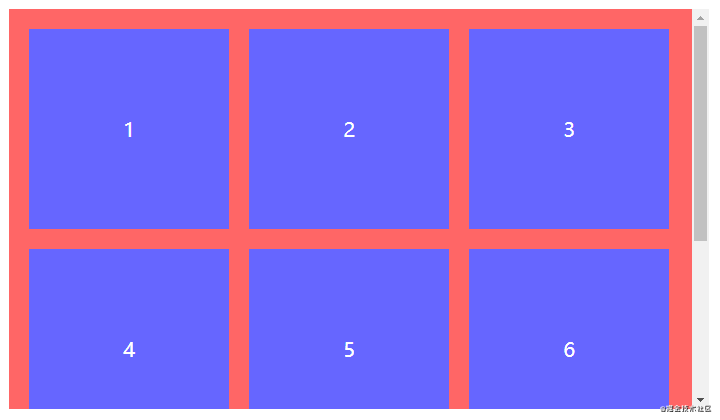
间距布局
间距布局指容器内节点从左往右从上往下排列且以特定间距间隔的占位布局。间距布局常见于各大列表,是笔者认为最重要的布局之一。为何如此简单的布局还是花费一些篇幅讲解呢?最近笔者查看了Github上很多与间隔布局相关的CSS代码,虽然整体效果看上去无大碍,但margin/padding和结构选择器却乱用,因此笔者想从零到一纠正间距布局的正确编码方式。
在进入编码环节前,笔者想重点讲解:nth-child()的点睛之笔。大部分同学可能只认得:nth-child(n)、:nth-child(2n-1)、:nth-child(2n)和:nth-child(xn)的日常用法,但其实还有一些你可能未见过的用法。在此笔者借这次机会将:nth-child()所有用法总结下,n/x/y代表正整数,最小值为1。
分析间距布局的一切特点,捕获特征很有利于将特征转换成CSS代码。
<li>
A:确定容器间的间距,使用margin声明
<li>
B:确定容器内的间距,使用padding声明,后续方便声明background-color(该步骤很易与上一步骤混淆,请特别注意)
<li>
C:确定靠近容器边界的节点与容器的间距,使用padding声明容器而不是使用margin声明节点(该步骤说明上一步骤的处理结果)
<li>
D:确认每行节点的左右间距,使用margin-left/margin-right(二选一)声明节点
<li>
E:确认最左列节点或最右列节点与容器的间距,使用margin-left:0声明最左列节点或使用margin-right:0声明最右列节点
<li>
F:除了首行节点,使用margin-top声明其余节点
<li>
G:若希望容器顶部底部留空,使用border-top/border-bottom代替padding-top/padding-bottom
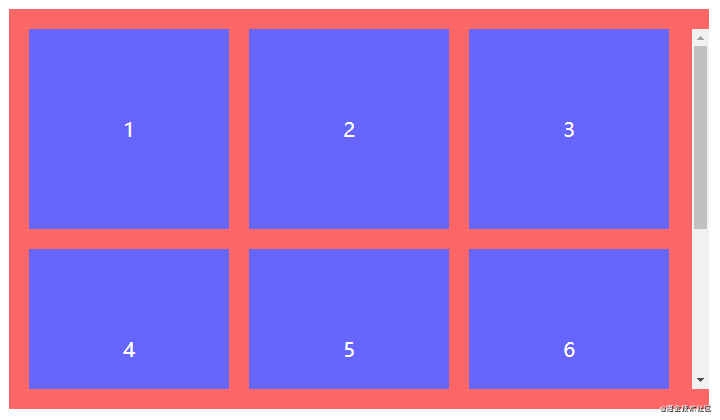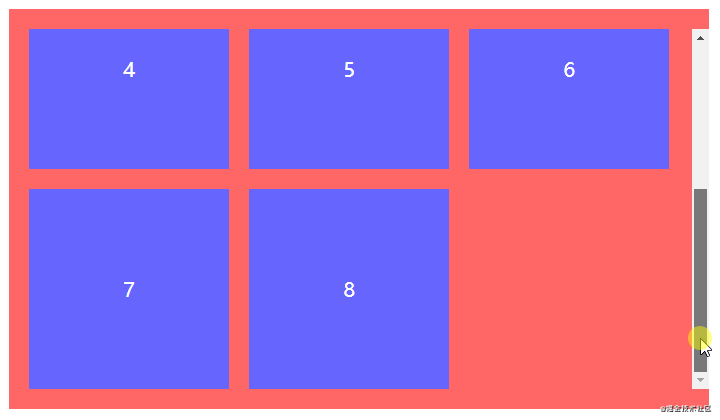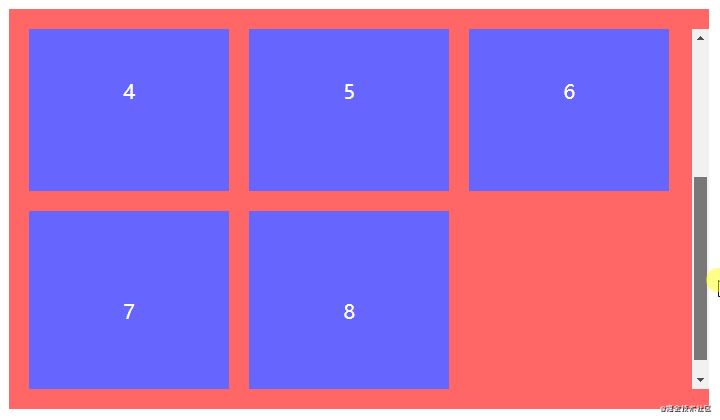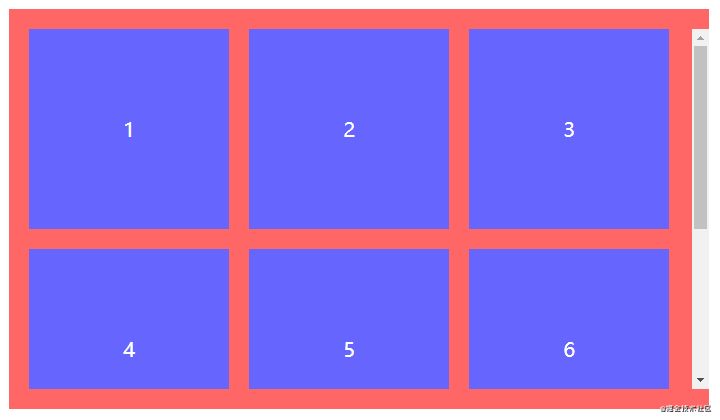
全部步骤串联起来理解可能会产生混乱,但结合以下代码理解相信就能很快熟悉。以一行排列3个节点总共8个节点为例,最终效果为三行三列。


<ul class="spacing-layout">
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
</ul>.spacing-layout {
display: flex;
overflow: auto;
flex-wrap: wrap;
margin-top: 20px; // 对应A
padding: 20px; // 对应B和C
// padding-top: 0; // 对应G
// padding-bottom: 0; // 对应G
// border-top: 20px solid #f66; // 对应G
// border-bottom: 20px solid #f66; // 对应G
width: 700px; // 稍微留空用于显示滚动条
height: 400px;
background-color: #f66;
li {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #66f;
line-height: 200px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 20px;
color: #fff;
&:not(:nth-child(3n)) {
margin-right: 20px; // 对应D和E
}
&:nth-child(n+4) {
margin-top: 20px; // 对应F
}
}
}空载布局
空载布局指容器内无任何节点时使用其他形式代替的占位布局。还有使用JS判断列表集合为空时显示占位符吗?相信很多使用MVVM框架开发的同学都会使用条件判断的方式渲染虚拟DOM,若列表长度不为0则渲染列表,否则渲染占位符。 <div>
<ul v-if="list.length">...</ul>
<div v-esle>Empty</div>
</div>然而CSS提供一个空判断的选择器:empty,这应该很少同学会注意到吧。
:empty作用于无子节点的节点,该子节点也包括行内匿名盒(单独的文本内容)。以下三种情况均视为非空状态,若不出现这三种状态则视为空状态,此时:empty才会触发。

<ul class="empty-layout">
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
</ul>
<ul class="empty-layout"></ul>$empty: "https://yangzw.vip/img/empty.svg";
.empty-layout {
overflow: auto;
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
outline: 1px solid #3c9;
&:empty {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
background: url($empty) no-repeat center/100px auto;
&::after {
margin-top: 90px;
font-weight: bold;
content: "没钱就没数据";
}
}
li {
padding: 0 10px;
height: 30px;
background-color: #09f;
line-height: 30px;
color: #fff;
&:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f90;
}
}
}另外还存在一种特殊的空载布局,就是不做任何处理。这样最终渲染的DOM只有容器,若已声明margin/padding/border但未声明width/height的情况下,就会出现以下占位效果。无任何子节点的容器还声明着margin/padding/border,看着都尴尬。

没事,:empty帮你搞掂!对于无任何子节点的容器直接声明display:none解决所有无效占位,当然也可作用于指定节点。一招制敌,劲! // 作用于所有节点
:empty {
display: none;
}
// 作用于指定节点
.empty-layout:empty {
display: none;
}多格布局
多格布局指容器内节点以动态数量的格子形式排列的占位布局。微信朋友圈的相册就是最常见的多格布局了,当单张照片排列、两张照片排列、三张照片排列等等,每种情况下照片的尺寸都可能不一致。笔者制作了一个动态多格相册怀念我家狗狗AB。大家感受下纯CSS实现动态数量的多格布局吧。
在此留个悬念,不讲解如何实现,看看大家能不能根据笔者列出的提示尝试将该效果复原。主要原理是根据结构选择器限制节点范围实现,在本文也可找到原理的答案喔!记得实现完再看以下源码哈!

<ul class="multigrid-layout">
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
<li class="item"><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://static.yangzw.vip/codepen/ab-3.jpg" class="lazy" alt="8個值得了解的純CSS版排版技巧" ></li>
</ul>@mixin square($count: 2) {
$length: calc((100% - #{$count} * 10px) / #{$count});
width: $length;
height: $length;
}
.multigrid-layout {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: flex-start;
align-content: flex-start;
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
li {
display: flex;
overflow: hidden;
justify-content: center;
margin: 5px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
@include square(3);
}
img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
object-fit: cover;
}
}
// 一个元素
.item:only-child {
border-radius: 10px;
width: auto;
max-width: 80%;
height: auto;
max-height: 80%;
}
// 两个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(2),
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(2) ~ .item:nth-child(2) {
@include square(2);
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(2) {
border-radius: 10px 0 0 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(2) ~ .item:nth-child(2) {
border-radius: 0 10px 10px 0;
}
// 三个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(3),
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(3) ~ .item:nth-child(2),
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(3) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
@include square(2);
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(3) {
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(3) ~ .item:nth-child(2) {
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(3) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
// 四个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4),
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4) ~ .item:nth-child(2),
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4) ~ .item:nth-child(3),
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4) ~ .item:nth-child(4) {
@include square(2);
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4) {
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4) ~ .item:nth-child(2) {
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(4) ~ .item:nth-child(4) {
border-bottom-right-radius: 10px;
}
// 五个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(5) {
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(5) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(5) ~ .item:nth-child(4) {
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
// 六个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(6) {
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(6) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(6) ~ .item:nth-child(4) {
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(6) ~ .item:nth-child(6) {
border-bottom-right-radius: 10px;
}
// 七个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(7) {
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(7) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(7) ~ .item:nth-child(7) {
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
// 八个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(8) {
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(8) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(8) ~ .item:nth-child(7) {
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
// 九个元素
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(9) {
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(9) ~ .item:nth-child(3) {
border-top-right-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(9) ~ .item:nth-child(7) {
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
.item:first-child:nth-last-child(9) ~ .item:nth-child(9) {
border-bottom-right-radius: 10px;
}总结
很多同学可能觉得CSS很简单,但真正玩起来也能与JS有得一比。笔者从事前端领域多年,一直致力于CSS技术的研究与应用,当然真的不是为了玩,而是在玩的过程里将实践到的知识充分应用于工作上。
JS重要但CSS同样重要,希望喜欢CSS的同学多多关注笔者,相信你一定会有更多CSS方面的收获。
原文地址:https://juejin.cn/post/6986873449721364510
作者:JowayYoung
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
|