Angular2 父子元件通訊方式
- php中世界最好的语言原創
- 2018-03-23 09:36:561888瀏覽
這次帶給大家Angular2 父子元件通訊方式,使用Angular2 父子元件通訊方式的注意事項有哪些,下面就是實戰案例,一起來看一下。
Angular2官方文件對元件互動這塊有詳細的介紹-->文件--元件之間的互動。依文檔介紹,元件間互動的方式一共有4種,包括:
透過輸入型綁定把資料從父元件傳到子元件(@Input decoration);子元件暴露一個EventEmitter屬性(@Output decoration),當事件發生時,利用該屬性emits向父元件發射事件。
父元件與子元件透過本機變數互動。 (# var)
父元件呼叫@ViewChild。
父元件和子元件透過服務來通訊。
我在這裡只總結、詳細介紹3種我在專案中使用過的方法,看完本文大概能做到如下的效果:
#建立項目,項目結構如下:
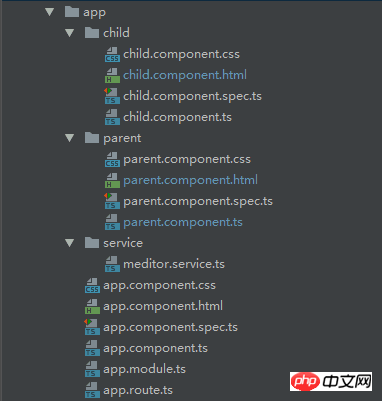
透過@Input、@Output裝飾器進行父、子元件間的通訊
@Input:此屬性綁定用於父元件傳遞資料給子元件。子元件可以透過以下兩種方法截取屬性的變更:
使用一個輸入屬性的setter,以攔截父元件中值得變更。
透過ngOnchanges()來截聽輸入屬性值的變化。
@Output:此資料綁定用於子元件傳遞資料和事件給父元件。
<!--parent.component.html-->
<p style="width: 1000px;margin: auto">
<p class="card" style="width: 500px;float: left">
<p class="card-header">
父组件
</p>
<p class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">父组件</h5>
<p class="form-group">
<label for="input">父组件输入:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="input"
placeholder="Input something"
[(ngModel)]="parentPrint"
>
<label for="output">父组件输出:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="output"
placeholder="Output something"
[(ngModel)]="contentFromChild"
>
</p>
</p>
</p>
<app-child
[fromParent]="parentPrint"
(fromChild)="fromChild($event)"
></app-child>
</p>
<!--child.component.html-->
<p class="card" style="width: 500px;">
<p class="card-header">
子组件
</p>
<p class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">子组件</h5>
<p class="form-group">
<label for="input">子组件输入:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="input"
placeholder="Input something"
[(ngModel)]="contentFromChild"
>
<label for="output">子组件输出:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="output"
placeholder="Output something"
[(ngModel)]="fromParent"
>
</p>
<button class="btn btn-primary" (click)="clickChild()">Output方式</button>
</p>
</p>
效果如下:(1、父元件輸入,子元件可同步輸出;2、子元件輸入需要(3、)點選按鈕觸發發射事件,將資料傳送給父元件。)
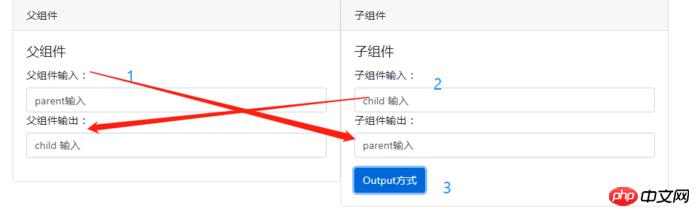
@Input:父元件輸入的同時,子元件能同步取得資料進行顯示。核心程式碼如下:
//父组件 parentPrint: any; //ts中,声明一个变量 [(ngModel)]="parentPrint" //html中,绑定变量,获取用户输入 //html中,将数据传给子组件 <app-child [fromParent]="parentPrint"></app-child> //子组件 @Input() fromParent; //ts中,用于直接接收从父组件获取的数据 [(ngModel)]="fromParent" //html中,用于显示数据
透過setter截聽輸入屬性值的變化,在子元件中宣告一個私有變數來取得父元件傳遞過來的數據,從而屏蔽上層取得下層資訊。 (簡單一點就是不讓父元件知道子元件用什麼東西去接收傳過來的資料)透過這種方法也可以獲得相同的效果。
//子组件
private _fromParent: any; //私有变量,通过setter获取父组件的数据
@Input() //通过setter获取父组件的数据
set fromParent(fromParent: any) {
this._fromParent = fromParent;
}
get fromParent(): any {
return this._fromParent;
}
@Output:父元件接收子元件的資料時,子元件暴露一個EventEmitter屬性,當事件發生時,子元件利用該屬性emits(向上彈射)事件。父元件綁定到這個事件屬性,並在事件發生時作出回應。核心程式碼如下:
//子组件
@Output() fromChild = new EventEmitter<any>(); //暴露一个输出属性
<button class="btn btn-primary" (click)="clickChild()">Output方式</button>
//触发发射函数,将数据发送给父组件
clickChild() {
console.log('click child' , this.contentFromChild);
this.fromChild.emit(this.contentFromChild);
}
//父组件
[(ngModel)]="contentFromChild" //绑定输出子组件的数据
//使用子组件,绑定事件属性
<app-child
[fromParent]="parentPrint"
(fromChild)="fromChild($event)"
></app-child>
//事件处理函数
fromChild(event) {
console.log(event);
this.contentFromChild = event;
}
父元件透過呼叫@ViewChild()來取得子元件的資料
如果父元件的類別需要讀取子元件的屬性和值或呼叫子元件的方法時,就可以把子元件當作ViewChild,注入到父元件裡面。 ViewChild顧名思義就是可以看見子元件裡面的屬性和方法。
<!--parent.component.html-->
<p style="width: 1000px;margin: auto">
<p class="card" style="width: 500px;float: left">
<p class="card-header">
父组件
</p>
<p class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">父组件</h5>
<p class="form-group">
<label for="viewoutput">ViewChild父组件输出:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="viewoutput"
placeholder="ViewChild父组件输出"
[(ngModel)]="viewOutput"
>
</p>
<button class="btn btn-primary" (click)="clickView()">ViewChild方式</button>
</p>
</p>
<app-child></app-child>
</p>
<!--child.component.html-->
<p class="card" style="width: 500px;">
<p class="card-header">
子组件
</p>
<p class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">子组件</h5>
<p class="form-group">
<label for="input">子组件输入:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="input"
placeholder="Input something"
[(ngModel)]="contentFromChild"
>
</p>
</p>
</p>
效果如下:
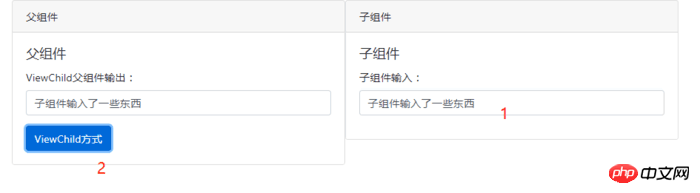
父元件核心程式碼:
//ts
@ViewChild(ChildComponent) // 使用viewChild导入引用
private childComponent: ChildComponent; // 将子组件注入到私有属性
//获取子组件数据并显示
clickView() {
//直接获取子组件的属性
this.viewOutput = this.childComponent.contentFromChild;
}
//html [(ngModel)]="viewOutput" <button class="btn btn-primary" (click)="clickView()">ViewChild方式</button>
父元件和子元件透過服務來通訊
父元件和它的子元件共用同一個服務,利用該服務在家庭內部實現雙向通訊。
<!--parent.component.html-->
<p style="width: 1000px;margin: auto">
<p class="card" style="width: 500px;float: left">
<p class="card-header">
父组件
</p>
<p class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">父组件</h5>
<p class="form-group">
<label for="serviceoutput">父组件服务输入:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="serviceoutput"
placeholder="服务输入"
[(ngModel)]="serviceInput"
>
</p>
<button class="btn btn-primary" (click)="clickService()">Service方式</button>
</p>
</p>
<app-child></app-child>
</p>
<!--child.component.html-->
<p class="card" style="width: 500px;">
<p class="card-header">
子组件
</p>
<p class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">子组件</h5>
<p class="form-group">
<label for="serviceoutput">子组件服务输入:</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="serviceoutput"
placeholder="服务输入"
[(ngModel)]="serviceInput"
>
</p>
<button class="btn btn-primary" (click)="clickService()">Service方式</button>
</p>
</p>
//服务
//meditor.service.ts
import {Injectable} from '@angular/core';
import {Subject} from 'rxjs/Subject';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs/Observable';
@Injectable()
export class MeditorService {
private subject = new Subject<MeditorMsg>();
constructor() {}
// 获取订阅者
public getObservable(): Observable<MeditorMsg> {
return this.subject.asObservable();
}
// 推送信息
public push(msg: MeditorMsg) {
this.subject.next(msg);
}
}
// 中间者信息
export interface MeditorMsg {
id: string;
body: any;
}
效果如下:
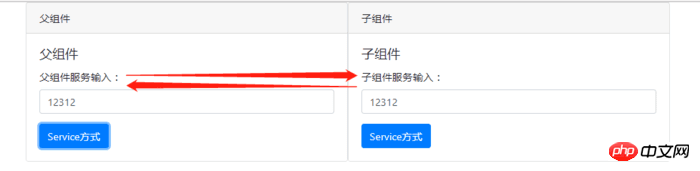
#父子元件的核心程式碼類似,在建構子中將此服務實例注入到自身,父子組件都有一個唯一的id。無論是父元件或子元件呼叫push()方法推送數據,雙方都能接收到數據,這時候就要根據id來判斷是要父元件使用資料還是子元件使用資料。核心程式碼如下:
subscription: Subscription = null; //初始化一个订阅对象
//子组件构造函数,用于监听数据推送
constructor(
private meditor: MeditorService
) {
this.subscription = meditor.getObservable().subscribe(
msg => {
console.log(msg);
if (msg.id === 'parent') { //id为parent,获取父组件数据
this.serviceInput = msg.body;
}
}
);
}
// 子组件将数据推送到中间着,给订阅者
clickService() {
this.meditor.push({id: 'parent', body: this.serviceInput});
}
//父组件构造函数,用于监听数据推送
constructor(
private meditor: MeditorService
) {
this.subscription = meditor.getObservable().subscribe(
msg => {
console.log(msg);
if (msg.id === 'child') { //id为child,获取子组件数据
this.serviceInput = msg.body;
}
}
);
}
// 父组件将数据推送到中间着,给订阅者
clickService() {
this.meditor.push({id: 'parent', body: this.serviceInput});
}
我上面写的还不是很完善,就是在生命周期结束前,也就是在onDestroy周期中,要取消订阅。
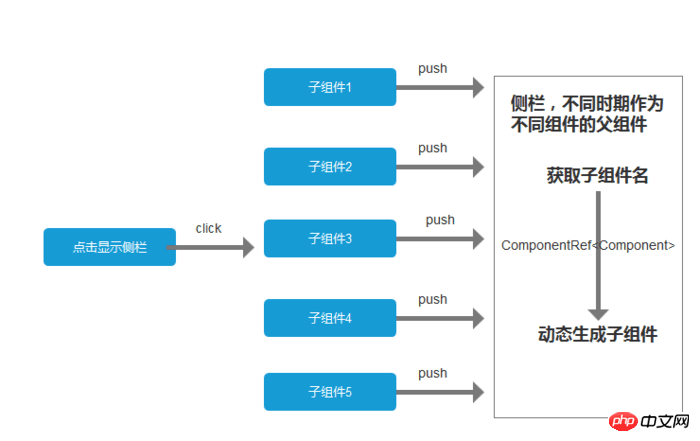
以上,就是最近在使用的组件交互的总结。个人觉得通过服务来交互的可扩展性更强。例如,我们项目中用到了一个动态显示的侧栏,不同时期点击显示侧栏要显示不同的东西。这个时候把侧栏作为父组件,子组件作为消息的一部分传递给父组件,父组件根据子组件名动态生成模板,显示在侧栏上面。说了这么多废话大概就是下图的意思:
最后附上demo源码:父子组件交互demo
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
以上是Angular2 父子元件通訊方式的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

