深入了解CSS建立佈局
- 高洛峰原創
- 2017-03-28 11:02:401333瀏覽
隨著對分離HTML元素的語義重要性與其表現的影響的不斷強調,CSS在HTML5元素佈局方面的作用越來越重要。
1. 定位內容
控制內容最簡單的方式就是透過定位,這允許你使用瀏覽器改變元素的佈局方式。
1.1 設定定位類型
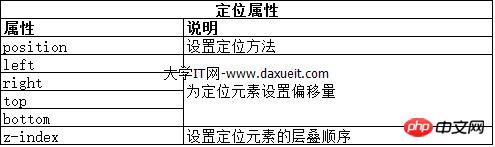
position 屬性設定了元素的定位方法。

position 屬性的不同值指定了元素定位所針對的不同元素。使用 top、bottom、left 和 right 屬性設定元素的偏移量的時候,指的是相對與 position 屬性指定的元素的偏移。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
img {top: 15px; left: 150px; border: medium double black; width: 150px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
There are lots of different kinds of fruit - there are over 500 varieties of banana alone.
By the time we add the countless types of apples, oranges, and other well-know fruit, we are faced with thousands of choices.
</p>
<p>
One of the most interesting aspects of fruit is the variety available in each country.
I live near London, in an area which is know for its apples.
</p>
<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banana.png" class="lazy" id="banana" alt="small banana" />
<p>
When travelling Asia, I was struck by how many different kinds of banana were available
- many of which had unique flavours and which were only available within a small region.
</p>
<p>
<button>Static</button>
<button>Relative</button>
<button>Absolute</button>
<button>Fixed</button>
</p>
<script>
var buttons = document.getElementsByTagName("button");
for( var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++){
buttons[i].onclick = function(e){
document.getElementById("banana").style.position = e.target.innerHTML;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>在上面的程式碼中,為頁面新增了一個小腳本,它可以基於被按下的按鈕改變img元素的position屬性的值。這裡將left屬性設為150px,將top屬性設為5px,意思是只要position值不設為static,img元素就會沿著水平軸偏移150像素,沿著垂直軸偏移15像素。下圖展示了 position 值從static到relative的變化。
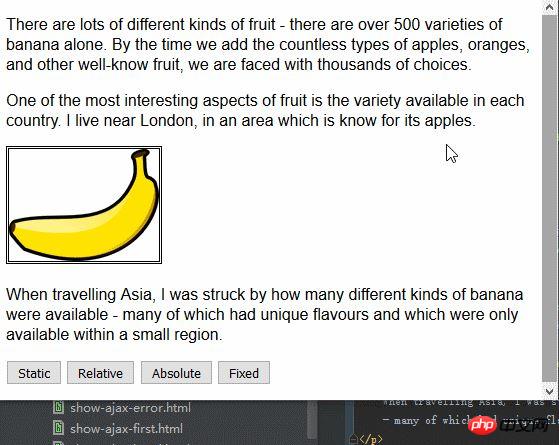
relative值為元素套用top、bottom、left和 right屬性,相對於 static 值所確定的位置重新定位元素。從圖中可以看到,left屬性和top屬性的取值會造成img元素向右、向下移動。
absolute值是根據position值不是static的最近祖先元素的位置來定位元素。在這個範例中不存在這樣的元素,也就是說元素是相對於body元素定位的,如下圖所示:

注意一下,如果捲動瀏覽器頁面,img元素會跟著剩餘的內容一起移動。可以將這個情況跟fixed值比較一下,如下圖就是fixed值定位效果:

使用fixed值,元素是相對於瀏覽器視窗定位的。也就是說元素總是佔據同樣的位置,無論剩餘內容是否向上向下捲動。
1.2 設定元素的層疊順序
z-index 屬性指定元素顯示的層疊順序。
z-index 屬性的值是數值,且允許取負值。值越小,在層疊順序中就越靠後。這個屬性只有在元素重疊的情況下才會派上用場。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
img {border: medium double black; background-color: lightgray; position: fixed;}
#banana { z-index: 1; top: 15px; left: 150px; }
#apple { z-index: 2; top: 25px; left: 120px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
There are lots of different kinds of fruit - there are over 500 varieties of banana alone.
By the time we add the countless types of apples, oranges, and other well-know fruit, we are faced with thousands of choices.
</p>
<p>
One of the most interesting aspects of fruit is the variety available in each country.
I live near London, in an area which is know for its apples.
</p>
<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banana-small.png" class="lazy" id="banana" alt="small banana" />
<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="imgs/apple.png" class="lazy" id="apple" alt="small apple" />
<p>
When travelling Asia, I was struck by how many different kinds of banana were available
- many of which had unique flavours and which were only available within a small region.
</p>
</body>
</html>此範例中,建立了兩個固位置的img元素,設定了它們top 和left 值使兩者部分影像重疊。 id值為apple的img元素的z-index值比id值為banana元素的z-index值大,因此蘋果圖像顯示在香蕉圖像上面。

z-index 屬性的預設值是0,因此瀏覽器預設會將圖像顯示在p元素上。
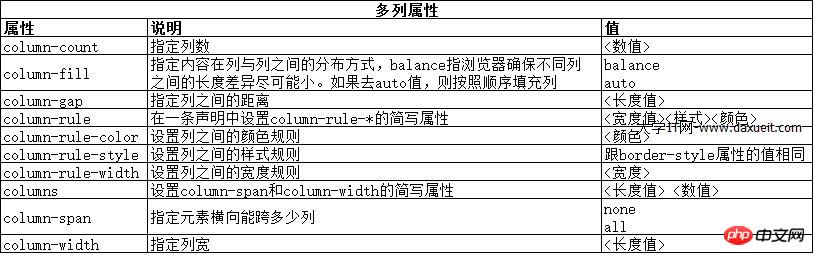
2. 建立多列佈局
多列特性允許在多個垂直列中佈局內容,跟報紙的排版方式類似。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
column-count: 3;
column-fill: balance;
column-rule: medium solid black;
column-gap: 1.5em;
}
img {
float: left;
border: medium double black;
background-color: lightgray;
padding: 2px;
margin: 2px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
There are lots of different kinds of fruit - there are over 500 varieties of banana alone.
By the time we add the countless types of apples, oranges, and other well-know fruit, we are faced with thousands of choices.
<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banana-small.png" class="lazy" id="banana" alt="small banana" />
One of the most interesting aspects of fruit is the variety available in each country.
I live near London, in an area which is know for its apples.
<img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="imgs/apple.png" class="lazy" id="apple" alt="small apple" />
When travelling Asia, I was struck by how many different kinds of banana were available
- many of which had unique flavours and which were only available within a small region.
And, of course, there are fruits which are unique
- I am put in mind of the durian, which is widely consumed in SE Asia and is know as the "king of fruits".
The durian is largely unknow in Europe and the USA
- if it is know at all, it is for the overwhelming smell, which is compared to a combination of almonds,
rotten onions and gym socks.
</div>
</body>
</html>
PS:暫發現IE、Edge、Opera瀏覽器顯示有效,而火狐和Google不支援。
從上圖可以看出,div元素中的內容從一列流向另一列,跟報紙中排版很像。在這個例子中,為img元素應用了float屬性,讓div元素中的文字內容可以流暢地環繞在圖像周圍。
上面的範例中使用了column-count屬性將頁面佈局分為三列。如果視窗大小調整,瀏覽器會自行調整寬度,從而保留佈局中的列數。另一種方法是指定列寬度。
<style type="text/css">
p {
column-width: 10em;
column-fill: balance;
column-rule: medium solid black;
column-gap: 1.5em;
}
img {
float: left;
border: medium double black;
background-color: lightgray;
padding: 2px;
margin: 2px;
}
</style>如果套用column-width 屬性,瀏覽器會透過新增或刪除列數來維持指定寬度。

3. 建立彈性盒佈局
弹性盒布局(也称伸缩盒)在CSS3中得到了进一步加强,为display属性添加了一个新值(flexbox),并定义了其他几个属性。使用弹性布局可以创建对浏览器窗口调整响应良好的流动页面。这是通过在包含元素之间分配容器块中未使用的空间来实现的。规范为弹性布局定义了如下新属性:
* flex-align
* flex-direction
* flex-order
* flex-pack
不过建议规范和实现之间还有差异,顶定义一下弹性盒要解决的问题。下面代码展示了一个有问题的简单布局。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
p {
float: left;
width: 150px;
border: medium double green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p id="first">
There are lots of different kinds of fruit - there are over 500 varieties of banana alone.
By the time we add the countless types of apples, oranges, and other well-know fruit, we are faced with thousands of choices.
</p>
<p id="second">
One of the most interesting aspects of fruit is the variety available in each country.
I live near London, in an area which is know for its apples.
</p>
<p id="third">
When travelling Asia, I was struck by how many different kinds of banana were available
- many of which had unique flavours and which were only available within a small region.
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>在上面代码中,div元素包含了三个p元素。将p元素显示在水平行中,用float属性很容易就能做到这一点。

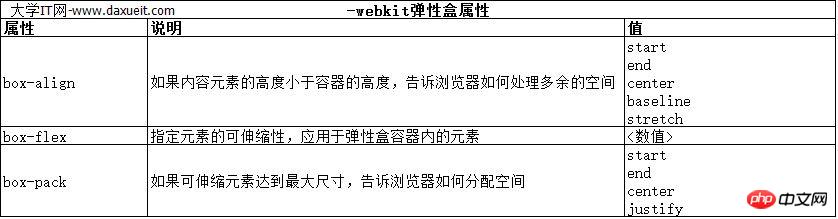
这里能使用弹性盒解决的问题是处理页面上p元素右边的空间块。解决这个问题有很多方式。在这个例子中,可以使用百分比宽度,但弹性盒解决方案更优雅,页面看起来流动性也会好很多。下表列出了实现弹性盒核心功能的三个 -webkit 属性(简单起见,表中省略了-webkit前缀):
3.1 创建简单的弹性盒
可以使用 display属性创建弹性盒。标准值是 flexbox, 不过在标准完成和实现之前,必须使用 -webkit-box 。 使用 box-flex 属性告诉浏览器如何分配元素之间的未使用空间。 display 属性的新值和 box-flex 属性如下面代码所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
p {
width: 150px;
border: medium double green;
background-color: lightgray;
margin: 2px;
}
#container{ display: -webkit-box;}
#second {-webkit-box-flex: 1;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<p id="first">
There are lots of different kinds of fruit - there are over 500 varieties of banana alone.
By the time we add the countless types of apples, oranges, and other well-know fruit, we are faced with thousands of choices.
</p>
<p id="second">
One of the most interesting aspects of fruit is the variety available in each country.
I live near London, in an area which is know for its apples.
</p>
<p id="third">
When travelling Asia, I was struck by how many different kinds of banana were available
- many of which had unique flavours and which were only available within a small region.
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>display 属性会应用到弹性盒容器。弹性盒容器是具有多余空间,且想对其中的内容应用弹性布局的元素。box-flex 属性会应用到弹性盒容器内的元素,告诉浏览器当容器大小改变时哪些元素的尺寸是弹性的。在这个例子中,选择了id值为second的p元素。
PS:从p元素样式声明中删除了float属性。可伸缩元素不能包含浮动元素。
可以从下图看出浏览器如何伸缩选择元素的尺寸:

3.2 伸缩多个元素
应用box-flex 告诉浏览器伸缩多个元素的尺寸。设置的值决定了浏览器分配空间的比例。修改前面例子的CCS文件如下:
<style type="text/css">
p {
width: 150px;
border: medium double green;
background-color: lightgray;
margin: 2px;
}
#container{ display: -webkit-box;}
#first { -webkit-box-flex: 3;}
#second {-webkit-box-flex: 1;}
</style>这里将box-flex 属性应用到了id值为first的p元素。此处box-flex属性的值是3,意思是浏览器为其分部的多余空间是为id值为second的p元素的三倍。当创建此类比例时,指的是元素的可伸缩性。只是使用这个比例来分配多余的空间,或者减少元素的尺寸,而不是改变它的首选尺寸。从下图可以看到这个比例时怎么应用到元素的。

3.3 处理垂直空间
box-align 属性告诉浏览器如何处理多余的垂直空间。默认情况下垂直拉伸元素以填充多余的空间。上面的例子就是这种情况,前两个p元素的尺寸是调整过的,内容下面多出了空的空间。
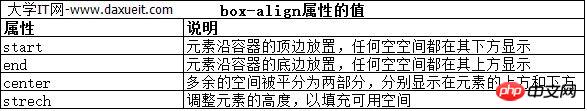
下面的代码展示了元素样式变为应用box-align属性。注意这个属性应用到可伸缩容器上,而不是内容元素。
p {
width: 150px;
border: medium double green;
background-color: lightgray;
margin: 2px;
}
#container{
display: -webkit-box;
-webkit-box-direction: reverse;
-webkit-box-align: end;
}
#first { -webkit-box-flex: 3;}
#second {-webkit-box-flex: 1;}此例中,使用了 end 值,这代表内容元素会沿着容器元素的底边放置,垂直方向任何多余的空间都会显示到内容元素上方。其呈现效果如下图所示:

3.4 处理最大尺寸
弹性盒伸缩时不会超过内容元素的最大尺寸。如果存在多余空间,浏览器会伸展元素,知道达到最大允许尺寸。box-pack属性定义了在所有的可伸缩元素均可达到最大尺寸的情况下,多余空间仍未分配完毕时应该如何处理。
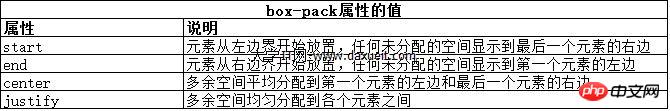
修改前面示例的CSS文件如下:
p {
width: 150px;
max-width: 250px;
border: medium double green;
background-color: lightgray;
margin: 2px;
}
#container{
display: -webkit-box;
-webkit-box-direction: reverse;
-webkit-box-align: end;
-webkit-box-pack: justify;
}
#first { -webkit-box-flex: 3;}
#second {-webkit-box-flex: 1;}这属性的效果如下图所示。在可伸缩p元素达到最大宽度后,浏览器开始在元素之间分配多余空间。注意,多余空间只是分配到元素与元素之间,第一个元素之前或者最后一个元素之后都没有分配。

4. 创建表格布局
使用 table 元素如此普遍的原因是它解决了一种常见的布局问题:创建承载内容的简单网格。幸好,我们可以使用CCS表格布局特性来设置页面布局,这很像使用 table 元素,但不会破坏语义重要性。创建CSS表格布局使用display属性。下表列出了跟这个特性相关的值。表中的每个值都与一个HTML元素对应。
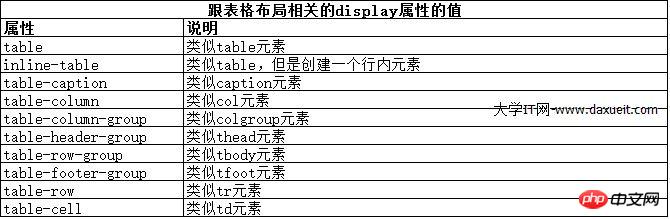
其中几个值的用法如下面代码所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
#table { display: table;}
div.row {display: table-row; background-color:lightgray; }
p { display: table-cell; border: thin solid green; padding: 15px; margin: 15px;}
img { float: left;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="table">
<div >
<p id="first">
There are lots of different kinds of fruit - there are over 500 varieties of banana alone.
By the time we add the countless types of apples, oranges, and other well-know fruit, we are faced with thousands of choices.
</p>
<p id="second">
One of the most interesting aspects of fruit is the variety available in each country.
I live near London, in an area which is know for its apples.
</p>
<p id="third">
When travelling Asia, I was struck by how many different kinds of banana were available
- many of which had unique flavours and which were only available within a small region.
</p>
</div>
<div class="row">
<p>
This is an apple. <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="imgs/apple.png" class="lazy" alt="apple" />
</p>
<p>
This is a banana. <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="imgs/banana-small.png" class="lazy" alt="banana" />
</p>
<p>
No picture here.
</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>这些取值的效果如下图所示:

CSS表格布局的一个优点是自动调整单元格大小,因此,行是由该行中内容最高的单元格决定的,列是由该列中内容最宽的单元格决定的,这从上图也能看出来。
以上是深入了解CSS建立佈局的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

