Linux指令基本格式及目錄處理指令
- 高洛峰原創
- 2016-11-14 12:38:311579瀏覽
指令提示字元
[root@localhost ~]#
root:目前登入使用者
localhost:主機名稱
~:目前所在的目錄,此處為「家」目錄
#:root超級使用者的提示符,如果是普通用戶,則為 $
指令格式
指令[選項] [參數]
中括號[] 表示可選
查詢目錄中的內容:ls
ls [選項] [檔案或目錄]
選項:
-a : 顯示所有文件,包括隱藏文件
-l : 顯示詳細資料
-d : 查看目錄屬性
-h : 人性化顯示檔案大小
-i : 顯示inode
-i 敲入命令,顯示結果分別如下:
[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg test [root@localhost ~]# ls -a. .. anaconda-ks.cfg .bash_history .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .cache .config .cshrc .tcshrc test [root@localhost ~]# ls -l总用量 4-rw-------. 1 root root 2752 Nov 10 02:51 anaconda-ks.cfg drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Nov 12 19:26 test [root@localhost ~]# ls -l anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-------. 1 root root 2752 Nov 10 02:51 anaconda-ks.cfg [root@localhost ~]# ls -ld test/drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Nov 12 19:26 test/ [root@localhost ~]# ls -lh总用量 4.0K -rw-------. 1 root root 2.7K Nov 10 02:51 anaconda-ks.cfg drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Nov 12 19:26 test [root@localhost ~]# ls -i71259104 anaconda-ks.cfg 36099565 test
請注意觀察ls -l 與ls -lh 命令的結果的區別
這裡需要解釋一下:
-rw-------. 1 root root 2.7K Nov 10 02:51 anaconda-ks.cfg drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Nov 12 19:26 test
首先第一個符號“-”(引號內的- ),表示文件類型(常用的有三種,即-表示文件,d表示目錄,l表示軟鏈接文件),此外還有不常用的,為塊設備文件,字符設備文件、套接字文件、管理文件。
在上述中,我們可以看到 anaconda-ks.cfg 是一個文件,而 test 是目錄(可理解為windows的資料夾的概念)。
其次,除去第一個符號,我們來看rw-------,一共有九個字符,需分為三組,分別為rw-,---,---,每組依序分別表示u所有者,g所屬群組,o其他人的權限。在上述中,分別對應為 root,root。即第一個root表示擁有者權限為root權限,第二個root表示所屬群組的權限也是root權限,對於其他人,則無所謂的權限可言。
其中,r表示可讀,w表示可寫,x表示執行的權限。
為了更明白,對於 anaconda-ks.cfg 這個文件,這裡列一個表格:
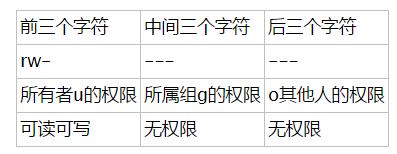
那麼,對於 test 這個文件 rwxr-xr-x,請讀者自行判斷它的權限。
在九個字元之後的點 “.”,表示ACL權限,之後的數字 1 表示引用計數,例如一個檔案有一個軟連結(類似windows快捷方式),那麼它的引用計數就是2。
root 後面的2.7k表示檔案的大小,再後面表示日期,最後是檔案的名稱。
目錄處理指令
建立目錄:mkdir
mkdir -p [目錄名稱]
-p : 遞歸創建
[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg test [root@localhost ~]# mkdir otherFolder[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg otherFolder test [root@localhost ~]# mkdir folder_2/test_2mkdir: 无法创建目录"folder_2/test_2": 没有那个文件或目录 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p folder_2/test_2[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg folder_2 otherFolder test [root@localhost ~]# ls folder_2/test_2
如上所示,mkdir 不加選項-p 時,可以建立一個目錄遞歸建立一個包含子目錄的目錄。加上 -p 即可遞歸創建。
切換所在目錄:cd
cd [目錄]
操作:
cd ~ : 進入目前使用者的家目錄
cd-: 进入上次目录
cd.. : 进入上一级目录
cd : 回到家目录
[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg folder_2 otherFolder test [root@localhost ~]# cd /folder_2/test_2[root@localhost test_2]# cd[root@localhost ~]# cd -/root/folder_2/test_2 [root@localhost test_2]# cd ../../otherFolder[root@localhost otherFolder]# cd ..[root@localhost ~]#
注意理清概念:相对路径和绝对路径
绝对路径:从根目录一级级找下去,需要写全路径
[root@localhost ~]# cd folder_2/test_2 [root@localhost test_2]#
相对路径:参照当前所在目录进行查找
[root@localhost test_2]# cd ../../otherFolder [root@localhost otherFolder]#
查询所在目录位置:pwd
pwd
可以说是最简单的命令了,查询所在目录的位置
[root@localhost ~]# pwd/root [root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg folder_2 otherFolder test [root@localhost ~]# cd folder_2/[root@localhost folder_2]# lstest_2 [root@localhost folder_2]# cd test_2/[root@localhost test_2]# pwd/root/folder_2/test_2
删除空目录:rmdir
rmdir [目录名]
只能删除空目录,这个命令用得比较少。
[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg folder_2 otherFolder test [root@localhost ~]# rmdir otherFolder[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg folder_2 test [root@localhost ~]# rmdir folder_2rmdir: 删除 "folder_2" 失败: 目录非空 [root@localhost ~]#
删除文件或目录:rm
rm -rf [文件或目录]
r 表示可以同时删除文件和目录,f表示强制删除
如果不添加任何选项,那么只可以删除文件,删除时提示是否确认删除
如果只添加选项 -r,那么可以删除文件也可以删除目录,删除时提示是否确认删除
如果添加了选项 -rf,那么将不做任何提示删除文件或目录
[root@localhost ~]# lsabc.txt anaconda-ks.cfg folder_2 test [root@localhost ~]# rm abc.txtrm:是否删除普通空文件 "abc.txt"?y [root@localhost ~]# rm testrm: 无法删除"test": 是一个目录 [root@localhost ~]# rm -r testrm:是否删除目录 "test"?y [root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg folder_2 [root@localhost ~]# rm -rf folder_2[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg [root@localhost ~]#
复制命令:cp
cp [选项] [原文件或目录] [目标目录]
选项:
-r : 复制目录
-p : 同时复制文件属性
-d : 若源文件是链接文件,则复制链接属性
-a : 包含以上所有选项,相当于 -rpd
在[目标目录]后面加上文件名,就是改名复制。
[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg bbc.txt folder_a folder_b [root@localhost ~]# cp bbc.txt folder_a[root@localhost ~]# ls folder_a/bbc.txt [root@localhost ~]# cp folder_a folder_bcp: 略过目录"folder_a"[root@localhost ~]# cp -r folder_a folder_b[root@localhost ~]# ls folder_bfolder_a test_1 [root@localhost ~]# ll总用量 4-rw-------. 1 root root 2752 Nov 10 02:51 anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 13 17:21 bbc.txt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 20 Nov 13 17:38 folder_a drwxr-xr-x. 4 root root 34 Nov 13 17:39 folder_b [root@localhost ~]# ll folder_a总用量 0-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 13 17:38 bbc.txt [root@localhost ~]# cp -a bbc.txt folder_b[root@localhost ~]# ll folder_b总用量 0-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 13 17:21 bbc.txt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 20 Nov 13 17:39 folder_a drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Nov 13 17:38 test_1 [root@localhost ~]#
这里需要解释一下的是,在原文件 bbc.txt 中,其修改时间为 17:21,在普通复制下,它的时间这个属性是不会被复制,我们可以看到复制后的bbc.txt的时间为17:38,如果需要连同属性一起复制,那么就加上 -pd 或者 直接 -a,如上所示,我们把bbc.txt复制到folder_b,这时我们查看属性的时候,时间属性和原属性是一致的。
在上述命令中,ll 是 ls -l 的简写。
剪切或改名命令:mv
mv [原文件或目录] [目标目录]
如果原文件或者目录 与 目标目录在同一个目录下,那么就是重命名
如果不在同一个目录下,那么就是剪切
通过以下实践理解:
[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg bbc.txt [root@localhost ~]# mv bbc.txt abc.txt[root@localhost ~]# lsabc.txt anaconda-ks.cfg [root@localhost ~]# mkdir test[root@localhost ~]# lsabc.txt anaconda-ks.cfg test [root@localhost ~]# mv abc.txt test/[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg test [root@localhost ~]# ls test/abc.txt [root@localhost ~]#
链接命令:ln
ln -s [原文件] [目标文件]
生成链接文件
-s : 创建软连接
硬链接的特征:
拥有相同 i 节点和存储block块,可以看做是同一个文件
可通过i节点识别,i节点是相同的
不能跨分区
不能针对目录使用
通过上述命令,可以理解为为某个内容添加一个标签,通过打开这个标签就可以进入这个内容,硬连接,即再生成一个标签,同样可以通过这个标签进入这个内容。
如果内容被修改,那么不管从硬链接的哪个文件进入,都是被修改的。
软链接的特征:
类似windows的快捷方式
软链接拥有自己的i节点和block块,但是数据块只保存原文件的文件名和I节点号,并没有实际的文件数据
lrwxrwxrwx l为软链接(软链接的权限都为rwxrwxrwx,这只是软链接本身的权限)
修改任意文件,另一个都改变
删除原文件,软链接不能用(和windows的快捷方式一样)
硬链接:
[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg [root@localhost ~]# mkdir folder[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg folder [root@localhost ~]# touch bbb.txt[root@localhost ~]# lsanaconda-ks.cfg bbb.txt folder [root@localhost ~]# ln bbb.txt folder/ccc.txt[root@localhost ~]# ll folder/总用量 0-rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 Nov 13 18:08 ccc.txt [root@localhost ~]# ll bbb.txt -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 Nov 13 18:08 bbb.txt
软链接:
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir folder_b[root@localhost ~]# ln -s bbb.txt folder_b/eee.txt[root@localhost ~]# ll 总用量 4-rw-------. 1 root root 2752 Nov 10 02:51 anaconda-ks.cfg -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 Nov 13 18:10 bbb.txt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 20 Nov 13 18:09 folder drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 20 Nov 13 18:11 folder_b [root@localhost ~]# ll folder_b总用量 0lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Nov 13 18:11 eee.txt -> bbb.txt [root@localhost ~]# rm -rf bbb.txt [root@localhost ~]# ll folder_b总用量 0lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Nov 13 18:11 eee.txt -> bbb.txt
删除了原文件,软链接的箭头目标为红色一闪一闪,表示找不到目标文件。
常用目录作用
[root@localhost ~]# ls / bin boot dev etc home lib lib64 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys temp tmp usr var
说明:
/ 根目录
/bin 命令保存目录(普通用户权限)
/sbin 命令保存目录(root权限)
/boot 启动目录,包含启动相关文件,和开机有关
/dev 设备文件保存目录
/etc 配置文件保存目录
/home 普通用户家目录
/lib 系统库保存目录
/mnt 系统挂载目录
/media 挂载目录(常用于光盘挂载)
/root 超级用户家目录
/tmp 临时目录
/proc 直接写入内存的
/sys 直接写入内存的
/usr 系统软件资源目录
/var 系统相关文档内容

