Rumah >pembangunan bahagian belakang >Tutorial Python >Lakukan analisis contoh menggunakan penyelarasan Python
Lakukan analisis contoh menggunakan penyelarasan Python
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBke hadapan
- 2023-05-08 17:52:261678semak imbas
Contoh: Masalah N-badan
Premis fizikal:
Hukum Newton
Persamaan pergerakan diskret Masa
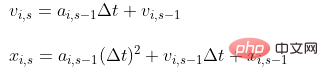
Kaedah pengiraan biasa
import numpy as np
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
Ns = [2**i for i in range(1,10)]
runtimes = []
def remove_i(x,i):
"从所有粒子中去除本粒子"
shape = (x.shape[0]-1,)+x.shape[1:]
y = np.empty(shape,dtype=float)
y[:i] = x[:i]
y[i:] = x[i+1:]
return y
def a(i,x,G,m):
"计算加速度"
x_i = x[i]
x_j = remove_i(x,i)
m_j = remove_i(m,i)
diff = x_j - x_i
mag3 = np.sum(diff**2,axis=1)**1.5
result = G * np.sum(diff * (m_j / mag3)[:,np.newaxis],axis=0)
return result
def timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt):
N = len(x0)
x1 = np.empty(x0.shape,dtype=float)
v1 = np.empty(v0.shape,dtype=float)
for i in range(N):
a_i0 = a(i,x0,G,m)
v1[i] = a_i0 * dt + v0[i]
x1[i] = a_i0 * dt**2 + v0[i] * dt + x0[i]
return x1,v1
def initial_cond(N,D):
x0 = np.array([[1,1,1],[10,10,10]])
v0 = np.array([[10,10,1],[0,0,0]])
m = np.array([10,10])
return x0,v0,m
def stimulate(N,D,S,G,dt):
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
x0,v0,m = initial_cond(N,D)
for s in range(S):
x1,v1 = timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt)
x0,v0 = x1,v1
t = 0
for i in x0:
ax.scatter(i[0],i[1],i[2],label=str(s*dt),c=["black","green","red"][t])
t += 1
t = 0
plt.show()
start = time.time()
stimulate(2,3,3000,9.8,1e-3)
stop = time.time()
runtimes.append(stop - start)Rajah rendering
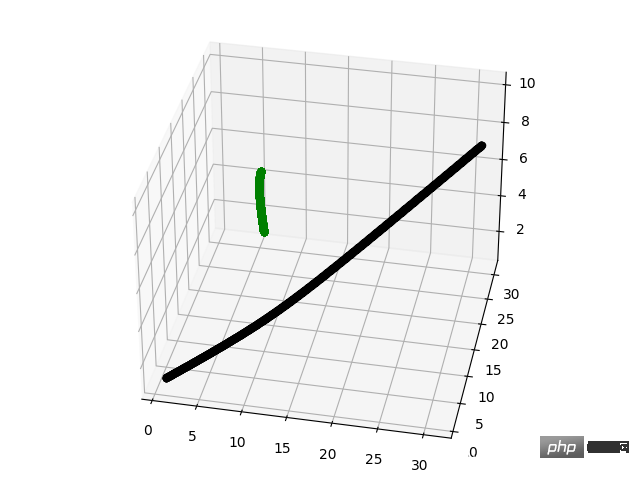
Python Parallelized Execution
Pertama sekali, kami memberikan, um, rentetan kod yang boleh digunakan untuk menulis program selari anda sendiri
import datetime
import multiprocessing as mp
def accessional_fun():
f = open("accession.txt","r")
result = float(f.read())
f.close()
return result
def final_fun(name, param):
result = 0
for num in param:
result += num + accessional_fun() * 2
return {name: result}
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
num_cores = int(mp.cpu_count())
print("你使用的计算机有: " + str(num_cores) + " 个核,当然了,Intel 7 以上的要除以2")
print("如果你使用的 Python 是 32 位的,注意数据量不要超过两个G")
print("请你再次检查你的程序是否已经改成了适合并行运算的样子")
pool = mp.Pool(num_cores)
param_dict = {'task1': list(range(10, 300)),
'task2': list(range(300, 600)),
'task3': list(range(600, 900)),
'task4': list(range(900, 1200)),
'task5': list(range(1200, 1500)),
'task6': list(range(1500, 1800)),
'task7': list(range(1800, 2100)),
'task8': list(range(2100, 2400)),
'task9': list(range(2400, 2700)),
'task10': list(range(2700, 3000))}
results = [pool.apply_async(final_fun, args=(name, param)) for name, param in param_dict.items()]
results = [p.get() for p in results]
end_time = datetime.datetime.now()
use_time = (end_time - start_time).total_seconds()
print("多进程计算 共消耗: " + "{:.2f}".format(use_time) + " 秒")
print(results)Hasil yang dijalankan ialah seperti berikut:

Kandungan dalam accession.txt ialah 2.5 Ini adalah masalah pengumpulan setiap kali pengumpulan dibuat, 2.5 dalam fail akan dibaca
jika perlu Masalah operasi serupa dengan masalah pengumpulan iaitu masalah operasi selari, maka kita boleh buat transformasi operasi selari
Beri contoh lain
import math
import time
import multiprocessing as mp
def final_fun(name, param):
result = 0
for num in param:
result += math.cos(num) + math.sin(num)
return {name: result}
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
num_cores = int(mp.cpu_count())
print("你使用的计算机有: " + str(num_cores) + " 个核,当然了,Intel 7 以上的要除以2")
print("如果你使用的 Python 是 32 位的,注意数据量不要超过两个G")
print("请你再次检查你的程序是否已经改成了适合并行运算的样子")
pool = mp.Pool(num_cores)
param_dict = {'task1': list(range(10, 3000000)),
'task2': list(range(3000000, 6000000)),
'task3': list(range(6000000, 9000000)),
'task4': list(range(9000000, 12000000)),
'task5': list(range(12000000, 15000000)),
'task6': list(range(15000000, 18000000)),
'task7': list(range(18000000, 21000000)),
'task8': list(range(21000000, 24000000)),
'task9': list(range(24000000, 27000000)),
'task10': list(range(27000000, 30000000))}
results = [pool.apply_async(final_fun, args=(name, param)) for name, param in param_dict.items()]
results = [p.get() for p in results]
end_time = time.time()
use_time = end_time - start_time
print("多进程计算 共消耗: " + "{:.2f}".format(use_time) + " 秒")
result = 0
for i in range(0,10):
result += results[i].get("task"+str(i+1))
print(result)
start_time = time.time()
result = 0
for i in range(10,30000000):
result += math.cos(i) + math.sin(i)
end_time = time.time()
print("单进程计算 共消耗: " + "{:.2f}".format(end_time - start_time) + " 秒")
print(result) Hasil operasi:
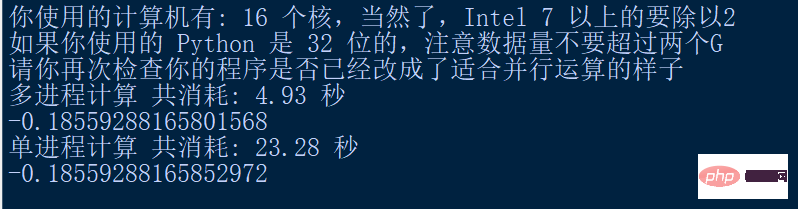
Peningkatan masalah mekanik:
import numpy as np
import time
from mpi4py import MPI
from mpi4py.MPI import COMM_WORLD
from types import FunctionType
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from multiprocessing import Pool
def remove_i(x,i):
shape = (x.shape[0]-1,) + x.shape[1:]
y = np.empty(shape,dtype=float)
y[:1] = x[:1]
y[i:] = x[i+1:]
return y
def a(i,x,G,m):
x_i = x[i]
x_j = remove_i(x,i)
m_j = remove_i(m,i)
diff = x_j - x_i
mag3 = np.sum(diff**2,axis=1)**1.5
result = G * np.sum(diff * (m_j/mag3)[:,np.newaxis],axis=0)
return result
def timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt,pool):
N = len(x0)
takes = [(i,x0,v0,G,m,dt) for i in range(N)]
results = pool.map(timestep_i,takes)
x1 = np.empty(x0.shape,dtype=float)
v1 = np.empty(v0.shape,dtype=float)
for i,x_i1,v_i1 in results:
x1[i] = x_i1
v1[i] = v_i1
return x1,v1
def timestep_i(args):
i,x0,v0,G,m,dt = args
a_i0 = a(i,x0,G,m)
v_i1 = a_i0 * dt + v0[i]
x_i1 = a_i0 * dt ** 2 +v0[i]*dt + x0[i]
return i,x_i1,v_i1
def initial_cond(N,D):
x0 = np.random.rand(N,D)
v0 = np.zeros((N,D),dtype=float)
m = np.ones(N,dtype=float)
return x0,v0,m
class Pool(object):
def __init__(self):
self.f = None
self.P = COMM_WORLD.Get_size()
self.rank = COMM_WORLD.Get_rank()
def wait(self):
if self.rank == 0:
raise RuntimeError("Proc 0 cannot wait!")
status = MPI.Status()
while True:
task = COMM_WORLD.recv(source=0,tag=MPI.ANY_TAG,status=status)
if not task:
break
if isinstance(task,FunctionType):
self.f = task
continue
result = self.f(task)
COMM_WORLD.isend(result,dest=0,tag=status.tag)
def map(self,f,tasks):
N = len(tasks)
P = self.P
Pless1 = P - 1
if self.rank != 0:
self.wait()
return
if f is not self.f:
self.f = f
requests = []
for p in range(1,self.P):
r = COMM_WORLD.isend(f,dest=p)
requests.append(r)
MPI.Request.waitall(requests)
results = []
for i in range(N):
result = COMM_WORLD.recv(source=(i%Pless1)+1,tag=i)
results.append(result)
return results
def __del__(self):
if self.rank == 0:
for p in range(1,self.p):
COMM_WORLD.isend(False,dest=p)
def simulate(N,D,S,G,dt):
x0,v0,m = initial_cond(N,D)
pool = Pool()
if COMM_WORLD.Get_rank()==0:
for s in range(S):
x1,v1 = timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt,pool)
x0,v0 = x1,v1
else:
pool.wait()
if __name__ == '__main__':
simulate(128,3,300,1.0,0.001)
Ps = [1,2,4,8]
runtimes = []
for P in Ps:
start = time.time()
simulate(128,3,300,1.0,0.001)
stop = time.time()
runtimes.append(stop - start)
print(runtimes)Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Lakukan analisis contoh menggunakan penyelarasan Python. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

