Rumah >hujung hadapan web >tutorial js >Analisis ringkas modul http dan perkongsian eksport dalam Nodejs
Analisis ringkas modul http dan perkongsian eksport dalam Nodejs
- 青灯夜游ke hadapan
- 2022-11-10 20:46:221340semak imbas
Artikel ini bercakap tentang asas nod, pemahaman dan kes modul http dan perkongsian eksport module.exports, saya harap ia akan membantu semua orang!

1. Modul http
Modul http ialah modul yang disediakan secara rasmi oleh Node.js untuk mencipta pelayan web. [Cadangan tutorial berkaitan: tutorial video nodejs]
Menggunakan kaedah http.createServer() yang disediakan oleh modul http, anda boleh menukar komputer biasa menjadi pelayan web dengan mudah, dengan itu menyediakan web perkhidmatan sumber kepada dunia luar.
1. Buat pelayan web
- Import modul http
- Buat contoh pelayan web
- Ikat acara permintaan contoh pelayan, dengar permintaan pelanggan
- Mulakan pelayan
Contoh: Dengar perkhidmatan 8080
// 导入 http 模块
const http = require('http')
// 创建 web 服务器实例
const server = http.createServer()
// 为服务器实例绑定 request 事件 监听客户端的请求
server.on('request', function (req, res) {
console.log('请求中...')
})
// 启动服务
server.listen(8080, function () {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1:8080')
})
2. objek permintaan req
Selagi pelayan menerima permintaan pelanggan, ia akan memanggil fungsi pemprosesan acara permintaan terikat kepada pelayan melalui server.on ()
Contoh: Dalam pengendali acara, akses data atau sifat berkaitan pelanggan
// 导入 http 模块
const http = require('http')
// 创建 web 服务器实例
const server = http.createServer()
// req 是请求对象 包含了与客户端相关的数据和属性
server.on('request', (req) => {
// req.url 客户端请求的 url 地址
const url = req.url
// req.method 是客户端请求的 method 类型
const method = req.method
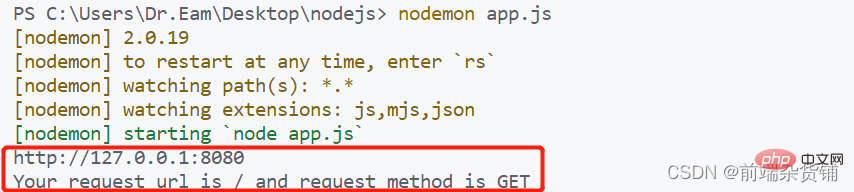
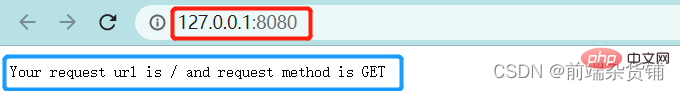
const str = `Your request url is ${url} and request method is ${method}`
console.log(str)
})
// 启动服务
server.listen(8080, function () {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1:8080')
})
3 , res response object
Dalam fungsi pemprosesan acara permintaan pelayan, jika anda ingin mengakses data atau atribut berkaitan pelayan, anda perlu menggunakan respons
Contoh: Permintaan respon
// 导入 http 模块
const http = require('http')
// 创建 web 服务器实例
const server = http.createServer()
// req 是请求对象 包含了与客户端相关的数据和属性
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// req.url 客户端请求的 url 地址
const url = req.url
// req.method 是客户端请求的 method 类型
const method = req.method
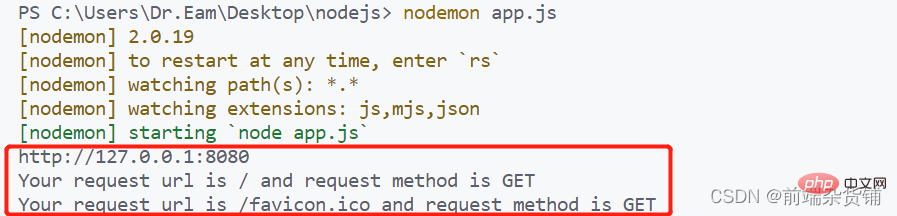
const str = `Your request url is ${url} and request method is ${method}`
console.log(str)
// 调用 res.end() 方法 向客户端响应一些内容
res.end(str)
})
// 启动服务
server.listen(8080, function () {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1:8080')
})
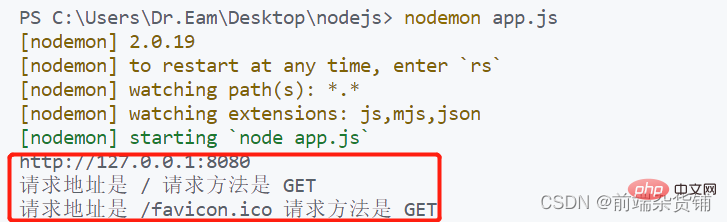
4 🎜>Apabila memanggil kaedah res.end( ), apabila menghantar kandungan bahasa Cina kepada pelanggan, aksara yang bercelaru akan berlaku dan format pengekodan kandungan tersebut perlu ditetapkan secara manual
Contoh: Menyelesaikan masalah bahasa Cina aksara// 导入 http 模块
const http = require('http')
// 创建 web 服务器实例
const server = http.createServer()
// req 是请求对象 包含了与客户端相关的数据和属性
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// req.url 客户端请求的 url 地址
const url = req.url
// req.method 是客户端请求的 method 类型
const method = req.method
const str = `请求地址是 ${url} 请求方法是 ${method}`
console.log(str)
// 设置 Content-Type 响应头 解决中文乱码问题
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8')
// 调用 res.end() 方法 向客户端响应一些内容
res.end(str)
})
// 启动服务
server.listen(8080, function () {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1:8080')
})
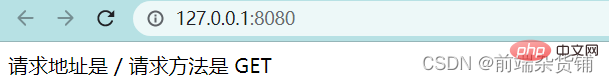
5. Membalas kandungan html yang berbeza mengikut url yang berbeza
Contoh: Langkah-langkahnya adalah seperti berikutDapatkan alamat url yang diminta
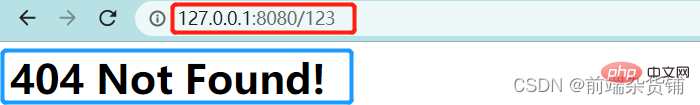
- Tetapkan kandungan respons lalai kepada 404 Not found
- Tentukan sama ada pengguna meminta / atau /index.html halaman utama
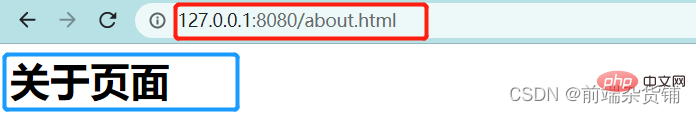
- Tentukan sama ada permintaan pengguna adalah /about.html Halaman Perihal
- Tetapkan pengepala respons Jenis Kandungan untuk mengelakkan aksara Cina yang kacau.
- Gunakan res.end() untuk membalas pelanggan dengan kandungan
// 导入 http 模块
const http = require('http')
// 创建 web 服务器实例
const server = http.createServer()
// req 是请求对象 包含了与客户端相关的数据和属性
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// req.url 客户端请求的 url 地址
const url = req.url
// 设置默认的内容为 404 Not Found
let content = '<h1>404 Not Found!</h1>'
// 用户请求页是首页
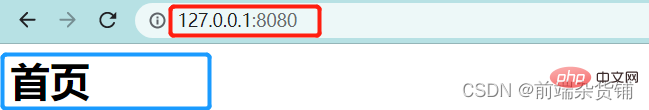
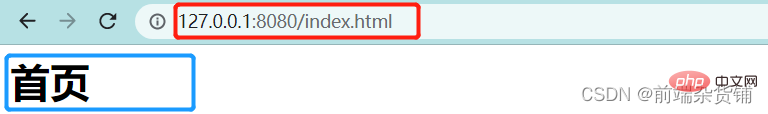
if(url === '/' || url === '/index.html') {
content = '<h1>首页</h1>'
} else if (url === '/about.html') {
content = '<h1>关于页面</h1>'
}
// 设置 Content-Type 响应头 防止中文乱码
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8')
// 调用 res.end() 方法 向客户端响应一些内容
res.end(content)
})
// 启动服务
server.listen(8080, function () {
console.log('http://127.0.0.1:8080')
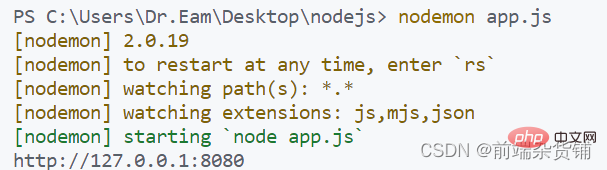
})
2 Klasifikasi modul dalam Node.js
Tiga klasifikasi modul utama
Modul terbina dalam: Disediakan secara rasmi oleh node.js, seperti fs , laluan, http, dll.- Modul tersuai: Setiap fail .js yang dibuat oleh pengguna ialah modul tersuai
- Modul pihak ketiga: Modul yang dibangunkan oleh pihak ketiga Sebelum digunakan Muat turun dahulu
2. Skop modul menghalang masalah. pencemaran berubah global
Contoh:
fail index.jsconst username = '张三'
function say() {
console.log(username);
}fail test.js
const custom = require('./index') console.log(custom)

3. module.exports object Dalam modul tersuai, anda boleh menggunakan objek module.exports ke
kongsi ahli dalam moduluntuk kegunaan luaran. Apabila kaedah require() luaran mengimport modul tersuai, perkara yang anda dapat ialah objek yang ditunjuk oleh module.exports
Contoh:
index.js failconst blog = '前端杂货铺'
// 向 module.exports 对象上挂载属性
module.exports.username = '李四'
// 向 module.exports 对象上挂载方法
module.exports.sayHello = function () {
console.log('Hello!')
}
module.exports.blog = blogfail test.js
const m = require('./index')
console.log(m)
4、共享成员时的注意点
使用 require() 方法导入模块时,导入的结果,永远以 module.exports 指向的对象为准
示例:
index.js 文件
module.exports.username = '李四'
module.exports.sayHello = function () {
console.log('Hello!')
}
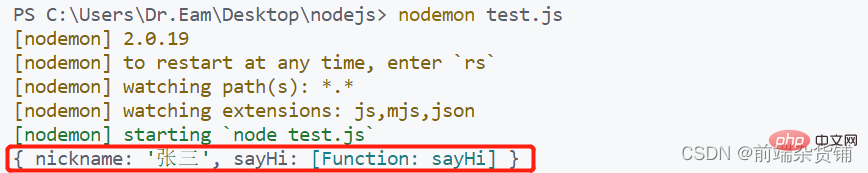
// 让 module.exports 指向一个新对象
module.exports = {
nickname: '张三',
sayHi() {
console.log('Hi!')
}
}test.js 文件
const m = require('./index') console.log(m)
5、exports 和 module.exports
默认情况下,exports 和 module.exports 指向同一个对象。
最终共享的结果,还是以 module.exports 指向的对象为准。
示例:
index1.js 文件
exports.username = '杂货铺'
module.exports = {
name: '前端杂货铺',
age: 21
}
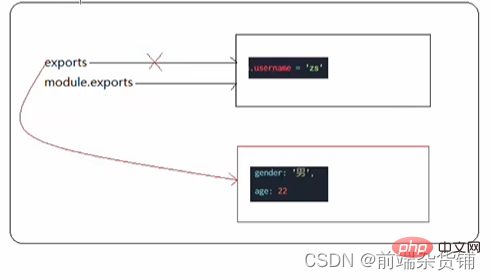
index2.js 文件
module.exports.username = 'zs'
exports = {
gender: '男',
age: 22
}
index3.js 文件
exports.username = '杂货铺' module.exports.age = 21

index4.js 文件
exports = {
gender: '男',
age: 21
}
module.exports = exports
module.exports.username = 'zs'
对 index2.js 文件结果的解析如下:
对 index4.js 文件结果的解析如下: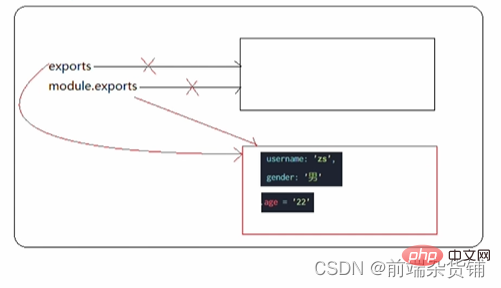
注意:为防止混乱,尽量不要在同一个模块中同时使用 exports 和 module.exports
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Analisis ringkas modul http dan perkongsian eksport dalam Nodejs. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
Artikel berkaitan
Lihat lagi- Analisis ringkas tentang cara nod melakukan log masuk pihak ketiga di Weibo
- Artikel yang menerangkan modulariti dalam es6 secara terperinci
- Apakah RPC? Mari kita bincangkan tentang cara melaksanakan komunikasi RPC dalam nod
- Mari kita bincangkan tentang pelaksanaan tak segerak dan pemanduan acara dalam Node
- Bagaimana untuk mendapatkan parameter dari baris arahan dalam nod

