使用TSQL查询数据和更新JSON数据
- 高洛峰asal
- 2016-12-06 13:31:411519semak imbas
JSON是一个非常流行的,用于数据交换的数据格式,主要用于Web和移动应用程序中。JSON 使用键/值对(Key:Value pair)存储数据,并且表示嵌套键值对和数组两种复杂数据类型,仅仅使用逗号(引用Key)和中括号(引用数组元素),就能路由到指定的属性或成员,使用简单,功能强大。在SQL Server 2016版本中支持JSON格式,使用Unicode字符类型表示JSON数据,并能对JSON数据进行验证,查询和修改。推荐一款JSON验证和格式化的工具:json formatter。
一,定义和验证JSON数据
使用nvarchar表示JSON数据,通过函数ISJSON函数验证JSON数据是否有效。
declare @json nvarchar(max)
set @json =
N'{
"info":{
"type":1,
"address":{
"town":"bristol",
"county":"avon",
"country":"england"
},
"tags":["sport", "water polo"]
},
"type":"basic"
}'
select isjson(@json)ISJSON 函数的格式是: ISJSON ( expression ) ,返回1,表示字符串是JSON数据;返回0,表示字符串不是JSON数据;返回NULL,表示 expression是NULL;
二,JSON 数据的PATH 表达式
Path 表达式分为两部分:Path Mode和Path。Path Mode是可选的(optional),有两种模式:lax和strict。
1,Path Mode
在Path 表达式的开始,可以通过lax 或 strict 关键字显式声明Path Mode,如果不声明,默认的Path Mode是lax。在lax 模式下,如果path表达式出错,那么JSON函数返回NULL。在strict模式下,如果Path表达式出错,那么JSON函数抛出错误;
2,Path 表达式
Path是访问JSON数据的途径,有四种运算符:
$:代表整个JSON 数据的内容;
逗号 . :表示JSON对象的成员,也叫做,字段(Field),或Key;
中括号 [] :表示数组中的元素,元素的起始位置是0;
Key Name:键的名字,通过Key Name来引用对应的Value;如果Key Name中包含空格,$,逗号,中括号,使用双引号;
例如,有如下JSON 数据,通过Path表达式,能够路由到JSON的各个属性:
{ "people":
[
{ "name": "John", "surname": "Doe" },
{ "name": "Jane", "surname": null, "active": true }
]
}Path表达式查询的数据是:
$:表示JSON的内容,是最外层大括号中的所有Item,本例是一个people数组,数组的下标是从0开始的;
$.people[0]:表示people数组的第一元素:{ "name": "Jane", "surname": null, "active": true }
$.people[0].name :从people数组的第一个元素中,查询Key是Name的Item对应的数据,本例是John;
$.people[1].surname:people数组中部存在surname 字段,由于该Path 表达式没有声明Path Mode,默认值是lax,当Path表达式出现错误时,返回NULL;
三,通过Path查询JSON数据
1,查询标量值(JSON_VALUE)
使用 JSON_VALUE(expression , path ) 函数,从JSON数据,根据Path 参数返回标量值,返回的数据是字符类型。
declare @json nvarchar(max)
set @json =
N'{
"info":{
"type":1,
"address":{
"town":"bristol",
"county":"avon",
"country":"england"
},
"tags":["sport", "water polo"]
},
"type":"basic"
}'
select
json_value(@json, '$.type') as type,
json_value(@json, '$.info.type') as info_type,
json_value(@json, '$.info.address.town') as town,
json_value(@json, '$.info.tags[0]') as tag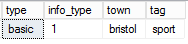
2,返回JSON数据(JSON_QUERY)
使用 JSON_QUERY ( expression [ , path ] ) 函数,根据Path 参数,返回JSON 数据(JSON fragment);参数path是可选的(optional),如果不指定option参数,那么默认的path是$,即,返回整个JSON数据。
declare @json nvarchar(max)
set @json =
N'{
"info":{
"type":1,
"address":{
"town":"bristol",
"county":"avon",
"country":"england"
},
"tags":["sport", "water polo"]
},
"type":"basic"
}'
select
json_query(@json, '$') as json_context,
json_query(@json, '$.info') as info,
json_query(@json, '$.info.address') as info_address,
json_query(@json, '$.info.tags') as info_tags
四,通过Path修改JSON数据
使用 JSON_MODIFY ( expression , path , newValue ) 修改JSON数据中的属性值,并返回修改之后的JSON数据,该函数修改JSON数据的流程是:
修改现有的属性:按照参数path从JSON数据中找到指定的属性,将该属性的Value修改为参数newValue,返回值是修改之后的JSON数据;
新增新的键值对(Key:Value pair):如果JSON数据中不存在指定的属性,那么按照参数Path,在指定的路径上新增键值对;
删除键值对(Key:Value pair):如果参数newValue的值是NULL,那么表示从JSON数据中删除指定的属性;
append 关键字:用于从JSON数组中,追加一个元素;
示例,对JSON数据进行update,insert,delete和追加数据元素
declare @info nvarchar(100) = '{"name":"john","skills":["c#","sql"]}'
-- update name
set @info = json_modify(@info, '$.name', 'mike')
-- insert surname
set @info = json_modify(@info, '$.surname', 'smith')
-- delete name
set @info = json_modify(@info, '$.name', null)
-- add skill
set @info = json_modify(@info, 'append $.skills', 'azure')
五,将JSON数据转换为关系表
OPENJSON函数是一个行集函数(RowSet),能够将JSON数据转换为关系表,
OPENJSON( jsonExpression [ , path ] ) [ WITH ( colName type [ column_path ] [ AS JSON ] [ , colName type [ column_path ] [ AS JSON ] ] [ , . . . n ] ) ]
path 参数:也叫table path,指定关系表在JSON数据中的路径;
column_path 参数:基于path参数,指定每个column在关系表JSON中的路径,应总是显式指定column path;
AS JSON 属性:如果指定AS JSON属性,那么 column的数据类型必须定义为nvarchar(max),表示该column的值是JSON数据;如果不指定AS JSON属性,那么该Column的值是标量值;
with 选项:指定关系表的Schema,应总是指定with选项;如果不指定with 选项,那么函数返回key,value和type三列;
示例,从JSON数据中,以关系表方式呈现数据
declare @json nvarchar(max)
set @json =
N'{
"info":{
"type":1,
"address":{
"town":"bristol",
"county":"avon",
"country":"england"
},
"tags":["sport", "water polo"]
},
"type":"basic"
}'
SELECT info_type,info_address,tags
FROM OPENJSON(@json, '$.info')
with
(
info_type tinyint 'lax $.type',
info_address nvarchar(max) 'lax $.address' as json,
tags nvarchar(max) 'lax $.tags' as json
)
六,将关系表数据以JSON格式存储
通过For JSON Auto/Path,将关系表数据存储为JSON格式,
Auto 模式:根据select语句中column的顺序,自动生成JSON数据的格式;
Path 模式:使用column name的格式来生成JSON数据的格式,column name使用逗号分隔(dot-separated)表示组-成员关系;
1,以Auto 模式生成JSON格式
select id, name, category from dbo.dt_json for json auto,root('json')
返回的数据格式是
{
"json":[
{
"id":1,
"name":"C#",
"category":"Computer"
},
{
"id":2,
"name":"English",
"category":"Language"
},
{
"id":3,
"name":"MSDN",
"category":"Web"
},
{
"id":4,
"name":"Blog",
"category":"Forum"
}
]
}
2,以Path模式生成JSON格式
select id as 'book.id', name as 'book.name', category as 'product.category' from dbo.dt_json for json path,root('json')
返回的数据格式是:
{
"json":[
{
"book":{
"id":1,
"name":"C#"
},
"product":{
"category":"Computer"
}
},
{
"book":{
"id":2,
"name":"English"
},
"product":{
"category":"Language"
}
},
{
"book":{
"id":3,
"name":"MSDN"
},
"product":{
"category":"Web"
}
},
{
"book":{
"id":4,
"name":"Blog"
},
"product":{
"category":"Forum"
}
}
]
}
以上就是使用TSQL查询数据和更新JSON数据的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

