Rumah >pembangunan bahagian belakang >Tutorial Python >AdaBoost - Kaedah Ensemble, Klasifikasi: Pembelajaran Mesin Terselia
AdaBoost - Kaedah Ensemble, Klasifikasi: Pembelajaran Mesin Terselia
- 王林asal
- 2024-07-18 21:00:01934semak imbas
Menggalak
Definisi dan Tujuan
Boosting ialah teknik pembelajaran ensemble yang digunakan dalam pembelajaran mesin untuk meningkatkan ketepatan model. Ia menggabungkan berbilang pengelas lemah (model yang berprestasi lebih baik sedikit daripada meneka rawak) untuk mencipta pengelas yang kuat. Tujuan utama peningkatan adalah untuk menggunakan pengelas lemah secara berurutan pada data, membetulkan ralat yang dibuat oleh pengelas sebelumnya dan dengan itu meningkatkan prestasi keseluruhan.
Objektif Utama:
- Tingkatkan Ketepatan: Tingkatkan ketepatan ramalan dengan menggabungkan output beberapa pengelas yang lemah.
- Kurangkan Bias dan Varian: Tangani isu bias dan varians untuk mencapai generalisasi model yang lebih baik.
- Kendalikan Data Kompleks: Model perhubungan kompleks dalam data dengan berkesan.
AdaBoost (Peningkatan Adaptif)
Definisi dan Tujuan
AdaBoost, singkatan kepada Adaptive Boosting, ialah algoritma rangsangan yang popular. Ia melaraskan wajaran kejadian yang dikelaskan secara salah supaya pengelas berikutnya lebih menumpukan pada kes yang sukar. Tujuan utama AdaBoost adalah untuk meningkatkan prestasi pengelas lemah dengan menekankan contoh yang sukar dikelaskan dalam setiap lelaran.
Objektif Utama:
- Pelarasan Berat: Tingkatkan berat kejadian tersalah klasifikasi untuk memastikan pengelas seterusnya memfokuskan padanya.
- Pembelajaran Berjujukan: Bina pengelas secara berurutan, di mana setiap pengelas baharu membetulkan ralat pendahulunya.
- Peningkatan Prestasi: Gabungkan pengelas lemah untuk membentuk pengelas yang kuat dengan kuasa ramalan yang lebih baik.
Bagaimana AdaBoost Berfungsi
-
Memulakan Berat:
- Berikan pemberat yang sama kepada semua contoh latihan. Untuk set data dengan n tika, setiap tika mempunyai berat 1/n.
-
Latih Pengelas Lemah:
- Latih pengelas lemah menggunakan set data berwajaran.
-
Ralat Kira Pengelas:
- Kira ralat pengelas lemah, iaitu jumlah pemberat kejadian tersalah klasifikasi.
-
Kira Berat Pengelas:
- Kira berat pengelas berdasarkan ralatnya. Berat diberikan oleh: alpha = 0.5 * log((1 - ralat) / ralat)
- Ralat yang lebih rendah menghasilkan berat pengelas yang lebih tinggi.
-
Kemas kini Wajaran Contoh:
- Laraskan berat kejadian. Naikkan wajaran kejadian tersalah klasifikasi dan kurangkan wajaran tika terkelas dengan betul.
- Berat yang dikemas kini sebagai contoh i ialah: berat[i] = berat[i] * exp(alfa * (salah klasifikasi ? 1 : -1))
- Normalkan pemberat untuk memastikan jumlahnya menjadi 1.
-
Gabungkan Pengelas Lemah:
- Pengkelas kuat terakhir ialah jumlah wajaran pengelas lemah: Pengelas akhir = tanda(jumlah(alfa * pengelas_lemah))
- Fungsi tanda menentukan label kelas berdasarkan jumlah.
Contoh AdaBoost (Pengkelasan Binari).
AdaBoost, singkatan kepada Adaptive Boosting, ialah teknik ensemble yang menggabungkan berbilang pengelas lemah untuk mencipta pengelas yang kuat. Contoh ini menunjukkan cara melaksanakan AdaBoost untuk klasifikasi binari menggunakan data sintetik, menilai prestasi model dan menggambarkan sempadan keputusan.
Contoh Kod Python
1. Import Perpustakaan
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
Blok ini mengimport pustaka yang diperlukan untuk manipulasi data, plot dan pembelajaran mesin.
2. Jana Data Contoh
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility # Generate synthetic data for 2 classes n_samples = 1000 n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 2 # Class 0: Centered around (-1, -1) X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 + [-1, -1] # Class 1: Centered around (1, 1) X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 + [1, 1] # Combine the data X = np.vstack([X0, X1]) y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class), np.ones(n_samples_per_class)]) # Shuffle the dataset shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples) X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
Blok ini menjana data sintetik dengan dua ciri, dengan pembolehubah sasaran y ditakrifkan berdasarkan pusat kelas, mensimulasikan senario pengelasan binari.
3. Pisahkan Set Data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
Blok ini membahagikan set data kepada set latihan dan ujian untuk penilaian model.
4. Cipta dan Latih Pengelas AdaBoost
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=3, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
Blok ini memulakan model AdaBoost dengan tunggul keputusan sebagai penganggar asas dan melatihnya menggunakan set data latihan.
5. Buat Ramalan
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
Blok ini menggunakan model terlatih untuk membuat ramalan pada set ujian.
6. Nilaikan Model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
Output:
Accuracy: 0.9400
Confusion Matrix:
[[96 8]
[ 4 92]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.96 0.92 0.94 104
1.0 0.92 0.96 0.94 96
accuracy 0.94 200
macro avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
weighted avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
Blok ini mengira dan mencetak laporan ketepatan, matriks kekeliruan dan pengelasan, memberikan cerapan tentang prestasi model.
7. Visualisasikan Sempadan Keputusan
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='RdYlBu')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='RdYlBu', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Binary Classification")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundary created by the AdaBoost model, illustrating how the model separates the two classes in the feature space.
Output:

This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for binary classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities. The visualization of the decision boundary aids in interpreting the model's predictions.
AdaBoost (Multiclass Classification) Example
AdaBoost is an ensemble learning technique that combines multiple weak classifiers to create a strong classifier. This example demonstrates how to implement AdaBoost for multiclass classification using synthetic data, evaluate the model's performance, and visualize the decision boundary for five classes.
Python Code Example
1. Import Libraries
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
This block imports the necessary libraries for data manipulation, plotting, and machine learning.
2. Generate Sample Data with 5 Classes
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility
n_samples = 2500 # Total number of samples
n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 5 # Ensure this is exactly n_samples // 5
# Class 0: Centered around (-2, -2)
X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [-2, -2]
# Class 1: Centered around (0, -2)
X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [0, -2]
# Class 2: Centered around (2, -2)
X2 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [2, -2]
# Class 3: Centered around (-1, 2)
X3 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [-1, 2]
# Class 4: Centered around (1, 2)
X4 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 + [1, 2]
# Combine the data
X = np.vstack([X0, X1, X2, X3, X4])
y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class),
np.ones(n_samples_per_class),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 2),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 3),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 4)])
# Shuffle the dataset
shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
This block generates synthetic data for five classes located in different regions of the feature space.
3. Split the Dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
This block splits the dataset into training and testing sets for model evaluation.
4. Create and Train the AdaBoost Classifier
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=10, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
This block initializes the AdaBoost classifier with a weak learner (decision stump) and trains it using the training dataset.
5. Make Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
This block uses the trained model to make predictions on the test set.
6. Evaluate the Model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
Output:
Accuracy: 0.9540
Confusion Matrix:
[[ 97 2 0 0 0]
[ 0 92 3 0 0]
[ 0 4 92 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 86 14]
[ 0 0 0 0 110]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 1.00 0.98 0.99 99
1.0 0.94 0.97 0.95 95
2.0 0.97 0.96 0.96 96
3.0 1.00 0.86 0.92 100
4.0 0.89 1.00 0.94 110
accuracy 0.95 500
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
This block calculates and prints the accuracy, confusion matrix, and classification report, providing insights into the model's performance.
7. Visualize the Decision Boundary
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='viridis')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='viridis', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Multiclass Classification (5 Classes)")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundaries created by the AdaBoost classifier, illustrating how the model separates the five classes in the feature space.
Output:
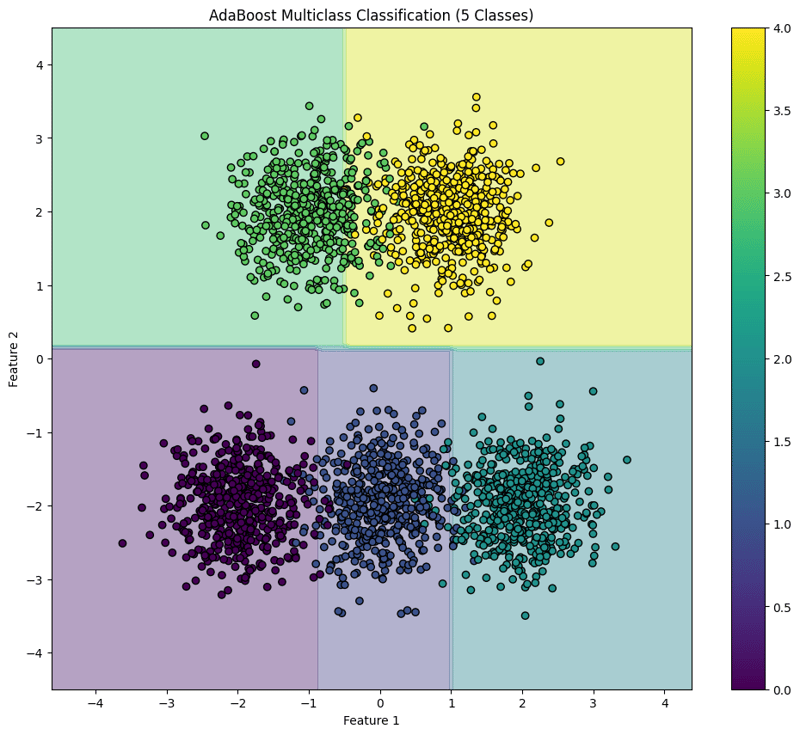
This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for multiclass classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities and the effectiveness of visualizing decision boundaries.
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci AdaBoost - Kaedah Ensemble, Klasifikasi: Pembelajaran Mesin Terselia. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

