대규모 언어 모델(llm)은 자연어 처리 분야에 혁명을 일으켰습니다. 이러한 모델의 크기와 복잡성이 증가함에 따라 추론을 위한 계산 요구 사항도 크게 증가합니다. 이 문제를 해결하려면 여러 GPU를 활용하는 것이 중요합니다.

따라서 이 기사에서는 주로 Accelerate 라이브러리 소개, 간단한 방법 및 작업 코드 예제, 다중 GPU를 사용한 성능 벤치마킹을 포함하여 여러 GPU에서 동시에 추론을 수행합니다.
이 기사에서는 여러 3090을 사용하여 여러 GPU에서 llama2-7b의 추론을 확장합니다.
기본 예제
먼저 Accelerate를 사용하여 다중 GPU "메시지 전달"을 보여주는 간단한 예를 소개합니다.
from accelerate import Accelerator from accelerate.utils import gather_object accelerator = Accelerator() # each GPU creates a string message=[ f"Hello this is GPU {accelerator.process_index}" ] # collect the messages from all GPUs messages=gather_object(message) # output the messages only on the main process with accelerator.print() accelerator.print(messages)
출력은 다음과 같습니다.
['Hello this is GPU 0', 'Hello this is GPU 1', 'Hello this is GPU 2', 'Hello this is GPU 3', 'Hello this is GPU 4']
Multi-GPU inference
다음은 간단한 비배치 추론 방법입니다. 코드는 매우 간단합니다. Accelerate 라이브러리가 이미 많은 작업을 수행했기 때문에 직접 사용할 수 있습니다.
from accelerate import Accelerator from accelerate.utils import gather_object from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer from statistics import mean import torch, time, json accelerator = Accelerator() # 10*10 Prompts. Source: https://www.penguin.co.uk/articles/2022/04/best-first-lines-in-books prompts_all=["The King is dead. Long live the Queen.","Once there were four children whose names were Peter, Susan, Edmund, and Lucy.","The story so far: in the beginning, the universe was created.","It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.","It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.","The sweat wis lashing oafay Sick Boy; he wis trembling.","124 was spiteful. Full of Baby's venom.","As Gregor Samsa awoke one morning from uneasy dreams he found himself transformed in his bed into a gigantic insect.","I write this sitting in the kitchen sink.","We were somewhere around Barstow on the edge of the desert when the drugs began to take hold.", ] * 10 # load a base model and tokenizer model_path="models/llama2-7b" model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path,device_map={"": accelerator.process_index},torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, ) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path) # sync GPUs and start the timer accelerator.wait_for_everyone() start=time.time() # divide the prompt list onto the available GPUs with accelerator.split_between_processes(prompts_all) as prompts:# store output of generations in dictresults=dict(outputs=[], num_tokens=0) # have each GPU do inference, prompt by promptfor prompt in prompts:prompt_tokenized=tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")output_tokenized = model.generate(**prompt_tokenized, max_new_tokens=100)[0] # remove prompt from output output_tokenized=output_tokenized[len(prompt_tokenized["input_ids"][0]):] # store outputs and number of tokens in result{}results["outputs"].append( tokenizer.decode(output_tokenized) )results["num_tokens"] += len(output_tokenized) results=[ results ] # transform to list, otherwise gather_object() will not collect correctly # collect results from all the GPUs results_gathered=gather_object(results) if accelerator.is_main_process:timediff=time.time()-startnum_tokens=sum([r["num_tokens"] for r in results_gathered ]) print(f"tokens/sec: {num_tokens//timediff}, time {timediff}, total tokens {num_tokens}, total prompts {len(prompts_all)}")
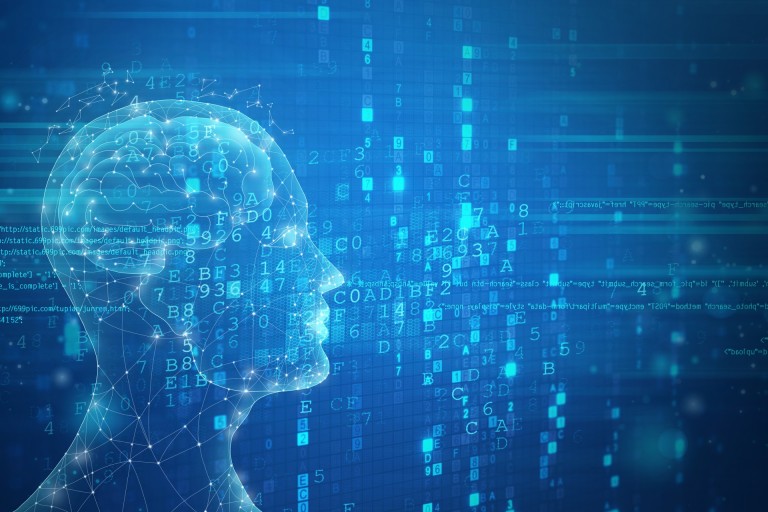
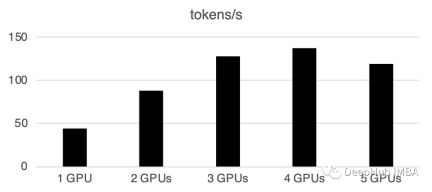
여러 GPU를 사용하면 약간의 통신 오버헤드가 발생합니다. 성능은 4개의 GPU에서 선형적으로 증가하고 이후에는 이는 특정 설정에서 안정적인 경향이 있습니다. 물론 여기의 성능은 모델 크기 및 양자화, 힌트 길이, 생성된 토큰 수 및 샘플링 전략과 같은 많은 매개변수에 따라 달라지므로 일반적인 사례만 논의합니다.
1 GPU: 44 토큰/초, 시간: 225.5초
2 GPU: 초당 88개 토큰 처리, 총 112.9초 시간
3 GPU: 초당 128개 토큰 처리, 총 77.6초
4 GPU: 137 토큰/초, 시간 : 72.7s
5 GPU: 초당 119개 토큰 처리, 총 소요 시간 83.8초
여러 GPU에서 일괄 처리
실제 세계에서는 일괄 추론을 사용하여 작업 속도를 높일 수 있습니다. 위로. 이는 GPU 간의 통신을 줄이고 추론 속도를 높입니다. 단일 데이터가 아닌 일괄 데이터를 모델에 입력하려면 prepare_prompts 함수만 추가하면 됩니다.
from accelerate import Accelerator from accelerate.utils import gather_object from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer from statistics import mean import torch, time, json accelerator = Accelerator() def write_pretty_json(file_path, data):import jsonwith open(file_path, "w") as write_file:json.dump(data, write_file, indent=4) # 10*10 Prompts. Source: https://www.penguin.co.uk/articles/2022/04/best-first-lines-in-books prompts_all=["The King is dead. Long live the Queen.","Once there were four children whose names were Peter, Susan, Edmund, and Lucy.","The story so far: in the beginning, the universe was created.","It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.","It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.","The sweat wis lashing oafay Sick Boy; he wis trembling.","124 was spiteful. Full of Baby's venom.","As Gregor Samsa awoke one morning from uneasy dreams he found himself transformed in his bed into a gigantic insect.","I write this sitting in the kitchen sink.","We were somewhere around Barstow on the edge of the desert when the drugs began to take hold.", ] * 10 # load a base model and tokenizer model_path="models/llama2-7b" model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path,device_map={"": accelerator.process_index},torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, ) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token # batch, left pad (for inference), and tokenize def prepare_prompts(prompts, tokenizer, batch_size=16):batches=[prompts[i:i + batch_size] for i in range(0, len(prompts), batch_size)]batches_tok=[]tokenizer.padding_side="left" for prompt_batch in batches:batches_tok.append(tokenizer(prompt_batch, return_tensors="pt", padding='longest', truncatinotallow=False, pad_to_multiple_of=8,add_special_tokens=False).to("cuda") )tokenizer.padding_side="right"return batches_tok # sync GPUs and start the timer accelerator.wait_for_everyone() start=time.time() # divide the prompt list onto the available GPUs with accelerator.split_between_processes(prompts_all) as prompts:results=dict(outputs=[], num_tokens=0) # have each GPU do inference in batchesprompt_batches=prepare_prompts(prompts, tokenizer, batch_size=16) for prompts_tokenized in prompt_batches:outputs_tokenized=model.generate(**prompts_tokenized, max_new_tokens=100) # remove prompt from gen. tokensoutputs_tokenized=[ tok_out[len(tok_in):] for tok_in, tok_out in zip(prompts_tokenized["input_ids"], outputs_tokenized) ] # count and decode gen. tokens num_tokens=sum([ len(t) for t in outputs_tokenized ])outputs=tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs_tokenized) # store in results{} to be gathered by accelerateresults["outputs"].extend(outputs)results["num_tokens"] += num_tokens results=[ results ] # transform to list, otherwise gather_object() will not collect correctly # collect results from all the GPUs results_gathered=gather_object(results) if accelerator.is_main_process:timediff=time.time()-startnum_tokens=sum([r["num_tokens"] for r in results_gathered ]) print(f"tokens/sec: {num_tokens//timediff}, time elapsed: {timediff}, num_tokens {num_tokens}")
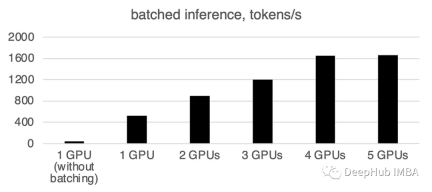
일괄 처리 속도가 크게 빨라지는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
다시 작성해야 할 내용은 다음과 같습니다. 1 GPU: 520개 토큰/초, 시간: 19.2초
두 개의 GPU는 초당 900개 토큰의 컴퓨팅 성능을 가지며 계산 시간은 11.1초입니다
3 GPU: 1205 토큰/초, 시간: 8.2s
4 GPU: 1655 토큰/초, 소요 시간: 6.0초
5 GPU: 1658 토큰/초 카드, 시간: 6.0초
요약
이 글을 기준으로 llama.cpp와 ctransformer는 다중 GPU 추론을 지원하지 않는 것으로 보입니다. 6월에 llama.cpp에 다중 GPU 병합이 있는 것으로 보이지만 공식적인 업데이트는 본 적이 없습니다. , 따라서 당분간 여기에서는 다중 GPU가 지원되지 않는 것으로 확인되었습니다. 여러 GPU를 지원할 수 있다고 확인한 사람이 있으면 메시지를 남겨주세요.
huggingface의 Accelerate 패키지는 여러 GPU를 사용할 수 있는 매우 편리한 옵션을 제공합니다. 추론을 위해 여러 GPU를 사용하면 성능이 크게 향상될 수 있지만 GPU 수가 증가하면 GPU 간 통신 비용이 크게 늘어납니다.
위 내용은 Accelerate 라이브러리를 사용하여 여러 GPU에서 LLM 추론의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
 AI 게임 개발May 02, 2025 am 11:17 AM
AI 게임 개발May 02, 2025 am 11:17 AM격변 게임 : AI 에이전트와의 게임 개발 혁명 Blizzard 및 Obsidian과 같은 업계 대기업의 재향 군인으로 구성된 게임 개발 스튜디오 인 Upheaval은 혁신적인 AI 구동 Platfor로 게임 제작에 혁명을 일으킬 준비가되어 있습니다.
 Uber는 Robotaxi 상점이되기를 원합니다. 제공자가 그들을 허락할까요?May 02, 2025 am 11:16 AM
Uber는 Robotaxi 상점이되기를 원합니다. 제공자가 그들을 허락할까요?May 02, 2025 am 11:16 AMUber의 Robotaxi 전략 : 자율 주행 차량을위한 승차원 생태계 최근 Curbivore 컨퍼런스에서 Uber의 Richard Willder는 Robotaxi 제공 업체를위한 승마 플랫폼이되기위한 전략을 공개했습니다. 그들의 지배적 인 위치를 활용합니다
 비디오 게임을하는 AI 요원은 미래의 로봇을 변화시킬 것입니다May 02, 2025 am 11:15 AM
비디오 게임을하는 AI 요원은 미래의 로봇을 변화시킬 것입니다May 02, 2025 am 11:15 AM비디오 게임은 특히 자율적 인 에이전트 및 실제 로봇의 개발에서 최첨단 AI 연구를위한 귀중한 테스트 근거로 입증되며, 인공 일반 정보 (AGI)에 대한 탐구에 잠재적으로 기여할 수 있습니다. 에이
 스타트 업 산업 단지, VC 3.0 및 James Currier 's ManifestoMay 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM
스타트 업 산업 단지, VC 3.0 및 James Currier 's ManifestoMay 02, 2025 am 11:14 AM진화하는 벤처 캐피탈 환경의 영향은 미디어, 재무 보고서 및 일상적인 대화에서 분명합니다. 그러나 투자자, 신생 기업 및 자금에 대한 구체적인 결과는 종종 간과됩니다. 벤처 캐피탈 3.0 : 패러다임
 Adobe 업데이트 Adobe Max London 2025에서 Creative Cloud and FireflyMay 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Adobe 업데이트 Adobe Max London 2025에서 Creative Cloud and FireflyMay 02, 2025 am 11:13 AMAdobe Max London 2025는 Creative Cloud and Firefly에 상당한 업데이트를 제공하여 접근성 및 생성 AI로의 전략적 전환을 반영했습니다. 이 분석에는 Adobe Leadership과의 사전 이벤트 브리핑의 통찰력이 포함되어 있습니다. (참고 : Adob
 모든 메타는 Llamacon에서 발표했습니다May 02, 2025 am 11:12 AM
모든 메타는 Llamacon에서 발표했습니다May 02, 2025 am 11:12 AMMeta의 Llamacon 발표는 OpenAi와 같은 폐쇄 된 AI 시스템과 직접 경쟁하도록 설계된 포괄적 인 AI 전략을 보여 주며 동시에 오픈 소스 모델을위한 새로운 수익원을 만듭니다. 이 다각적 인 접근법은 Bo를 대상으로합니다
 AI가 정상적인 기술에 지나지 않는다는 제안에 대한 양조 논쟁May 02, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI가 정상적인 기술에 지나지 않는다는 제안에 대한 양조 논쟁May 02, 2025 am 11:10 AM이 결론에 대한 인공 지능 분야에는 심각한 차이가 있습니다. 어떤 사람들은 "황제의 새로운 옷"을 폭로 할 때라고 주장하는 반면, 인공 지능은 단지 일반적인 기술이라는 생각에 강력하게 반대합니다. 논의합시다. 이 혁신적인 AI 혁신에 대한 분석은 다양한 영향력있는 AI 복잡성을 식별하고 설명하는 것을 포함하여 AI 분야의 최신 발전을 다루는 진행중인 Forbes 열의 일부입니다 (링크를 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오). 공통 기술로서의 인공 지능 첫째,이 중요한 토론을위한 토대를 마련하기 위해서는 몇 가지 기본 지식이 필요합니다. 현재 인공 지능을 발전시키는 데 전념하는 많은 연구가 있습니다. 전반적인 목표는 인공 일반 지능 (AGI) 및 가능한 인공 슈퍼 인텔리전스 (AS)를 달성하는 것입니다.
 모델 시민, AI 가치가 다음 비즈니스 척도 인 이유May 02, 2025 am 11:09 AM
모델 시민, AI 가치가 다음 비즈니스 척도 인 이유May 02, 2025 am 11:09 AM회사의 AI 모델의 효과는 이제 핵심 성과 지표입니다. AI 붐 이후 생일 초대장 작성부터 소프트웨어 코드 작성에 이르기까지 생성 AI는 모든 데 사용되었습니다. 이로 인해 언어 모드가 확산되었습니다


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

Dreamweaver Mac版
시각적 웹 개발 도구

WebStorm Mac 버전
유용한 JavaScript 개발 도구

MinGW - Windows용 미니멀리스트 GNU
이 프로젝트는 osdn.net/projects/mingw로 마이그레이션되는 중입니다. 계속해서 그곳에서 우리를 팔로우할 수 있습니다. MinGW: GCC(GNU Compiler Collection)의 기본 Windows 포트로, 기본 Windows 애플리케이션을 구축하기 위한 무료 배포 가능 가져오기 라이브러리 및 헤더 파일로 C99 기능을 지원하는 MSVC 런타임에 대한 확장이 포함되어 있습니다. 모든 MinGW 소프트웨어는 64비트 Windows 플랫폼에서 실행될 수 있습니다.

에디트플러스 중국어 크랙 버전
작은 크기, 구문 강조, 코드 프롬프트 기능을 지원하지 않음

Eclipse용 SAP NetWeaver 서버 어댑터
Eclipse를 SAP NetWeaver 애플리케이션 서버와 통합합니다.







