Vue에서 Vue.nextTick을 이해하는 데 도움이 되는 유용한 정보를 공유합니다.
- 青灯夜游앞으로
- 2022-03-22 11:37:122412검색
이 글은 여러분과 함께 Vue당신이 모르는 Vue.nextTick의 순수한 정보와 소개가 모두에게 도움이 되길 바랍니다!

Vue를 사용해본 친구들은
$nextTick을 어느 정도 알고 계시죠~ 정식으로 nextTick을 설명하기 전에, Vue가 업데이트할 때비동기라는 점을 분명히 아셔야 할 것 같습니다. DOM.code>, 다음 설명 과정은 컴포넌트 업데이트와 함께 설명할 예정이니까요~ 더 이상 고민하지 않고 바로 본론으로 들어가겠습니다. (이 글에서는 v2.6.14$nextTick~ 在正式讲解nextTick之前,我想你应该清楚知道 Vue 在更新 DOM 时是异步执行的,因为接下来讲解过程会结合组件更新一起讲~ 事不宜迟,我们直进主题吧(本文以v2.6.14版本的Vue源码进行讲解)【相关推荐:vuejs视频教程】
一、nextTick小测试
你真的了解nextTick吗?来,直接上题~
<template>
<div id="app">
<p ref="name">{{ name }}</p>
<button @click="handleClick">修改name</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data () {
return {
name: '井柏然'
}
},
mounted() {
console.log('mounted', this.$refs.name.innerText)
},
methods: {
handleClick () {
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1', this.$refs.name.innerText))
this.name = 'jngboran'
console.log('sync log', this.$refs.name.innerText)
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2', this.$refs.name.innerText))
}
}
}
</script>请问上述代码中,当点击按钮“修改name”时,'nextTick1','sync log','nextTick2'对应的this.$refs.name.innerText分别会输出什么?注意,这里打印的是DOM的innerText~(文章结尾处会贴出答案)
如果此时的你有非常坚定的答案,那你可以不用继续往下看了~但如果你对自己的答案有所顾虑,那不如跟着我,接着往下看。相信你看完,不需要看到答案都能有个肯定的答案了~!
二、nextTick源码实现
源码位于core/util/next-tick中。可以将其分为4个部分来看,直接上代码
1. 全局变量
callbacks队列、pending状态
const callbacks = [] // 存放cb的队列 let pending = false // 是否马上遍历队列,执行cb的标志
2. flushCallbacks
遍历callbacks执行每个cb
function flushCallbacks () {
pending = false // 注意这里,一旦执行,pending马上被重置为false
const copies = callbacks.slice(0)
callbacks.length = 0
for (let i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]() // 执行每个cb
}
}3. nextTick的异步实现
根据执行环境的支持程度采用不同的异步实现策略
let timerFunc // nextTick异步实现fn
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
// Promise方案
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(flushCallbacks) // 将flushCallbacks包装进Promise.then中
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
// MutationObserver方案
let counter = 1
const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks) // 将flushCallbacks作为观测变化的cb
const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter)) // 创建文本节点
// 观测文本节点变化
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
})
// timerFunc改变文本节点的data,以触发观测的回调flushCallbacks
timerFunc = () => {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2
textNode.data = String(counter)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
// setImmediate方案
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
}
} else {
// 最终降级方案setTimeout
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}- 这里用个真实案例加深对
MutationObserver的理解。毕竟比起其他三种异步方案,这个应该是大家最陌生的const observer = new MutationObserver(() => console.log('观测到文本节点变化')) const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(1)) observer.observe(textNode, { characterData: true }) console.log('script start') setTimeout(() => console.log('timeout1')) textNode.data = String(2) // 这里对文本节点进行值的修改 console.log('script end') - 知道对应的输出会是怎么样的吗?
script start、script end会在第一轮宏任务中执行,这点没问题setTimeout会被放入下一轮宏任务执行MutationObserver是微任务,所以会在本轮宏任务后执行,所以先于setTimeout
- 结果如下图:

4. nextTick方法实现
cb、Promise方式
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
// 往全局的callbacks队列中添加cb
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
// 这里是支持Promise的写法
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
if (!pending) {
pending = true
// 执行timerFunc,在下一个Tick中执行callbacks中的所有cb
timerFunc()
}
// 对Promise的实现,这也是我们使用时可以写成nextTick.then的原因
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}- 深入细节,理解
pending有什么用,如何运作?
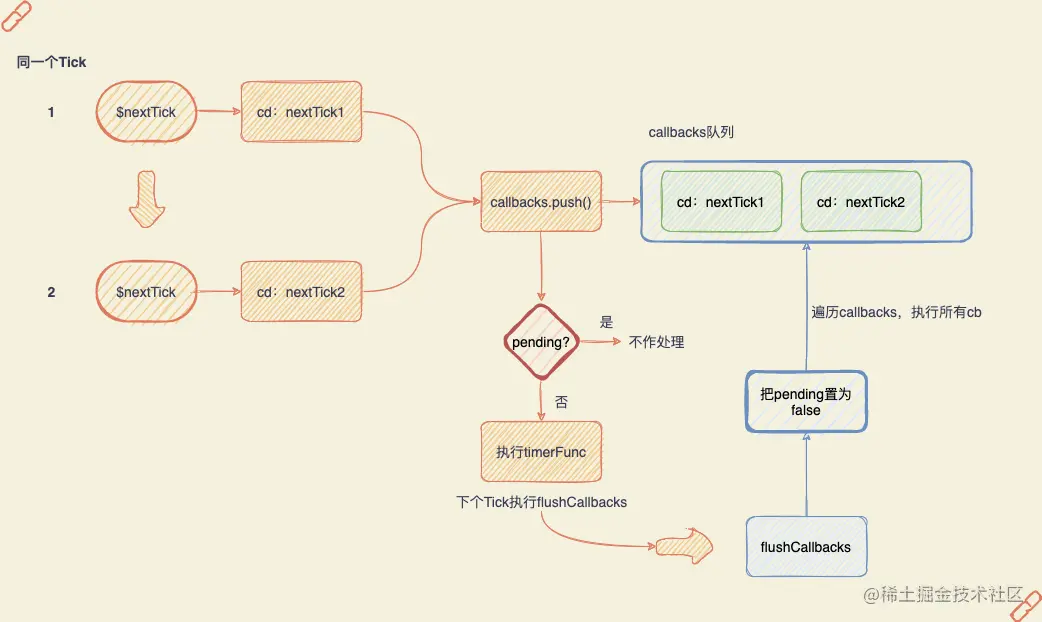
案例1,同一轮Tick中执行2次$nextTick,timerFunc只会被执行一次
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1')) this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2'))
- 用图看看更直观?
三、Vue组件的异步更新
这里如果有对Vue组件化、派发更新不是十分了解的朋友,可以先戳这里,看图解Vue响应式原理了解下Vue组件化和派发更新的相关内容再回来看噢~
Vue的异步更新DOM其实也是使用nextTick来实现的,跟我们平时使用的$nextTick其实是同一个~
这里我们回顾一下,当我们改变一个属性值的时候会发生什么?

根据上图派发更新过程,我们从watcher.update开时讲起,以渲染Watcher为例,进入到queueWatcher里
1. queueWatcher做了什么?
// 用来存放Wathcer的队列。注意,不要跟nextTick的callbacks搞混了,都是队列,但用处不同~
const queue: Array<Watcher> = []
function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id // 拿到Wathcer的id,这个id每个watcher都有且全局唯一
if (has[id] == null) {
// 避免添加重复wathcer,这也是异步渲染的优化做法
has[id] = true
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher)
}
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true
// 这里把flushSchedulerQueue推进nextTick的callbacks队列中
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
}
}
}
2. flushSchedulerQueue 버전의 Vue 소스코드를 사용하여 설명합니다.) [ 관련 권장사항: vuejs 비디오 튜토리얼】
1. NextTick 퀴즈- nextTick을 정말 이해하셨나요? 어서 질문으로 직행~
function flushSchedulerQueue () {
currentFlushTimestamp = getNow()
flushing = true
let watcher, id
// 排序保证先父后子执行更新,保证userWatcher在渲染Watcher前
queue.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
// 遍历所有的需要派发更新的Watcher执行更新
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index]
id = watcher.id
has[id] = null
// 真正执行派发更新,render -> update -> patch
watcher.run()
}
}위 코드에서 버튼을 클릭하면 "이름 수정", 'nextTick1', '동기화 로그' code>, <code>'nextTick2'의 해당 this.$refs.name.innerText 출력은 무엇입니까? 참고 여기에 인쇄된 내용은 DOM의 innerText입니다~(답변은 글 마지막에 게시됩니다)
여기에 인쇄된 내용은 DOM의 innerText입니다~(답변은 글 마지막에 게시됩니다)
이번에 매우 확고한 답변이 있다면 그럴 필요는 없습니다. 계속 읽어보세요~ 하지만 당신이 옳다면 당신의 답변에 대해 우려가 있다면 저를 팔로우하고 계속 읽어보세요. 꼭 읽어보시면 답을 보지 않고도 확실한 답을 얻으실 수 있을 거라 믿습니다~!
2. NextTick 소스코드 구현
소스코드는 core/util/next-tick에 있습니다. 4개 부분으로 나누어 코드🎜1. 전역 변수🎜🎜🎜콜백 대기열, 보류 중으로 직접 이동할 수 있습니다. status 🎜this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1', this.$refs.name.innerText))
this.name = 'jngboran'
console.log('sync log', this.$refs.name.innerText)
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2', this.$refs.name.innerText))
🎜2. flushCallbacks🎜🎜🎜콜백을 탐색하여 각 cb🎜rrreee🎜3. nextTick의 비동기 구현🎜🎜🎜실행 환경의 지원 수준에 따라 다양한 비동기 구현 전략을 채택하세요🎜rrreee🎜🎜다음은 실제 사례입니다. MutationObserver에 대한 이해를 심화시킵니다. 결국, 다른 세 가지 비동기 솔루션에 비해 이 솔루션은 모든 사람에게 가장 생소할 것입니다. 해당 출력이 어떻게 될지 아시나요? 🎜🎜script start, script end는 매크로 작업의 첫 번째 라운드에서 실행됩니다. 이는 아니요 문제 🎜🎜🎜🎜setTimeout는 다음 매크로 작업 실행에 포함됩니다🎜🎜🎜🎜MutationObserver는 마이크로 작업이므로 이번 라운드 후에 실행됩니다. 매크로 작업이므로 먼저 setTimeout🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜에서 결과는 아래와 같습니다.
 🎜🎜🎜
🎜🎜🎜4. nextTick 메소드 구현🎜🎜🎜 <code>cb, Promise 메소드🎜rrreee🎜🎜자세히 살펴보고 pending이 무엇에 사용되는지, 어떻게 사용되는지 이해하세요. 작동해요? 🎜🎜🎜사례 1, $nextTick은 동일한 Tick 라운드에서 두 번 실행되고 timerFunc는 한 번만 실행됩니다
🎜rrreee🎜🎜그 이상입니다. 그림으로 직관적인가요? 🎜🎜🎜 🎜🎜
🎜🎜 3. Vue 구성 요소의 비동기 업데이트🎜🎜Vue구성 요소화🎜 및 배포 업데이트🎜에 익숙하지 않은 친구가 있는 경우 먼저 Vue 응답성 원리 그림을 보려면 여기를 클릭하세요🎜Vue 구성 요소 이해 배포 업데이트 관련 내용 보러 오세요~🎜🎜Vue의 비동기 업데이트🎜DOM은 실제로 nextTick을 사용하여 구현되는데, 이는 실제로 우리가 일반적으로 사용하는 $nextTick과 동일합니다~🎜 🎜여기서 리뷰합니다 , 속성 값을 변경하면 어떻게 되나요? 🎜🎜 🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어
🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어 queueWatcher🎜 1. queueWatcher는 어떤 역할을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee2. flushSchedulerQueue는 무엇을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜마지막으로 컴포넌트의 비동기 업데이트 과정을 이해하기 위한 그림🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜 넷째, 질문 자체로 돌아가서🎜🎜위의 nextTick 소스코드 분석을 거쳐, 신비한 베일 . 이때는 더 이상 고민할 필요 없이 확실하게 답을 말할 수 있어야 합니다. 여러분의 생각이 맞는지 함께 확인해보세요! 🎜1、如图所示,mounted时候的innerText是“井柏然”的中文

2、接下来是点击按钮后,打印结果如图所示

-
没错,输出结果如下(意不意外?惊不惊喜?)
sync log 井柏然
nextTick1 井柏然
nextTick2 jngboran
-
下面简单分析一下每个输出:
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1', this.$refs.name.innerText))
this.name = 'jngboran'
console.log('sync log', this.$refs.name.innerText)
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2', this.$refs.name.innerText))
sync log:这个同步打印没什么好说了,相信大部分童鞋的疑问点都不在这里。如果不清楚的童鞋可以先回顾一下EventLoop,这里不多赘述了~
nextTick1:注意其虽然是放在$nextTick的回调中,在下一个tick执行,但是他的位置是在this.name = 'jngboran'的前。也就是说,他的cb会比App组件的派发更新(flushSchedulerQueue)更先进入队列,当nextTick1打印时,App组件还未派发更新,所以拿到的还是旧的DOM值。
nextTick2就不展开了,大家可以自行分析一下。相信大家对它应该是最肯定的,我们平时不就是这样拿到更新后的DOM吗?
最后来一张图加深理解

写在最后,nextTick其实在Vue中也算是比较核心的一个东西了。因为贯穿整个Vue应用的组件化、响应式的派发更新与其息息相关~深入理解nextTick的背后实现原理,不仅能让你在面试的时候一展风采,更能让你在日常开发工作中,少走弯路少踩坑!好了,本文到这里就暂告一段落了,如果读完能让你有所收获,就帮忙点个赞吧~画图不易、创作艰辛鸭~
flushCallbacks🎜🎜🎜콜백을 탐색하여 각 cb🎜rrreee🎜3. nextTick의 비동기 구현🎜🎜🎜실행 환경의 지원 수준에 따라 다양한 비동기 구현 전략을 채택하세요🎜rrreee🎜🎜다음은 실제 사례입니다. MutationObserver에 대한 이해를 심화시킵니다. 결국, 다른 세 가지 비동기 솔루션에 비해 이 솔루션은 모든 사람에게 가장 생소할 것입니다. 해당 출력이 어떻게 될지 아시나요? 🎜🎜script start, script end는 매크로 작업의 첫 번째 라운드에서 실행됩니다. 이는 아니요 문제 🎜🎜🎜🎜setTimeout는 다음 매크로 작업 실행에 포함됩니다🎜🎜🎜🎜MutationObserver는 마이크로 작업이므로 이번 라운드 후에 실행됩니다. 매크로 작업이므로 먼저 setTimeout🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜에서 결과는 아래와 같습니다.
 🎜🎜🎜
🎜🎜🎜4. nextTick 메소드 구현🎜🎜🎜 <code>cb, Promise 메소드🎜rrreee🎜🎜자세히 살펴보고 pending이 무엇에 사용되는지, 어떻게 사용되는지 이해하세요. 작동해요? 🎜🎜🎜사례 1, $nextTick은 동일한 Tick 라운드에서 두 번 실행되고 timerFunc는 한 번만 실행됩니다
🎜rrreee🎜🎜그 이상입니다. 그림으로 직관적인가요? 🎜🎜🎜 🎜🎜
🎜🎜 3. Vue 구성 요소의 비동기 업데이트🎜🎜Vue구성 요소화🎜 및 배포 업데이트🎜에 익숙하지 않은 친구가 있는 경우 먼저 Vue 응답성 원리 그림을 보려면 여기를 클릭하세요🎜Vue 구성 요소 이해 배포 업데이트 관련 내용 보러 오세요~🎜🎜Vue의 비동기 업데이트🎜DOM은 실제로 nextTick을 사용하여 구현되는데, 이는 실제로 우리가 일반적으로 사용하는 $nextTick과 동일합니다~🎜 🎜여기서 리뷰합니다 , 속성 값을 변경하면 어떻게 되나요? 🎜🎜 🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어
🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어 queueWatcher🎜 1. queueWatcher는 어떤 역할을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee2. flushSchedulerQueue는 무엇을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜마지막으로 컴포넌트의 비동기 업데이트 과정을 이해하기 위한 그림🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜 넷째, 질문 자체로 돌아가서🎜🎜위의 nextTick 소스코드 분석을 거쳐, 신비한 베일 . 이때는 더 이상 고민할 필요 없이 확실하게 답을 말할 수 있어야 합니다. 여러분의 생각이 맞는지 함께 확인해보세요! 🎜1、如图所示,mounted时候的innerText是“井柏然”的中文

2、接下来是点击按钮后,打印结果如图所示

-
没错,输出结果如下(意不意外?惊不惊喜?)
sync log 井柏然
nextTick1 井柏然
nextTick2 jngboran
-
下面简单分析一下每个输出:
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1', this.$refs.name.innerText))
this.name = 'jngboran'
console.log('sync log', this.$refs.name.innerText)
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2', this.$refs.name.innerText))
sync log:这个同步打印没什么好说了,相信大部分童鞋的疑问点都不在这里。如果不清楚的童鞋可以先回顾一下EventLoop,这里不多赘述了~
nextTick1:注意其虽然是放在$nextTick的回调中,在下一个tick执行,但是他的位置是在this.name = 'jngboran'的前。也就是说,他的cb会比App组件的派发更新(flushSchedulerQueue)更先进入队列,当nextTick1打印时,App组件还未派发更新,所以拿到的还是旧的DOM值。
nextTick2就不展开了,大家可以自行分析一下。相信大家对它应该是最肯定的,我们平时不就是这样拿到更新后的DOM吗?
最后来一张图加深理解

写在最后,nextTick其实在Vue中也算是比较核心的一个东西了。因为贯穿整个Vue应用的组件化、响应式的派发更新与其息息相关~深入理解nextTick的背后实现原理,不仅能让你在面试的时候一展风采,更能让你在日常开发工作中,少走弯路少踩坑!好了,本文到这里就暂告一段落了,如果读完能让你有所收获,就帮忙点个赞吧~画图不易、创作艰辛鸭~
script start, script end는 매크로 작업의 첫 번째 라운드에서 실행됩니다. 이는 아니요 문제 🎜🎜🎜🎜setTimeout는 다음 매크로 작업 실행에 포함됩니다🎜🎜🎜🎜MutationObserver는 마이크로 작업이므로 이번 라운드 후에 실행됩니다. 매크로 작업이므로 먼저 setTimeout🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜에서 결과는 아래와 같습니다. 🎜🎜🎜
🎜🎜🎜4. nextTick 메소드 구현🎜🎜🎜 <code>cb, Promise 메소드🎜rrreee🎜🎜자세히 살펴보고 pending이 무엇에 사용되는지, 어떻게 사용되는지 이해하세요. 작동해요? 🎜🎜🎜사례 1, $nextTick은 동일한 Tick 라운드에서 두 번 실행되고 timerFunc는 한 번만 실행됩니다
🎜rrreee🎜🎜그 이상입니다. 그림으로 직관적인가요? 🎜🎜🎜 🎜🎜
🎜🎜 3. Vue 구성 요소의 비동기 업데이트🎜🎜Vue구성 요소화🎜 및 배포 업데이트🎜에 익숙하지 않은 친구가 있는 경우 먼저 Vue 응답성 원리 그림을 보려면 여기를 클릭하세요🎜Vue 구성 요소 이해 배포 업데이트 관련 내용 보러 오세요~🎜🎜Vue의 비동기 업데이트🎜DOM은 실제로 nextTick을 사용하여 구현되는데, 이는 실제로 우리가 일반적으로 사용하는 $nextTick과 동일합니다~🎜 🎜여기서 리뷰합니다 , 속성 값을 변경하면 어떻게 되나요? 🎜🎜 🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어
🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어 queueWatcher🎜 1. queueWatcher는 어떤 역할을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee2. flushSchedulerQueue는 무엇을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜마지막으로 컴포넌트의 비동기 업데이트 과정을 이해하기 위한 그림🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜 넷째, 질문 자체로 돌아가서🎜🎜위의 nextTick 소스코드 분석을 거쳐, 신비한 베일 . 이때는 더 이상 고민할 필요 없이 확실하게 답을 말할 수 있어야 합니다. 여러분의 생각이 맞는지 함께 확인해보세요! 🎜1、如图所示,mounted时候的innerText是“井柏然”的中文

2、接下来是点击按钮后,打印结果如图所示

-
没错,输出结果如下(意不意外?惊不惊喜?)
sync log 井柏然
nextTick1 井柏然
nextTick2 jngboran
-
下面简单分析一下每个输出:
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1', this.$refs.name.innerText))
this.name = 'jngboran'
console.log('sync log', this.$refs.name.innerText)
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2', this.$refs.name.innerText))
sync log:这个同步打印没什么好说了,相信大部分童鞋的疑问点都不在这里。如果不清楚的童鞋可以先回顾一下EventLoop,这里不多赘述了~
nextTick1:注意其虽然是放在$nextTick的回调中,在下一个tick执行,但是他的位置是在this.name = 'jngboran'的前。也就是说,他的cb会比App组件的派发更新(flushSchedulerQueue)更先进入队列,当nextTick1打印时,App组件还未派发更新,所以拿到的还是旧的DOM值。
nextTick2就不展开了,大家可以自行分析一下。相信大家对它应该是最肯定的,我们平时不就是这样拿到更新后的DOM吗?
最后来一张图加深理解

写在最后,nextTick其实在Vue中也算是比较核心的一个东西了。因为贯穿整个Vue应用的组件化、响应式的派发更新与其息息相关~深入理解nextTick的背后实现原理,不仅能让你在面试的时候一展风采,更能让你在日常开发工作中,少走弯路少踩坑!好了,本文到这里就暂告一段落了,如果读完能让你有所收获,就帮忙点个赞吧~画图不易、创作艰辛鸭~
nextTick을 사용하여 구현되는데, 이는 실제로 우리가 일반적으로 사용하는 $nextTick과 동일합니다~🎜 🎜여기서 리뷰합니다 , 속성 값을 변경하면 어떻게 되나요? 🎜🎜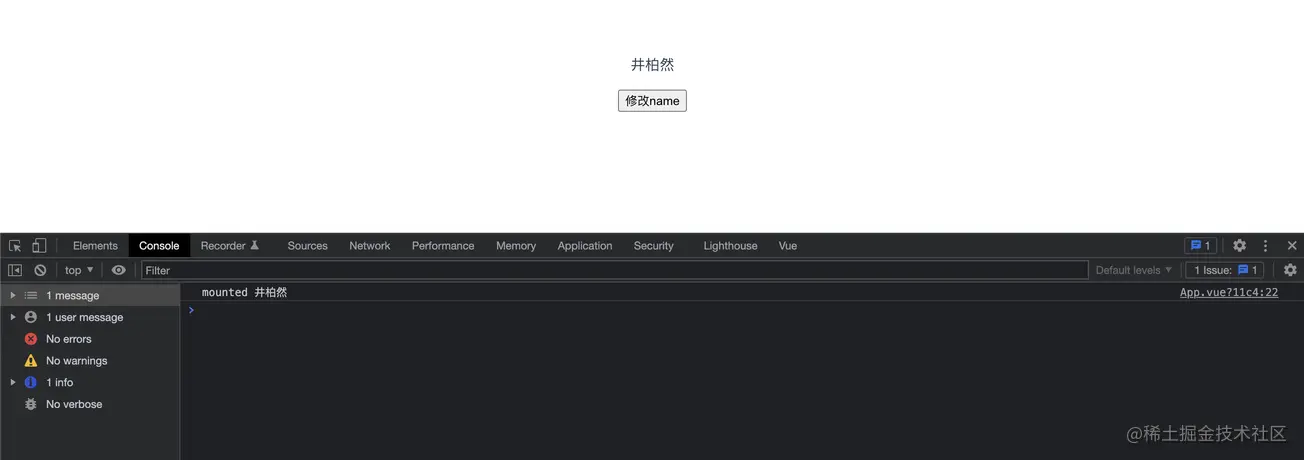 🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어
🎜🎜에 따르면 위 그림에서는 watcher.update가 열릴 때 디스패치 업데이트 프로세스부터 시작합니다. Rendering Watcher🎜를 예로 들어 queueWatcher🎜 1. queueWatcher는 어떤 역할을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee2. flushSchedulerQueue는 무엇을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜마지막으로 컴포넌트의 비동기 업데이트 과정을 이해하기 위한 그림🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜 넷째, 질문 자체로 돌아가서🎜🎜위의 nextTick 소스코드 분석을 거쳐, 신비한 베일 . 이때는 더 이상 고민할 필요 없이 확실하게 답을 말할 수 있어야 합니다. 여러분의 생각이 맞는지 함께 확인해보세요! 🎜1、如图所示,mounted时候的innerText是“井柏然”的中文

2、接下来是点击按钮后,打印结果如图所示

-
没错,输出结果如下(意不意外?惊不惊喜?)
sync log 井柏然
nextTick1 井柏然
nextTick2 jngboran
-
下面简单分析一下每个输出:
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1', this.$refs.name.innerText))
this.name = 'jngboran'
console.log('sync log', this.$refs.name.innerText)
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2', this.$refs.name.innerText))
sync log:这个同步打印没什么好说了,相信大部分童鞋的疑问点都不在这里。如果不清楚的童鞋可以先回顾一下EventLoop,这里不多赘述了~
nextTick1:注意其虽然是放在$nextTick的回调中,在下一个tick执行,但是他的位置是在this.name = 'jngboran'的前。也就是说,他的cb会比App组件的派发更新(flushSchedulerQueue)更先进入队列,当nextTick1打印时,App组件还未派发更新,所以拿到的还是旧的DOM值。
nextTick2就不展开了,大家可以自行分析一下。相信大家对它应该是最肯定的,我们平时不就是这样拿到更新后的DOM吗?
最后来一张图加深理解

写在最后,nextTick其实在Vue中也算是比较核心的一个东西了。因为贯穿整个Vue应用的组件化、响应式的派发更新与其息息相关~深入理解nextTick的背后实现原理,不仅能让你在面试的时候一展风采,更能让你在日常开发工作中,少走弯路少踩坑!好了,本文到这里就暂告一段落了,如果读完能让你有所收获,就帮忙点个赞吧~画图不易、创作艰辛鸭~
flushSchedulerQueue는 무엇을 하나요? 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜마지막으로 컴포넌트의 비동기 업데이트 과정을 이해하기 위한 그림🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜 넷째, 질문 자체로 돌아가서🎜🎜위의 nextTick 소스코드 분석을 거쳐, 신비한 베일 . 이때는 더 이상 고민할 필요 없이 확실하게 답을 말할 수 있어야 합니다. 여러분의 생각이 맞는지 함께 확인해보세요! 🎜1、如图所示,mounted时候的innerText是“井柏然”的中文

2、接下来是点击按钮后,打印结果如图所示
-
没错,输出结果如下(意不意外?惊不惊喜?)
sync log 井柏然
nextTick1 井柏然
nextTick2 jngboran
-
下面简单分析一下每个输出:
this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1', this.$refs.name.innerText)) this.name = 'jngboran' console.log('sync log', this.$refs.name.innerText) this.$nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick2', this.$refs.name.innerText))
sync log:这个同步打印没什么好说了,相信大部分童鞋的疑问点都不在这里。如果不清楚的童鞋可以先回顾一下EventLoop,这里不多赘述了~nextTick1:注意其虽然是放在$nextTick的回调中,在下一个tick执行,但是他的位置是在this.name = 'jngboran'的前。也就是说,他的cb会比App组件的派发更新(flushSchedulerQueue)更先进入队列,当nextTick1打印时,App组件还未派发更新,所以拿到的还是旧的DOM值。nextTick2就不展开了,大家可以自行分析一下。相信大家对它应该是最肯定的,我们平时不就是这样拿到更新后的DOM吗?
最后来一张图加深理解
写在最后,nextTick其实在Vue中也算是比较核心的一个东西了。因为贯穿整个Vue应用的组件化、响应式的派发更新与其息息相关~深入理解nextTick的背后实现原理,不仅能让你在面试的时候一展风采,更能让你在日常开发工作中,少走弯路少踩坑!好了,本文到这里就暂告一段落了,如果读完能让你有所收获,就帮忙点个赞吧~画图不易、创作艰辛鸭~
위 내용은 Vue에서 Vue.nextTick을 이해하는 데 도움이 되는 유용한 정보를 공유합니다.의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

