집 >데이터 베이스 >MySQL 튜토리얼 >Jdbc--특정 코드 구현
Jdbc--특정 코드 구현
- 黄舟원래의
- 2017-02-11 11:10:391569검색
1. 연결 가져오기
1) jar 패키지를 프로젝트 디렉터리에 복사합니다.
2) 클래스 경로가 다음과 같도록 프로젝트의 buildpath 환경 변수에 jar 패키지를 추가합니다. 또한 빌드 경로와 일치합니다. 일관성이 있어 클래스 로더가 특정 하위 클래스를 쉽게 로드할 수 있습니다
3) 드라이버 클래스를 반사 로드하면 드라이버가 자동으로 등록됩니다4) 드라이버 관리자를 통해 연결을 얻습니다.
현재 프로젝트 아래에 jdbc.properties 파일을 생성합니다. 해당 파일의 내용은 다음과 같습니다(Oracle 및 MySql 데이터베이스에 연결하는 데 필요한 네 가지 매개 변수는 다음과 같습니다. 드라이버 로드, 데이터베이스에 연결하기 위한 IP 및 포트 획득), 사용자 이름, 비밀번호), 호출 및 수정을 용이하게 하는 것이 목적입니다!
#driverClass = oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver #url = jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl #user = scott#password = tigerdriverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/companyuser = root password = 123456
연결을 얻고 연결을 닫는 구체적인 구현은 다음과 같습니다.
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 获取连接
* 1) 把jar包复制到项目目录下
* 2) 把jar包加入项目的buildpath环境变量中, 使得classpath也和buildpath一致, 让类加载器便于加载具体子类
* 3) 反射加载驱动程序类, 会自动注册驱动程序
* 4) 通过驱动程序管理器获取连接.
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class DriverTest {
// 使用Properties类对象的getPropety方法与FileInputStream方法获取文件中的内容,从而创建Connection对象
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}
}모든 jdbc 작업에는 연결이 필요하므로 연결을 설정하는 방법과 리소스를 닫는 방법을 JdbcUtil 클래스에 고정된 방법으로 넣어서 사용하기 쉽도록 했습니다. :
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtil {
// 获取建立连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass); // 只需要加载类, 类的静态语句块就会被执行, 创建驱动程序对象,并把此对象注册到驱动程序管理器中.
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
// 关闭资源
public static void close(Connection connection) {
close(connection, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
close(connection, statement, null);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}Statement 수업
이제 데이터베이스와 통신할 수 있습니다. 먼저, 해당하는 User 클래스를 만들어야 합니다. Statement 클래스에서 생성된 회사 데이터베이스의 사용자 테이블에:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class User {
private String user;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String user, String password) {
super();
this.user = user;
this.password = password;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [user=" + user + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}Statement를 사용하여 사용자 테이블을 생성하고 세 개의 데이터 행을 삽입합니다.
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.junit.Test;
// 使用Statement执行创建user表,并插入三行数据
public class StatementTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();// 获取执行体对象
// 执行SQL
// 创建user表
String sql = "create table if not exists user(user varchar(50), password varchar(100))";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql); // 执行的DDL语句, 还可以执行DML
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('admin','admin')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user1','user1')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
rows = statement.executeUpdate("insert into user values('user2','123456')");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected..");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, statement);
}
}
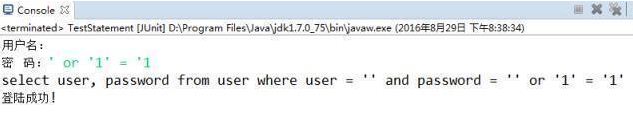
}그러나 문에는 단점이 있습니다. SQL 문을 철자해야 할 뿐만 아니라 SQL의 문제도 있습니다. 주입의 구체적인 문제는 다음의 작은 예에 반영되어 있습니다.
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestStatement {
// 弊端:需要拼写sql语句,并且存在SQL注入的问题
@Test
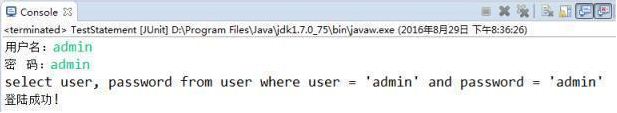
public void testLogin() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
System.out.print("密 码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
String sql = "select user, password from user where user = '"
+ userName + "' and password = '" + password + "'";
System.out.println(sql);
User user = get(sql, User.class);
if(user != null){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
}else{
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
public <T> T get(String sql, Class<T> clazz) {// (sql, Customer.class)
T t = null;
Connection conn = null;
Statement stam = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
stam = conn.createStatement();
rs = stam.executeQuery(sql);
// 获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// 获取结果集的列数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// //1. 获取列的名称
// String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
// 1. 获取列的别名
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 注意:
// 获取结果集中(相当于数据表)列的名称(别名)
// 2. 根据列名获取对应数据表中的数据
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(columnName);
// 3. 将数据表中得到的数据,封装进对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); // 注意:反射根据Java中类的属性获取Field对象
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//JDBCUtils.close(rs, stam, conn);
}
return t;
}
}
이 프로그램의 경우 로그인하려면 올바른 사용자 이름과 해당 비밀번호를 사용해야 합니다. 위 프로그램을 통해 사용자 이름과 비밀번호는 다음과 같습니다:
+-------+------------+
| 사용자 | 비밀번호 |
+-------+----------+
| 관리자 |
| user1 |
| user2 |
+--- ------------+
PreparedStatement 클래스
순서 SQL 삽입 문제를 방지하려면 하위 클래스인 ReadyStatement를 사용하여 실행 본문을 미리 컴파일해야 합니다. 아래에서 ReadyStatement를 연습해 보겠습니다.
// 이름, 성별, 전화 속성을 포함하는 Customer 클래스 작성
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String gender;
private String phone;
public Customer(String name, int age, String gender, String phone,) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.phone = phone;
}
public Customer() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", phone=" + phone + "]";
}
}테스트 클래스의 ReadyStatment 실행기 개체를 사용하여 해당 테이블을 생성합니다. 그리고 2개의 데이터를 삽입합니다.
public class PreparedStatementTest {
@Test
public void exer1() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "create table if not exists customer(name varchar(30), gender enum('男','女') default '男', phone varchar(20))";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement); // 在获取新的预编译对象前,一定要先关闭原来的.
String sql2 = "insert into customer(name, gender, phone) values(?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); // 要想重新执行新的SQL,必须再次预编译
preparedStatement.setString(1, "张三");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "13343493434");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
preparedStatement.setString(1, "李四");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "1322243434");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected.");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
// 并通过客户端验证.
}
}age에 속성을 추가하고 Customer 클래스의 가중치를 두 배로 늘리고 Customer 테이블에 해당 열을 추가하고 레코드를 추가합니다.
public class PreparedStatementTest {
// 在Customer类中添加属性int age,double weight,给Customer表中添加对应的列,并添加记录
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add age int after name";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "alter table customer add weight double";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 50);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "男");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "134234234234");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 98.5);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 添加记录
@Test
public void test4() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "alter table customer add birthdate date";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.close(null, preparedStatement);
sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "赵六");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 60);
preparedStatement.setString(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setString(4, "13882342323");
preparedStatement.setDouble(5, 40);
preparedStatement.setString(6, "1960-2-3");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
// 再添加记录
@Test
public void test5() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into customer(name, age, gender, phone, weight, birthdate) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "张七");
preparedStatement.setObject(2, 20);
preparedStatement.setObject(3, "女");
preparedStatement.setObject(4, "1343434343");
preparedStatement.setObject(5, 58.8);
preparedStatement.setObject(6, "1980-3-8");
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (rows == 1) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
} 추가 위와 같이 매번 반복되는 동일한 코드입니다. 여기서는 범용 업데이트 작업을 설정하고 이를 도구 클래스에 대한 범용 업데이트 작업으로 CommonUtil 클래스에 저장합니다. 구체적인 구현은 다음과 같습니다:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class CommonUtil {
/**
* 通用更新操作
* @param sql 一个可以包含?的SQL语句
* @param values SQL中有多少个?,可变参数就有多少个具体值
* @return 更新以后影响的记录数
*/
public static int commonUpdate(String sql, Object... values) throws FileNotFoundException,
ClassNotFoundException, IOException,
SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtil.getConnection(); // 获取连接
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 把带有?的SQL编译
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) { // 可变参数的长度就是?的个数
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, values[i]); // 统一给所有的?替换成具体的值
}
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 替换完?或没有?, 执行更新操作
} finally {
JdbcUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement); // 关闭资源
}
}
}
ResultSet 클래스지금까지 우리는 데이터베이스 데이터 구현 테이블 생성, 삽입, 업데이트, 삭제는 데이터베이스 작업에서 더 어려운 쿼리입니다. 쿼리 결과 세트 ResultSet 클래스를 사용해야 합니다.
아아앙
위는 Jdbc 관련 코드 구현 내용, 더 많은 관련 내용 PHP 중국어 웹사이트(www.php.cn)에 주목하세요!

