집 >백엔드 개발 >C#.Net 튜토리얼 >C#의 파일 처리
C#의 파일 처리
- 王林원래의
- 2024-09-03 15:23:46907검색
The operations of file creation, reading the contents from the file, writing the contents to the file, file appending, etc., is referred to as file handling. When the file is opened for reading and writing, it is called a stream, which is a byte sequence used for communication; the stream is of two types input stream to read the file, output stream to write the file, these two streams are handled by system.IO namespace in C#. It consists of file structure and directory structure information. There are classes in the system.IO namespace to support file handling in c#. The list of classes is:
- Binary Reader: This class is used to read primitive data from the binary stream.
- Binary Writer: This class is used to write primitive data into the binary stream.
- File stream: Data is read and written from the file using this class.
Examples of File Handling in C#
Following are the examples of file handling in C#:
Example #1
C# program to demonstrate binary reader, binary writer, file stream classes to create a file, read the contents from the file and write contents into the file.
using System;
using System.IO;
public class BinStream
{
public BinStream()
{
Writerfunc();
Readerfunc();
}
public static void Main()
{
BinStream bs1 = new BinStream();
Console.ReadLine();
}
private void Writerfunc()
{
try
{
Console.Out.WriteLine("Let's get started ...");
//a FileStream is opened on the file "new"
FileStream fout1 = new FileStream("new.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate,
FileAccess.Write, FileShare.ReadWrite);
//a BinaryWriter is created from the FileStream
BinaryWriter bw1 = new BinaryWriter(fout1);
//arbitrary variables are created
string name1 = "Shobha";
int age1 = 28;
double height1 = 5.5;
bool single1 = true;
char gender1 = 'F';
//values are written to the file
bw1.Write(name1);
bw1.Write(age1);
bw1.Write(height1);
bw1.Write(single1);
bw1.Write(gender1);
//file and free resources are closed
bw1.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Data updated!");
Console.WriteLine();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("occurance of an input output exception :" + e);
}
}
private void Readerfunc()
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Lets get started to Read ...");
//FileStream is opened in Read mode
FileStream fin1 = new FileStream("new.txt", FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read, FileShare.ReadWrite);
//a BinaryReader is created from the FileStream
BinaryReader br1 = new BinaryReader(fin1);
//start of the file is searched
br1.BaseStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
//the file is read and the values are stored to the variables
string name1 = br1.ReadString();
int age1 = br1.ReadInt32();
double height1 = br1.ReadDouble();
bool single1 = br1.ReadBoolean();
char gender1 = br1.ReadChar();
//the data is displayed on the console
Console.WriteLine("Your Name :" + name1);
Console.WriteLine("Your Age :" + age1);
Console.WriteLine("Your Height :" + height1);
Console.WriteLine("Are you Single? :" + single1);
Console.WriteLine("Your Gender M/F:" + gender1);
<em> </em>//stream is closed and the resources are freed
br1.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Read the data successfully!");
}
catch (IOException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("occurance of an input output exception :" + e);
}
}
}
The output of the above code is shown below:

- Buffered Stream: This class provides temporary storage for a stream of bytes.
- Memory stream: The streamed data stored in the memory can be randomly accessed using this class
Example #2
C# program to demonstrate the use of buffered stream class and memory stream class
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
public class Program
{
public void Main()
{
var check = Stopwatch.StartNew();
// buffer writes to a MemoryStream by using buffered stream.
using (MemoryStream memory = new MemoryStream())
using (BufferedStream stream = new BufferedStream(memory))
{
// a byte is written 5 million times.
for (int i = 0; i < 5000000; i++)
{
stream.WriteByte(5);
}
}
check.Stop();
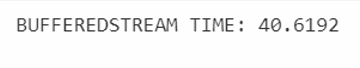
Console.WriteLine("BUFFEREDSTREAM TIME: " + check.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
}
}
The output of the above code is shown in the snapshot below:
- Directory: This class manipulated the structure of the directory.
- Directory info: Operations are performed on the directories using this class.
Example #3
C# program to demonstrate the use of directory class and directory info class
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace CSharp
{
class Programcheck
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//directory name is provided along with complete location. DirectoryInfo directory = new DirectoryInfo(@"C:\\Users\\shivakumarsh\\Desktop\\dir1");
try
{
// A check is done to see if directory exists or no
if (directory.Exists)
{
Console.WriteLine("A directory by this name already exists");
return;
}
// a new directory is created.
directory.Create();
Console.WriteLine("New directory is created");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Directory cannot be created: {0}", e.ToString());
}
}
}
}
The output of the above code is shown in the snapshot below:

- Drive info: Drives are provided with information using this class.
Example #4
C# program to demonstrate the use of drive info class
using System;
using System.IO;
class Programcheck
{
static void Main()
{
//the drive names are printed.
var drives1 = DriveInfo.GetDrives();
foreach (DriveInfo info in drives1)
{
Console.WriteLine(info.Name);
}
}
}
The output of the above program is shown in the snapshot below:

- File: Files are manipulated using this class
- File info: Operations are performed on the files using this class.
- Path: Operations are performed on the path information using this class.
- Stream Reader: Characters are read from the byte stream using this class.
- Stream writer: Characters are written into the byte stream using this class.
Example #5
C# program to demonstrate the use of the file, file info, path, stream reader, stream writer class
using System;
using System.IO;
class programcheck
{
public static void Main()
{
string path1 = Path.GetTempFileName();
var file1 = new FileInfo(path1);
//A file is created to write into it
using (StreamWriter swe = file1.CreateText())
{
swe.WriteLine("Welcome");
swe.WriteLine("to");
swe.WriteLine("C#");
}
// A file is opened to read from it
using (StreamReader sre = file.OpenText())
{
var sh = "";
while ((sh = sre.ReadLine()) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(sh);
}
}
try
{
string path22 = Path.GetTempFileName();
var file2 = new FileInfo(path22);
// making sure there is no target
file2.Delete();
// File is copied.
file1.CopyTo(path22);
Console.WriteLine($"{path1} was copied to {path22}.");
// newly created file is deleted.
file2.Delete();
Console.WriteLine($"{path2} was deleted.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine($" failed process: {e.ToString()}");
}
}
}
The output of the above code is shown in the snapshot below:

- String Reader: Reading can be done from the string buffer using this class.
- String Writer: Writing can be done into the string buffer using this class.
Example #5
C# program to demonstrate the use of string reader and string writer class
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace CSharp
{
public class check
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
StringWriter strn = new StringWriter();
strn.WriteLine("Welcome to C#");
strn.Close();
// Creating an instance of StringReader and StringWriter is passed
StringReader read = new StringReader(strn.ToString());
// data is being read
while (read.Peek() > -1)
{
Console.WriteLine(read.ReadLine());
}
}
}
}
The output of the above code is shown in the snapshot below:

위 내용은 C#의 파일 처리의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

