PHP 쓰기 파일
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB원래의
- 2024-08-29 13:02:40671검색
PHP에는 파일에 대해 다양한 작업을 수행하는 데 사용되는 다양한 내장 함수가 있습니다. 파일에 대한 생성, 열기, 읽기, 쓰기 및 기타 작업을 수행할 수도 있습니다.
무료 소프트웨어 개발 과정 시작
웹 개발, 프로그래밍 언어, 소프트웨어 테스팅 등
PHP 쓰기 파일 기능
다음은 PHP에서 기본적으로 사용할 수 있는 주요 기능입니다.
1. fopen()
먼저 파일에 쓰려면 해당 파일을 만드는 방법을 알아야 합니다. 이는 open() 함수의 도움으로 수행됩니다. 파일을 여는 이름으로 오해의 소지가 있을 수 있지만, PHP에서는 Linux의 vi 함수처럼 파일을 생성하고 여는 데 동일한 함수가 사용됩니다. 이 함수는 실행되자마자 파일이 있는지 확인하고 생성만 합니다. 아래 예에서는 동일한 내용을 보여줍니다.
코드:
<?php
// Creating a file for test
$myfile = fopen("test.txt", "w")
?>
출력:
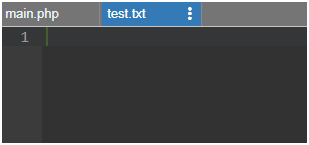
2. fwrite()
파일을 생성한 후 필요한 내용을 작성해야 하므로 이 기능을 동일하게 사용합니다. 이 기능은 파일의 끝(EOF)에 도달하거나 먼저 오는 순서에 따라 지정한 길이에 도달한 경우에만 중지됩니다.
구문:
fwrite(file, string, length)
- 여기서 file은 작성해야 하는 파일을 설명하는 필수 필드입니다
- 문자열은 열린 파일에 쓰도록 문자열에 지시하는 또 다른 필수 매개변수입니다
- length는 선택적 매개변수이며 기록할 최대 바이트 수를 제공합니다
코드:
<?php
// Your code here!
$f = fopen("testfile.txt", "w");
$text = "Random data here\n";
fwrite($f, $text);
?>
출력:
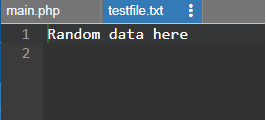
여기서 testfile.txt가 생성된 파일이고 $text에 할당된 문자열 값이 해당 파일에 기록됩니다.
3. file_put_contents()
이것은 PHP에서 파일에 내용을 쓰는 데 사용할 수 있는 또 다른 함수입니다. 파일에 액세스할 때 따라야 하는 동일한 순서의 특정 수의 규칙이 있습니다.
- FILE_USE_INCLUDE_PATH라는 속성이 있는데, 설정 시 파일 이름의 복사본이 포함되어 있는지 경로를 확인합니다.
- 파일 존재 여부를 확인한 후 생성
- 다음으로 파일을 엽니다
- LOCK_EX 속성을 설정하면 파일이 잠깁니다
- FILE_APPEND 속성이 설정되면 파일 끝으로 이동하고 그렇지 않으면 파일 내용이 지워집니다.
- 이제 필요한 데이터를 파일에 씁니다.
- 파일을 닫고 잠금이 있으면 해제합니다
구문:
file_put_contents(filename, text, mode, context)
- 여기서 filename은 필수 매개변수이며 작성해야 하는 파일의 전체 경로를 알려줍니다. 따라서 이 함수는 파일을 확인하고 생성합니다.
- text는 파일에 써야 하는 데이터인 또 다른 필수 필드입니다. 단순 문자열, 문자열 배열 또는 데이터 스트림 형식일 수 있습니다.
- mode는 파일에 대한 다양한 작업 방법을 제공하는 선택적 필드입니다. 가능한 값은 다음과 같습니다.
-
- FILE_USE_INCLUDE_PATH: 포함 디렉터리 경로에서 지정된 파일 이름을 검색합니다.
-
- FILE_APPEND: 데이터를 덮어쓰는 대신 파일에 데이터를 추가합니다.
-
- LOCK_EX: 파일을 쓸 때 명시적으로 잠금을 설정합니다.
- context는 파일의 컨텍스트를 제공하는 선택적 매개변수입니다. 이는 기본적으로 스트림의 동작을 변경할 수 있는 다양한 옵션입니다.
반환 값: 이 함수는 성공 시 파일에 기록된 총 바이트 수를 반환하고, 실패하면 FALSE 값을 반환합니다.
아래는 예시입니다.
코드:
<?php
echo file_put_contents("filetest.txt","Testing for file write");
?>
출력:
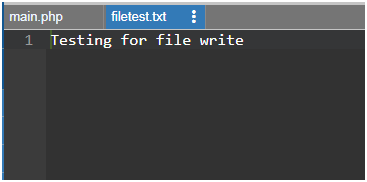
여기서 우리가 만들고 있는 파일은 첫 번째 매개변수로 주어지고, 다음 매개변수는 해당 파일에 쓰여진 텍스트입니다.
4. 덮어쓰기
이미 데이터가 기록되어 있는 위 파일에 덮어쓸 수 있습니다. 파일에 이미 존재하는 데이터는 모두 정리되고 새로운 빈 파일로 시작됩니다. 아래 예에서는 기존 파일을 열고 새 데이터를 작성해 보겠습니다.
아래는 예시입니다.
코드:
<?php
$f = fopen("testfile.txt", "w");
$text = "Random data here\n";
$filetext = "Over writing the data\n";
fwrite($f, $filetext);
$filetext = "File Dummy Data\n";
fwrite($f, $filetext);
fclose($f);
?>
출력:
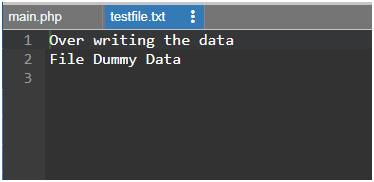
Here we are overwriting data in testfile.txt, so whatever is mentioned in the $filetext string value, the same will be written to the file. And when we use the same write command again by changing data given to the $filetext, then the old data is cleaned up and occupied by the latest text value that is provided.
At the end of the file, we always should close it by using the close() function which we have opened using the fwrite() function. As shown in the above example, we also use the \n, which represents the newline equivalent to pressing the enter button on our keyboard.
Now let us take an example and see how to include more data in our file.
Examples to Implement of PHP Write File
Below are the examples of PHP Write File:
Example #1
First, we add 2 lines of data using the below code:
Code:
<?php $testf = "TestFile.txt"; $filehandle = fopen($testf, 'w'); $fdata = "Julian Caesar\n"; fwrite($filehandle, $fdata); $fdata = "Harry James\n"; fwrite($filehandle, $fdata); print "Data writing completed"; fclose($filehandle); ?>
Output:
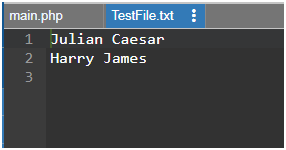
This creates a file TestFile.txt having 2 lines of data as mentioned.
Example #2
We will append another 2 names in the same file as shown below:
Code:
<?php $testf = "TestFile.txt"; $filehandle = fopen($testf, 'a'); $fdata = "Lilly Potter\n"; fwrite($filehandle, $fdata); $fdata = "Edward Cullen\n"; fwrite($filehandle, $fdata); print "Data has been appended"; fclose($filehandle); ?>
Output:
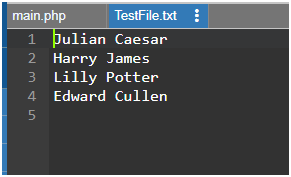
This example appends the given names to the same file as in the first example.
Conclusion
As shown above, there are various methods and steps that need to be followed when we want to write to a file in PHP. fwrite() is one of the main functions to do this and is used majorly for writing data to a file. They can do basic writing of data to our file but should be used in combination with other mandatory functions like open() and close(), without which it is not possible to perform operations on the file if it does not exist.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to the PHP Write File. Here we discuss the Introduction and its Functions of PHP Write File along with examples and Code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more-
- Overview of Abstract Class in Python
- What is Abstract Class in PHP?
- Socket Programming in PHP with Methods
- PHP chop() | How to Work?
위 내용은 PHP 쓰기 파일의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

