ホームページ >ウェブフロントエンド >jsチュートリアル >カプセル化モーションフレームワークの実践におけるスライディングフォーカスカルーセル図の説明
カプセル化モーションフレームワークの実践におけるスライディングフォーカスカルーセル図の説明
- 小云云オリジナル
- 2018-01-15 14:24:281694ブラウズ
この記事では主に、動きのフレームをカプセル化して左右上下にスライドするフォーカスカルーセル図(例)を紹介します。編集者はこれがとても良いものだと思ったので、皆さんの参考として今から共有します。編集者をフォローして見てみましょう。皆さんのお役に立てれば幸いです。
この記事では、ユニバーサル均一モーション フレームワークの構築 (例付きで説明)、このフレームワークに基づいて、バッファ モーション エフェクトを追加し、モーション フレームを使用してスライドを作成します (上から下へ)。左右)。

バッファの動きには通常 2 つの共通の症状があります。たとえば、p を 0 から 500 まで動かすと、1 つはイベントがトリガーされると非常に速くなり、もう 1 つはイベントがトリガーされると遅くなり、その後ゆっくりと速度が上がります。最初に速度を落とすことを意識しましょう。たとえば、高速道路を降りたばかりの車が時速 40 キロメートルに進入することです。 40km/hで最後に40km/hに変わります。120km/h→40km/h、または40km/h→0km/hになります。このような動きをプログラムで表現できるのでしょうか?

目標距離 (500) - 現在の距離 (200) / 係数 (12 など) を使用して、速度の減速変化を実現できます。 現在の距離が開始点であり、分子が分子です。 (500 - 0) が最も大きいので、現在の距離が 500 に近い場合、分子は最も小さく、分割後の速度も最も小さくなります。
<style>
p{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background:red;
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.querySelector( "input" ),
oBox = document.querySelector( '#box' ),
speed = 0, timer = null;
oBtn.onclick = function(){
timer = setInterval( function(){
speed = ( 500 - oBox.offsetLeft ) / 8;
oBox.style.left = oBox.offsetLeft + speed + 'px';
}, 30 );
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="动起来">
<p id="box"></p>
</body>しかし、pは素直に500pxの目標位置で停止せず、最終的には497.375pxで停止します。理由は現在の速度と現在値を確認してください
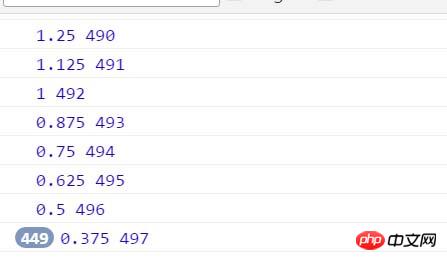
。速度は常に 0.375 で停止し、取得された現在の距離は 497px で停止することがわかりますか? ここで問題が発生します。p は 497.375px で止まりませんか?コンピュータは浮動小数点数を処理する際に精度が低下します。小さなテストを個別に行うことができます:
<p id="box"></p> <script> var oBox = document.querySelector( '#box' ); alert( oBox.offsetLeft ); </script>
このコードによって取得される左オフセットは、インライン スタイルで記述された 30.2px ではなく、30px であることがわかります。現在位置を取得する際に小数点以下は四捨五入されるため、速度は常に0.375pxで止まり、位置は常に497で止まります。そのため、目標に到達するには速度を1にして速度を四捨五入する必要があります。 up ( Math .ceil )、速度を 1 に変更すると、p は 500 に達することもできます
oBtn.onclick = function(){
timer = setInterval( function(){
speed = ( 500 - oBox.offsetLeft ) / 8;
if( speed > 0 ) {
speed = Math.ceil( speed );
}
console.log( speed, oBox.offsetLeft );
oBox.style.left = oBox.offsetLeft + speed + 'px';
}, 30 );
}2 番目の質問、p の位置が 900 にある場合、つまり、900 から 500 に移動します。 、そのような方法はありますか 需要はどうですか? 必ず 1 つあるはずです。カルーセルの画像は右から左に次のようになります。
<style>
#box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background:red;
position: absolute;
left: 900px;
}
</style>
<script>// <![CDATA[
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.querySelector( "input" ),
oBox = document.querySelector( '#box' ),
speed = 0, timer = null;
oBtn.onclick = function(){
timer = setInterval( function(){
speed = ( 500 - oBox.offsetLeft ) / 8;
if( speed > 0 ) {
speed = Math.ceil( speed );
}
oBox.style.left = oBox.offsetLeft + speed + 'px';
}, 30 );
}
}
// ]]></script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="动起来">
<p id="box"></p>
</body>この時点では、最終的な速度は 503.5px で停止します。反対方向の速度については、-1 に変更する必要があります。なので、方向を切り捨てる (Math.floor) を使用します
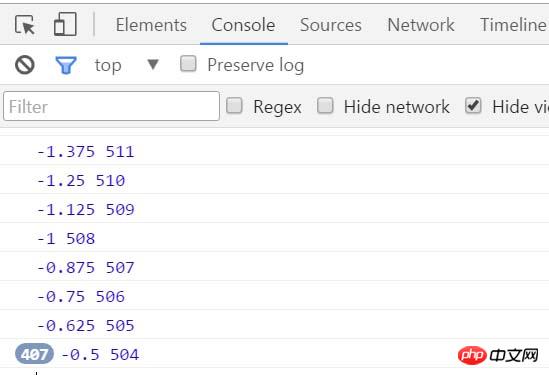
oBtn.onclick = function(){
timer = setInterval( function(){
speed = ( 500 - oBox.offsetLeft ) / 8;
if( speed > 0 ) {
speed = Math.ceil( speed );
}else {
speed = Math.floor( speed );
}
console.log( speed, oBox.offsetLeft );
oBox.style.left = oBox.offsetLeft + speed + 'px';
}, 30 );
}次に、このバッファモーションを均一モーションフレームに統合すると、次のようになります:
function css(obj, attr, value) {
if (arguments.length == 3) {
obj.style[attr] = value;
} else {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
function animate(obj, attr, fn) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
var cur = 0;
var target = 0;
var speed = 0;
obj.timer = setInterval(function () {
var bFlag = true;
for (var key in attr) {
if (key == 'opacity ') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, key));
}
target = attr[key];
speed = ( target - cur ) / 8;
speed = speed > 0 ? Math.ceil(speed) : Math.floor(speed);
if (cur != target) {
bFlag = false;
if (key == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + ( cur + speed ) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[key] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}
if (bFlag) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
fn && fn.call(obj);
}
}, 30 );
}この均一モーションフレームを使用すると、スライドショーを実行します:
上下のスライドの HTML スタイル ファイル:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>slide - by ghostwu</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/slide3.css" rel="external nofollow" > <script src="js/animate.js"></script> <script src="js/slide.js"></script> </head> <body> <p id="slide"> <p id="slide-img"> <p id="img-container"> <img src="./img/1.jpg" alt=""> <img src="./img/2.jpg" alt=""> <img src="./img/3.jpg" alt=""> <img src="./img/4.jpg" alt=""> <img src="./img/5.jpg" alt=""> </p> </p> <p id="slide-nums"> <ul> <li class="active"></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> </body> </html>
slide3.css ファイル:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
li {
list-style-type: none;
}
#slide {
width: 800px;
height: 450px;
position: relative;
margin:20px auto;
}
#slide-img {
position: relative;
width: 800px;
height: 450px;
overflow: hidden;
}
#img-container {
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
height: 2250px;
/*font-size:0px;*/
}
#img-container img {
display: block;
float: left;
}
#slide-nums {
position: absolute;
right:10px;
bottom:10px;
}
#slide-nums li {
float: left;
margin:0px 10px;
background: white;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 20px;
border-radius:10px;
text-indent:-999px;
opacity:0.6;
filter:alpha(opacity:60);
cursor:pointer;
}
#slide-nums li.active {
background: red;
}animate.js ファイル:
function css(obj, attr, value) {
if (arguments.length == 3) {
obj.style[attr] = value;
} else {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
function animate(obj, attr, fn) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
var cur = 0;
var target = 0;
var speed = 0;
obj.timer = setInterval(function () {
var bFlag = true;
for (var key in attr) {
if (key == 'opacity ') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, key));
}
target = attr[key];
speed = ( target - cur ) / 8;
speed = speed > 0 ? Math.ceil(speed) : Math.floor(speed);
if (cur != target) {
bFlag = false;
if (key == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + ( cur + speed ) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[key] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}
if (bFlag) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
fn && fn.call(obj);
}
}, 30 );
}slide.js ファイル:
window.onload = function () {
function Slide() {
this.oImgContainer = document.getElementById("img-container");
this.aLi = document.getElementsByTagName("li");
this.index = 0;
}
Slide.prototype.bind = function () {
var that = this;
for (var i = 0; i < this.aLi.length; i++) {
this.aLi[i].index = i;
this.aLi[i].onmouseover = function () {
that.moveTop( this.index );
}
}
}
Slide.prototype.moveTop = function (i) {
this.index = i;
for( var j = 0; j < this.aLi.length; j++ ){
this.aLi[j].className = '';
}
this.aLi[this.index].className = 'active';
animate( this.oImgContainer, {
"top" : -this.index * 450,
"left" : 0
});
}
var oSlide = new Slide();
oSlide.bind();
}左右のスライドのスタイルを変更するだけです
スタイルファイル:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
li {
list-style-type: none;
}
#slide {
width: 800px;
height: 450px;
position: relative;
margin:20px auto;
}
#slide-img {
position: relative;
width: 800px;
height: 450px;
overflow: hidden;
}
#img-container {
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
width: 4000px;
}
#img-container img {
display: block;
float: left;
}
#slide-nums {
position: absolute;
right:10px;
bottom:10px;
}
#slide-nums li {
float: left;
margin:0px 10px;
background: white;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 20px;
border-radius:10px;
text-indent:-999px;
opacity:0.6;
filter:alpha(opacity:60);
cursor:pointer;
}
#slide-nums li.active {
background: red;
}js呼び出しファイル:
window.onload = function () {
function Slide() {
this.oImgContainer = document.getElementById("img-container");
this.aLi = document.getElementsByTagName("li");
this.index = 0;
}
Slide.prototype.bind = function () {
var that = this;
for (var i = 0; i < this.aLi.length; i++) {
this.aLi[i].index = i;
this.aLi[i].onmouseover = function () {
that.moveLeft( this.index );
}
}
}
Slide.prototype.moveLeft = function (i) {
this.index = i;
for( var j = 0; j < this.aLi.length; j++ ){
this.aLi[j].className = '';
}
this.aLi[this.index].className = 'active';
animate( this.oImgContainer, {
"left" : -this.index * 800
});
}
var oSlide = new Slide();
oSlide.bind();
}関連する推奨事項:
バッファリングモーションフレームを実装するJavaScriptの例
以上がカプセル化モーションフレームワークの実践におけるスライディングフォーカスカルーセル図の説明の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

