ホームページ >バックエンド開発 >C#.Net チュートリアル >Shapeを使ったアニメーション例を詳しく解説
Shapeを使ったアニメーション例を詳しく解説
- 零下一度オリジナル
- 2017-06-23 15:05:471954ブラウズ
前回の記事はほぼDoubleAnimationの応用についてでしたが、今回はPointAnimationについての記事です。
1.PointAnimationを使う
PointAnimationを使うとShapeを変形させることができますが、結局のところ、WPFで作られたほとんどのソフトウェアはそれほど凝ったものである必要はありません。
1.1 XAML での PointAnimation の使用
<Storyboard x:Name="Storyboard2" RepeatBehavior="Forever" AutoReverse="True" Duration="0:0:4"><PointAnimation Storyboard.TargetProperty="(Path.Data).(PathGeometry.Figures)[0].(PathFigure.StartPoint)" Storyboard.TargetName="Path2" To="0,0" EnableDependentAnimation="True" /><PointAnimation Storyboard.TargetProperty="(Path.Data).(PathGeometry.Figures)[0].(PathFigure.Segments)[0].(LineSegment.Point)" Storyboard.TargetName="Path2" To="100,0" EnableDependentAnimation="True" /><ColorAnimation To="#FF85C82E" Storyboard.TargetProperty="(Shape.Fill).(SolidColorBrush.Color)" Storyboard.TargetName="Path2" /></Storyboard>…<Path Margin="0,20,0,0" x:Name="Path2" Fill="GreenYellow"><Path.Data><PathGeometry><PathFigure StartPoint="50,0"><LineSegment Point="50,0" /><LineSegment Point="0,100" /><LineSegment Point="0,100" /><LineSegment Point="100,100" /><LineSegment Point="100,100" /></PathFigure></PathGeometry></Path.Data></Path>

この例での最大の問題点は、プロパティ パス構文を覚えられない場合は、Blend 生成に頼るのが最善です。
1.2 コードで PointAnimation を使用する
チャートなどのポイントがたくさんある場合、PointAnimation は通常 C# コードで使用されます:
_storyboard = new Storyboard();
Random random = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < _pathFigure.Segments.Count; i++)
{var animation = new PointAnimation { Duration = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3) };
Storyboard.SetTarget(animation, _pathFigure.Segments[i]);
Storyboard.SetTargetProperty(animation, "(LineSegment.Point)");
animation.EnableDependentAnimation = true;
animation.EasingFunction = new QuarticEase { EasingMode = EasingMode.EaseOut };
animation.To = new Point((_pathFigure.Segments[i] as LineSegment).Point.X, (i % 2 == 0 ? 1 : -1) * i * 1.2 + 60);
_storyboard.Children.Add(animation);
}
_storyboard.Begin();
直接 SetTarget できるため、 so プロパティ - パス構文は非常に単純です。 SetTarget,所以Property-path语法就可以很简单。
2. 扩展PointAnimation
上面两个例子的动画都还算简单,如果更复杂些,XAML或C#代码都需要写到很复杂。我参考了这个网页 想做出类似的动画,但发现需要写很多XAML所以放弃用PointAnimation实现。这个页面的动画核心是这段HTML:
<polygon fill="#FFD41D" points="97.3,0 127.4,60.9 194.6,70.7 145.9,118.1 157.4,185.1 97.3,153.5 37.2,185.1 48.6,118.1 0,70.7 67.2,60.9">
<animate id="animation-to-check" begin="indefinite" fill="freeze" attributeName="points" dur="500ms" to="110,58.2 147.3,0 192.1,29 141.7,105.1 118.7,139.8 88.8,185.1 46.1,156.5 0,125 23.5,86.6 71.1,116.7"/>
<animate id="animation-to-star" begin="indefinite" fill="freeze" attributeName="points" dur="500ms" to="97.3,0 127.4,60.9 194.6,70.7 145.9,118.1 157.4,185.1 97.3,153.5 37.2,185.1 48.6,118.1 0,70.7 67.2,60.9"/> </polygon>只需一组Point的集合就可以控制所有Point的动画,确实比PointAnimation高效很多。 在WPF中可以通过继承Timeline实现一个PointCollectionAnimamtion,具体可以参考这个项目。可惜的是虽然UWP的Timeline类并不封闭,但完全不知道如何继承并派生一个自定义的Animation。
这时候需要稍微变通一下思维。可以将DoubleAnimation理解成这样:Storyboard将TimeSpan传递给DoubleAnimation,DoubleAnimation通过这个TimeSpan(有时还需要结合EasingFunction)计算出目标属性的当前值最后传递给目标属性,如下图所示:

既然这样,也可以接收到这个计算出来的Double,再通过Converter计算出目标的PointCollection值:
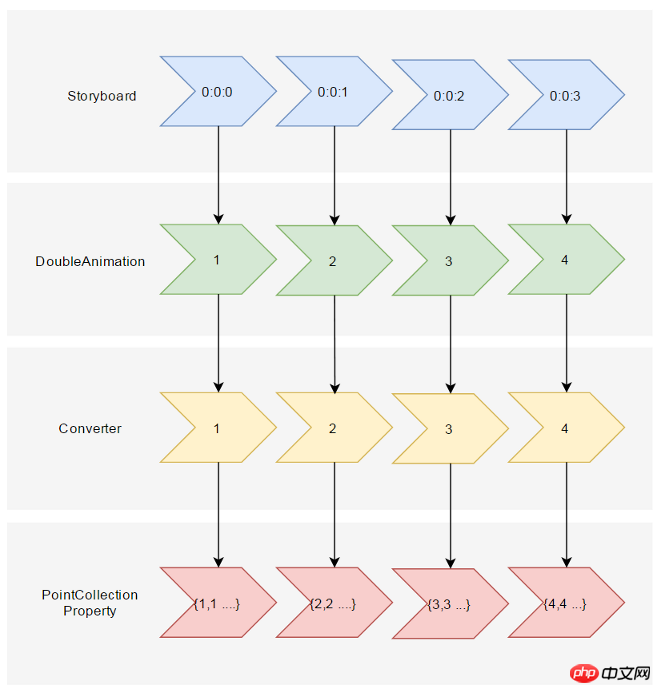
假设告诉这个Converter当传入的Double值(命名为Progress)为0的时候,PointCollection是{0,0 1,1 …},Progress为100时PointCollection是{1,1 2,2 …},当Progress处于其中任何值时的计算方法则是:
private PointCollection GetCurrentPoints(PointCollection fromPoints, PointCollection toPoints, double percentage)
{var result = new PointCollection();for (var i = 0;
i < Math.Min(fromPoints.Count, toPoints.Count);
i++)
{
var x = (1 - percentage / 100d) * fromPoints[i].X + percentage / 100d * toPoints[i].X;
var y = (1 - percentage / 100d) * fromPoints[i].Y + percentage / 100d * toPoints[i].Y;
result.Add(new Point(x, y));
}return result;
}这样就完成了从TimeSpan到PointCollection的转换过程。然后就是定义在XAML上的使用方式。参考上面PointCollectionAnimation,虽然多了个Converter,但XAML也应该足够简洁:
<local:ProgressToPointCollectionBridge x:Name="ProgressToPointCollectionBridge"><PointCollection>97.3,0 127.4,60.9 194.6,70.7 145.9,118.1 157.4,185.1 97.3,153.5 37.2,185.1 48.6,118.1 0,70.7 67.2,60.9</PointCollection><PointCollection>110,58.2 147.3,0 192.1,29 141.7,105.1 118.7,139.8 88.8,185.1 46.1,156.5 0,125 23.5,86.6 71.1,116.7</PointCollection></local:ProgressToPointCollectionBridge><Storyboard x:Name="Storyboard1" FillBehavior="HoldEnd"><DoubleAnimation Duration="0:0:2" To="100" FillBehavior="HoldEnd" Storyboard.TargetProperty="(local:ProgressToPointCollectionBridge.Progress)" Storyboard.TargetName="ProgressToPointCollectionBridge" EnableDependentAnimation="True"/></Storyboard>…<Polygon x:Name="polygon" Points="{Binding Source={StaticResource ProgressToPointCollectionBridge},Path=Points}" Stroke="DarkOliveGreen" StrokeThickness="2" Height="250" Width="250" Stretch="Fill" />最终我选择了将这个Converter命名为ProgressToPointCollectionBridge。可以看出Polygon 将Points绑定到ProgressToPointCollectionBridge,DoubleAnimation 改变ProgressToPointCollectionBridge.Progress,从而改变Points。XAML的简洁程度还算令人满意,如果需要操作多个点的话相对于PointAnimation的优势就很大。
运行结果如下:

完整的XAML:
<UserControl.Resources><local:ProgressToPointCollectionBridge x:Name="ProgressToPointCollectionBridge"><PointCollection>97.3,0 127.4,60.9 194.6,70.7 145.9,118.1 157.4,185.1 97.3,153.5 37.2,185.1 48.6,118.1 0,70.7 67.2,60.9</PointCollection><PointCollection>110,58.2 147.3,0 192.1,29 141.7,105.1 118.7,139.8 88.8,185.1 46.1,156.5 0,125 23.5,86.6 71.1,116.7</PointCollection></local:ProgressToPointCollectionBridge><Storyboard x:Name="Storyboard1" FillBehavior="HoldEnd"><DoubleAnimation Duration="0:0:2" To="100" FillBehavior="HoldEnd" Storyboard.TargetProperty="(local:ProgressToPointCollectionBridge.Progress)" Storyboard.TargetName="ProgressToPointCollectionBridge" EnableDependentAnimation="True"><DoubleAnimation.EasingFunction><ElasticEase EasingMode="EaseInOut" /></DoubleAnimation.EasingFunction></DoubleAnimation><ColorAnimation Duration="0:0:2" To="#FF48F412" Storyboard.TargetProperty="(Shape.Fill).(SolidColorBrush.Color)" Storyboard.TargetName="polygon" d:IsOptimized="True"><ColorAnimation.EasingFunction><ElasticEase EasingMode="EaseInOut" /></ColorAnimation.EasingFunction></ColorAnimation></Storyboard></UserControl.Resources><Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot" Background="White"><Polygon x:Name="polygon" Points="{Binding Source={StaticResource ProgressToPointCollectionBridge},Path=Points}" Stroke="DarkOliveGreen" StrokeThickness="2" Height="250" Width="250" Stretch="Fill" Fill="#FFEBF412" /></Grid>ProgressToPointCollectionBridge:
[ContentProperty(Name = nameof(Children))]public class ProgressToPointCollectionBridge : DependencyObject
{public ProgressToPointCollectionBridge()
{
Children = new ObservableCollection<PointCollection>();
}/// <summary>/// 获取或设置Points的值/// </summary>public PointCollection Points
{get { return (PointCollection) GetValue(PointsProperty); }set { SetValue(PointsProperty, value); }
}/// <summary>/// 获取或设置Progress的值/// </summary>public double Progress
{get { return (double) GetValue(ProgressProperty); }set { SetValue(ProgressProperty, value); }
}/// <summary>/// 获取或设置Children的值/// </summary>public Collection<PointCollection> Children
{get { return (Collection<PointCollection>) GetValue(ChildrenProperty); }set { SetValue(ChildrenProperty, value); }
}protected virtual void OnProgressChanged(double oldValue, double newValue)
{UpdatePoints();
}protected virtual void OnChildrenChanged(Collection<PointCollection> oldValue, Collection<PointCollection> newValue)
{var oldCollection = oldValue as INotifyCollectionChanged;if (oldCollection != null)
oldCollection.CollectionChanged -= OnChildrenCollectionChanged;var newCollection = newValue as INotifyCollectionChanged;if (newCollection != null)
newCollection.CollectionChanged += OnChildrenCollectionChanged;UpdatePoints();
}private void OnChildrenCollectionChanged(object sender, NotifyCollectionChangedEventArgs e)
{UpdatePoints();
}private void UpdatePoints()
{if (Children == null || Children.Any() == false)
{
Points = null;
}else if (Children.Count == 1)
{var fromPoints = new PointCollection();for (var i = 0; i < Children[0].Count; i++)
fromPoints.Add(new Point(0, 0));var toPoints = Children[0];
Points = GetCurrentPoints(fromPoints, toPoints, Progress);
}else{var rangePerSection = 100d / (Children.Count - 1);var fromIndex = Math.Min(Children.Count - 2, Convert.ToInt32(Math.Floor(Progress / rangePerSection)));
fromIndex = Math.Max(fromIndex, 0);var toIndex = fromIndex + 1;
PointCollection fromPoints;if (fromIndex == toIndex)
{
fromPoints = new PointCollection();for (var i = 0; i < Children[0].Count; i++)
fromPoints.Add(new Point(0, 0));
}else{
fromPoints = Children.ElementAt(fromIndex);
}var toPoints = Children.ElementAt(toIndex);
var percentage = (Progress / rangePerSection - fromIndex) * 100;
Points = GetCurrentPoints(fromPoints, toPoints, percentage);
}
}private PointCollection GetCurrentPoints(PointCollection fromPoints, PointCollection toPoints, double percentage)
{var result = new PointCollection();for (var i = 0;
i < Math.Min(fromPoints.Count, toPoints.Count);
i++)
{
var x = (1 - percentage / 100d) * fromPoints[i].X + percentage / 100d * toPoints[i].X;
var y = (1 - percentage / 100d) * fromPoints[i].Y + percentage / 100d * toPoints[i].Y;
result.Add(new Point(x, y));
}return result;
}#region DependencyProperties#endregion}3. 结语
如果将DoubleAnimation说成“对目标的Double属性做动画”,那PointAnimation可以说成“对目标的Point.X和Point.Y两个Double属性同时做动画”,ColorAnimation则是“对目标的Color.A、R、G、B四个Int属性同时做动画”。这样理解的话PointAnimation和ColorAnimation只不过是DoubleAnimation的延伸而已,进一步的说,通过DoubleAnimation应该可以延伸出所有类型属性的动画。不过我并不清楚怎么在UWP上自定义动画,只能通过本文的折衷方式扩展。虽然XAML需要写复杂些,但这样也有它的好处:
不需要了解太多Animation相关类的知识,只需要有依赖属性、绑定等基础知识就够了。
不会因为动画API的改变而更改,可以兼容WPF、Silverlight和UWP(大概吧,我没有真的在WPF上测试这些代码)。
-
代码足够简单,省去了计算TimeSpan及EasingFunction的步骤。 稍微修改下还可以做成泛型的
2. PointAnimation を拡張するAnimationBridge 808ed36a4929ba137db2b9ee76c79186
このとき、少し考え方を変える必要があります。 DoubleAnimation は次のように理解できます。次の図に示すように、Storyboard は TimeSpan を DoubleAnimation に渡し、DoubleAnimation はこの TimeSpan (場合によっては EasingFunction と組み合わせて) を使用してターゲット属性の現在の値を計算し、最終的にターゲット属性に渡します。
 🎜🎜この場合、計算されたDoubleを受け取ってから計算することもできますConverter を介してターゲットの PointCollection 値: 🎜🎜
🎜🎜この場合、計算されたDoubleを受け取ってから計算することもできますConverter を介してターゲットの PointCollection 値: 🎜🎜 🎜🎜この Converter に次のことを伝えるとします。受信した Double 値 (Progress という名前) が 0 の場合、PointCollection は {0,0 1,1...}、Progress が 100 の場合、PointCollection は {1,1 2,2...}、Progress が任意の場合これらの値の計算方法は :🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜 これで、TimeSpan から PointCollection への変換プロセスが完了しました。次に、XAML で定義されたそれを使用する方法があります。上記の PointCollectionAnimation を参照すると、追加のコンバーターがありますが、XAML は十分に簡潔である必要があります: 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜 最終的に、このコンバーターに
🎜🎜この Converter に次のことを伝えるとします。受信した Double 値 (Progress という名前) が 0 の場合、PointCollection は {0,0 1,1...}、Progress が 100 の場合、PointCollection は {1,1 2,2...}、Progress が任意の場合これらの値の計算方法は :🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜 これで、TimeSpan から PointCollection への変換プロセスが完了しました。次に、XAML で定義されたそれを使用する方法があります。上記の PointCollectionAnimation を参照すると、追加のコンバーターがありますが、XAML は十分に簡潔である必要があります: 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜 最終的に、このコンバーターに ProgressToPointCollectionBridge という名前を付けることにしました。 Polygon が Points を ProgressToPointCollectionBridge にバインドし、DoubleAnimation が ProgressToPointCollectionBridge.Progress を変更して、Points を変更していることがわかります。 XAML のシンプルさは非常に満足のいくもので、複数のポイントを操作する必要がある場合には、PointAnimation よりも大きな利点があります。 🎜🎜実行結果は次のとおりです: 🎜🎜 🎜🎜完全な XAML: 🎜 🎜rrreee 🎜🎜ProgressToPointCollectionBridge:🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜3. 結論🎜🎜DoubleAnimation が「ターゲットの Double プロパティをアニメーション化している」と言われる場合、PointAnimation は「ターゲットの Point の 2 つの Double プロパティをアニメーション化している」と言えます。 「Animation」、ColorAnimation は「ターゲットの Color.A、R、G、B の 4 つの Int プロパティを同時にアニメーション化します。」このように理解すると、PointAnimation と ColorAnimation は DoubleAnimation の拡張にすぎません。さらに、DoubleAnimation はあらゆる種類の属性のアニメーションを拡張できるはずです。ただし、UWP でアニメーションをカスタマイズする方法がわかりません。この記事の妥協的な方法で拡張するしかありません。 XAML はより複雑に記述する必要がありますが、次のような利点もあります。 🎜
🎜🎜完全な XAML: 🎜 🎜rrreee 🎜🎜ProgressToPointCollectionBridge:🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜3. 結論🎜🎜DoubleAnimation が「ターゲットの Double プロパティをアニメーション化している」と言われる場合、PointAnimation は「ターゲットの Point の 2 つの Double プロパティをアニメーション化している」と言えます。 「Animation」、ColorAnimation は「ターゲットの Color.A、R、G、B の 4 つの Int プロパティを同時にアニメーション化します。」このように理解すると、PointAnimation と ColorAnimation は DoubleAnimation の拡張にすぎません。さらに、DoubleAnimation はあらゆる種類の属性のアニメーションを拡張できるはずです。ただし、UWP でアニメーションをカスタマイズする方法がわかりません。この記事の妥協的な方法で拡張するしかありません。 XAML はより複雑に記述する必要がありますが、次のような利点もあります。 🎜- 🎜 アニメーション関連のクラスについて詳しく知る必要はありません。依存関係の属性とバインディングがあります。基本的な部分は待ちます。 🎜🎜
- 🎜 はアニメーション API の変更によって変更されることはなく、WPF、Silverlight、UWP と互換性があります (おそらく、これらのコードを WPF で実際にテストしたわけではありません)。 🎜🎜
- 🎜 コードは非常に単純で、TimeSpan と EasingFunction を計算する手順が不要です。 わずかに変更を加えれば、PointCollection 以外のデータ型のサポートを提供する汎用の
AnimationBridge <にすることもできます。 🎜🎜🎜🎜 前回の記事を踏まえると、UWP で提供されていない機能は将来的に代替メソッドで実装できると常々感じています。Binding と dependencyProperty はまさに UWP 開発者の強い味方です。 🎜🎜4. リファレンス🎜🎜SVG シェイプ モーフィングの仕組み🎜Gadal MetaSyllabus🎜
以上がShapeを使ったアニメーション例を詳しく解説の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

