YOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy while maintaining real-time processing speeds. This article explores the key innovations in YOLO v12, highlighting how it surpasses the previous versions while minimizing computational costs without compromising detection efficiency.
Table of contents
- What’s New in YOLO v12?
- Key Improvements Over Previous Versions
- Computational Efficiency Enhancements
- YOLO v12 Model Variants
- Let’s compare YOLO v11 and YOLO v12 Models
- Expert Opinions on YOLOv11 and YOLOv12
- Conclusion
What’s New in YOLO v12?
Previously, YOLO models relied on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for object detection due to their speed and efficiency. However, YOLO v12 makes use of attention mechanisms, a concept widely known and used in Transformer models which allow it to recognize patterns more effectively. While attention mechanisms have originally been slow for real-time object detection, YOLO v12 somehow successfully integrates them while maintaining YOLO’s speed, leading to an Attention-Centric YOLO framework.
Key Improvements Over Previous Versions
1. Attention-Centric Framework
YOLO v12 combines the power of attention mechanisms with CNNs, resulting in a model that is both faster and more accurate. Unlike its predecessors which relied solely on CNNs, YOLO v12 introduces optimized attention modules to improve object recognition without adding unnecessary latency.
2. Superior Performance Metrics
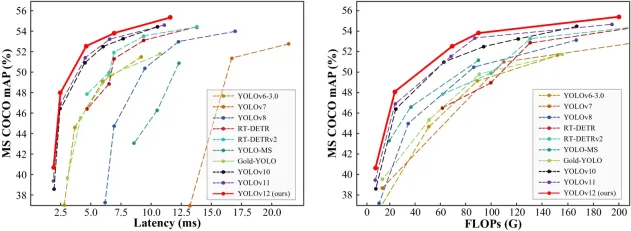
Comparing performance metrics across different YOLO versions and real-time detection models reveals that YOLO v12 achieves higher accuracy while maintaining low latency.
- The mAP (Mean Average Precision) values on datasets like COCO show YOLO v12 outperforming YOLO v11 and YOLO v10 while maintaining comparable speed.
- The model achieves a remarkable 40.6% accuracy (mAP) while processing images in just 1.64 milliseconds on an Nvidia T4 GPU. This performance is superior to YOLO v10 and YOLO v11 without sacrificing speed.
3. Outperforming Non-YOLO Models
YOLO v12 surpasses previous YOLO versions; it also outperforms other real-time object detection frameworks, such as RT-Det and RT-Det v2. These alternative models have higher latency yet fail to match YOLO v12’s accuracy.
Computational Efficiency Enhancements
One of the major concerns with integrating attention mechanisms into YOLO models was their high computational cost (Attention Mechanism) and memory inefficiency. YOLO v12 addresses these issues through several key innovations:
1. Flash Attention for Memory Efficiency
Traditional attention mechanisms consume a large amount of memory, making them impractical for real-time applications. YOLO v12 introduces Flash Attention, a technique that reduces memory consumption and speeds up inference time.
2. Area Attention for Lower Computation Cost
To further optimize efficiency, YOLO v12 employs Area Attention, which focuses only on relevant regions of an image instead of processing the entire feature map. This technique dramatically reduces computation costs while retaining accuracy.

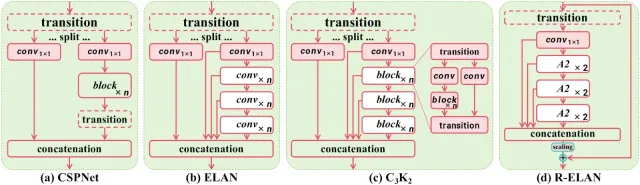
3. R-ELAN for Optimized Feature Processing
YOLO v12 also introduces R-ELAN (Re-Engineered ELAN), which optimizes feature propagation making the model more efficient in handling complex object detection tasks without increasing computational demands.
YOLO v12 Model Variants
YOLO v12 comes in five different variants, catering to different applications:
- N (Nano) & S (Small): Designed for real-time applications where speed is crucial.
- M (Medium): Balances accuracy and speed, suitable for general-purpose tasks.
- L (Large) & XL (Extra Large): Optimized for high-precision tasks where accuracy is prioritized over speed.
Also read:
- A Step-by-Step Introduction to the Basic Object Detection Algorithms (Part 1)
- A Practical Implementation of the Faster R-CNN Algorithm for Object Detection (Part 2)
- A Practical Guide to Object Detection using the Popular YOLO Framework – Part III (with Python codes)
Let’s compare YOLO v11 and YOLO v12 Models
We’ll be experimenting with YOLO v11 and YOLO v12 small models to understand their performance across various tasks like object counting, heatmaps, and speed estimation.
1. Object Counting
YOLO v11
import cv2
from ultralytics import solutions
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("highway.mp4")
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file"
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)), int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)))
# Define region points
region_points = [(20, 1500), (1080, 1500), (1080, 1460), (20, 1460)] # Lower rectangle region counting
# Video writer (MP4 format)
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("object_counting_output.mp4", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"), fps, (w, h))
# Init ObjectCounter
counter = solutions.ObjectCounter(
show=False, # Disable internal window display
region=region_points,
model="yolo11s.pt",
)
# Process video
while cap.isOpened():
success, im0 = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
im0 = counter.count(im0)
# Resize to fit screen (optional — scale down for large videos)
im0_resized = cv2.resize(im0, (640, 360)) # Adjust resolution as needed
# Show the resized frame
cv2.imshow("Object Counting", im0_resized)
video_writer.write(im0)
# Press 'q' to exit
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
video_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Output
YOLO v12
import cv2
from ultralytics import solutions
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("highway.mp4")
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file"
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)), int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)))
# Define region points
region_points = [(20, 1500), (1080, 1500), (1080, 1460), (20, 1460)] # Lower rectangle region counting
# Video writer (MP4 format)
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("object_counting_output.mp4", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"), fps, (w, h))
# Init ObjectCounter
counter = solutions.ObjectCounter(
show=False, # Disable internal window display
region=region_points,
model="yolo12s.pt",
)
# Process video
while cap.isOpened():
success, im0 = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
im0 = counter.count(im0)
# Resize to fit screen (optional — scale down for large videos)
im0_resized = cv2.resize(im0, (640, 360)) # Adjust resolution as needed
# Show the resized frame
cv2.imshow("Object Counting", im0_resized)
video_writer.write(im0)
# Press 'q' to exit
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
video_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Output
2. Heatmaps
YOLO v11
import cv2
from ultralytics import solutions
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("mall_arial.mp4")
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file"
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
# Video writer
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("heatmap_output_yolov11.mp4", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"), fps, (w, h))
# In case you want to apply object counting + heatmaps, you can pass region points.
# region_points = [(20, 400), (1080, 400)] # Define line points
# region_points = [(20, 400), (1080, 400), (1080, 360), (20, 360)] # Define region points
# region_points = [(20, 400), (1080, 400), (1080, 360), (20, 360), (20, 400)] # Define polygon points
# Init heatmap
heatmap = solutions.Heatmap(
show=True, # Display the output
model="yolo11s.pt", # Path to the YOLO11 model file
colormap=cv2.COLORMAP_PARULA, # Colormap of heatmap
# region=region_points, # If you want to do object counting with heatmaps, you can pass region_points
# classes=[0, 2], # If you want to generate heatmap for specific classes i.e person and car.
# show_in=True, # Display in counts
# show_out=True, # Display out counts
# line_width=2, # Adjust the line width for bounding boxes and text display
)
# Process video
while cap.isOpened():
success, im0 = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
im0 = heatmap.generate_heatmap(im0)
im0_resized = cv2.resize(im0, (w, h))
video_writer.write(im0_resized)
cap.release()
video_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Output
YOLO v12
import cv2
from ultralytics import solutions
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("mall_arial.mp4")
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file"
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
# Video writer
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("heatmap_output_yolov12.mp4", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"), fps, (w, h))
# In case you want to apply object counting + heatmaps, you can pass region points.
# region_points = [(20, 400), (1080, 400)] # Define line points
# region_points = [(20, 400), (1080, 400), (1080, 360), (20, 360)] # Define region points
# region_points = [(20, 400), (1080, 400), (1080, 360), (20, 360), (20, 400)] # Define polygon points
# Init heatmap
heatmap = solutions.Heatmap(
show=True, # Display the output
model="yolo12s.pt", # Path to the YOLO11 model file
colormap=cv2.COLORMAP_PARULA, # Colormap of heatmap
# region=region_points, # If you want to do object counting with heatmaps, you can pass region_points
# classes=[0, 2], # If you want to generate heatmap for specific classes i.e person and car.
# show_in=True, # Display in counts
# show_out=True, # Display out counts
# line_width=2, # Adjust the line width for bounding boxes and text display
)
# Process video
while cap.isOpened():
success, im0 = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
im0 = heatmap.generate_heatmap(im0)
im0_resized = cv2.resize(im0, (w, h))
video_writer.write(im0_resized)
cap.release()
video_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Output
3. Speed Estimation
YOLO v11
import cv2
from ultralytics import solutions
import numpy as np
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("cars_on_road.mp4")
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file"
# Capture video properties
w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
# Video writer
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("speed_management_yolov11.mp4", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"), fps, (w, h))
# Define speed region points (adjust for your video resolution)
speed_region = [(300, h - 200), (w - 100, h - 200), (w - 100, h - 270), (300, h - 270)]
# Initialize SpeedEstimator
speed = solutions.SpeedEstimator(
show=False, # Disable internal window display
model="yolo11s.pt", # Path to the YOLO model file
region=speed_region, # Pass region points
# classes=[0, 2], # Optional: Filter specific object classes (e.g., cars, trucks)
# line_width=2, # Optional: Adjust the line width
)
# Process video
while cap.isOpened():
success, im0 = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
# Estimate speed and draw bounding boxes
out = speed.estimate_speed(im0)
# Draw the speed region on the frame
cv2.polylines(out, [np.array(speed_region)], isClosed=True, color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
# Resize the frame to fit the screen
im0_resized = cv2.resize(out, (1280, 720)) # Resize for better screen fit
# Show the resized frame
cv2.imshow("Speed Estimation", im0_resized)
video_writer.write(out)
# Press 'q' to exit
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
video_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Output
YOLO v12
import cv2
from ultralytics import solutions
import numpy as np
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("cars_on_road.mp4")
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file"
# Capture video properties
w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
# Video writer
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("speed_management_yolov12.mp4", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v"), fps, (w, h))
# Define speed region points (adjust for your video resolution)
speed_region = [(300, h - 200), (w - 100, h - 200), (w - 100, h - 270), (300, h - 270)]
# Initialize SpeedEstimator
speed = solutions.SpeedEstimator(
show=False, # Disable internal window display
model="yolo12s.pt", # Path to the YOLO model file
region=speed_region, # Pass region points
# classes=[0, 2], # Optional: Filter specific object classes (e.g., cars, trucks)
# line_width=2, # Optional: Adjust the line width
)
# Process video
while cap.isOpened():
success, im0 = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
# Estimate speed and draw bounding boxes
out = speed.estimate_speed(im0)
# Draw the speed region on the frame
cv2.polylines(out, [np.array(speed_region)], isClosed=True, color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
# Resize the frame to fit the screen
im0_resized = cv2.resize(out, (1280, 720)) # Resize for better screen fit
# Show the resized frame
cv2.imshow("Speed Estimation", im0_resized)
video_writer.write(out)
# Press 'q' to exit
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
video_writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Output
Also Read: Top 30+ Computer Vision Models For 2025
Expert Opinions on YOLOv11 and YOLOv12
Muhammad Rizwan Munawar — Computer Vision Engineer at Ultralytics
“YOLOv12 introduces flash attention, which enhances accuracy, but it requires careful CUDA setup. It’s a solid step forward, especially for complex detection tasks, though YOLOv11 remains faster for real-time needs. In short, choose YOLOv12 for accuracy and YOLOv11 for speed.”
Linkedin Post – Is YOLOv12 really a state-of-the-art model? ?
Muhammad Rizwan, recently tested YOLOv11 and YOLOv12 side by side to break down their real-world performance. His findings highlight the trade-offs between the two models:
- Frames Per Second (FPS): YOLOv11 maintains an average of 40 FPS, while YOLOv12 lags behind at 30 FPS. This makes YOLOv11 the better choice for real-time applications where speed is critical, such as traffic monitoring or live video feeds.
- Training Time: YOLOv12 takes about 20% longer to train than YOLOv11. On a small dataset with 130 training images and 43 validation images, YOLOv11 completed training in 0.009 hours, while YOLOv12 needed 0.011 hours. While this might seem minor for small datasets, the difference becomes significant for larger-scale projects.
- Accuracy: Both models achieved similar accuracy after fine-tuning for 10 epochs on the same dataset. YOLOv12 didn’t dramatically outperform YOLOv11 in terms of accuracy, suggesting the newer model’s improvements lie more in architectural enhancements than raw detection precision.
- Flash Attention: YOLOv12 introduces flash attention, a powerful mechanism that speeds up and optimizes attention layers. However, there’s a catch — this feature isn’t natively supported on the CPU, and enabling it with CUDA requires careful version-specific setup. For teams without powerful GPUs or those working on edge devices, this can become a roadblock.
The PC specifications used for testing:
- GPU: NVIDIA RTX 3050
- CPU: Intel Core-i5-10400 @2.90GHz
- RAM: 64 GB
The model specifications:
- Model = YOLO11n.pt and YOLOv12n.pt
- Image size = 640 for inference
Conclusion
YOLO v12 marks a significant leap forward in real-time object detection, combining CNN speed with Transformer-like attention mechanisms. With improved accuracy, lower computational costs, and a range of model variants, YOLO v12 is poised to redefine the landscape of real-time vision applications. Whether for autonomous vehicles, security surveillance, or medical imaging, YOLO v12 sets a new standard for real-time object detection efficiency.
What’s Next?
- YOLO v13 Possibilities: Will future versions push the attention mechanisms even further?
- Edge Device Optimization: Can Flash Attention or Area Attention be optimized for lower-power devices?
To help you better understand the differences, I’ve attached some code snippets and output results in the comparison section. These examples illustrate how both YOLOv11 and YOLOv12 perform in real-world scenarios, from object counting to speed estimation and heatmaps. I’m excited to see how you guys perceive this new release! Are the improvements in accuracy and attention mechanisms enough to justify the trade-offs in speed? Or do you think YOLOv11 still holds its ground for most applications?
以上がオブジェクト検出にYolo V12を使用する方法は?の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。
 ほとんどが使用されています10 Power BIチャート - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 pm 12:05 PM
ほとんどが使用されています10 Power BIチャート - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 pm 12:05 PMMicrosoft PowerBIチャートでデータ視覚化の力を活用する 今日のデータ駆動型の世界では、複雑な情報を非技術的な視聴者に効果的に伝えることが重要です。 データの視覚化は、このギャップを橋渡しし、生データを変換するi
 AIのエキスパートシステムApr 16, 2025 pm 12:00 PM
AIのエキスパートシステムApr 16, 2025 pm 12:00 PMエキスパートシステム:AIの意思決定力に深く飛び込みます 医療診断から財務計画まで、あらゆることに関する専門家のアドバイスにアクセスできることを想像してください。 それが人工知能の専門家システムの力です。 これらのシステムはプロを模倣します
 3人の最高の雰囲気コーダーがこのAI革命をコードで分解するApr 16, 2025 am 11:58 AM
3人の最高の雰囲気コーダーがこのAI革命をコードで分解するApr 16, 2025 am 11:58 AMまず第一に、これがすぐに起こっていることは明らかです。さまざまな企業が、現在AIによって書かれているコードの割合について話しており、これらは迅速なクリップで増加しています。すでに多くの仕事の移動があります
 滑走路AIのGen-4:AIモンタージュはどのように不条理を超えることができますかApr 16, 2025 am 11:45 AM
滑走路AIのGen-4:AIモンタージュはどのように不条理を超えることができますかApr 16, 2025 am 11:45 AM映画業界は、デジタルマーケティングからソーシャルメディアまで、すべてのクリエイティブセクターとともに、技術的な岐路に立っています。人工知能が視覚的なストーリーテリングのあらゆる側面を再構築し始め、エンターテイメントの風景を変え始めたとき
 5日間のISRO AI無料コースを登録する方法は? - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 am 11:43 AM
5日間のISRO AI無料コースを登録する方法は? - 分析VidhyaApr 16, 2025 am 11:43 AMISROの無料AI/MLオンラインコース:地理空間技術の革新へのゲートウェイ インド宇宙研究機関(ISRO)は、インドのリモートセンシング研究所(IIRS)を通じて、学生と専門家に素晴らしい機会を提供しています。
 AIのローカル検索アルゴリズムApr 16, 2025 am 11:40 AM
AIのローカル検索アルゴリズムApr 16, 2025 am 11:40 AMローカル検索アルゴリズム:包括的なガイド 大規模なイベントを計画するには、効率的なワークロード分布が必要です。 従来のアプローチが失敗すると、ローカル検索アルゴリズムは強力なソリューションを提供します。 この記事では、Hill ClimbingとSimulについて説明します
 OpenaiはGPT-4.1でフォーカスをシフトし、コーディングとコスト効率を優先しますApr 16, 2025 am 11:37 AM
OpenaiはGPT-4.1でフォーカスをシフトし、コーディングとコスト効率を優先しますApr 16, 2025 am 11:37 AMこのリリースには、GPT-4.1、GPT-4.1 MINI、およびGPT-4.1 NANOの3つの異なるモデルが含まれており、大規模な言語モデルのランドスケープ内のタスク固有の最適化への動きを示しています。これらのモデルは、ようなユーザー向けインターフェイスをすぐに置き換えません
 プロンプト:ChatGptは偽のパスポートを生成しますApr 16, 2025 am 11:35 AM
プロンプト:ChatGptは偽のパスポートを生成しますApr 16, 2025 am 11:35 AMChip Giant Nvidiaは、月曜日に、AI Supercomputersの製造を開始すると述べました。これは、大量のデータを処理して複雑なアルゴリズムを実行できるマシンを初めて初めて米国内で実行します。発表は、トランプSI大統領の後に行われます


ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

AI Hentai Generator
AIヘンタイを無料で生成します。

人気の記事

ホットツール

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser は、オンライン試験を安全に受験するための安全なブラウザ環境です。このソフトウェアは、あらゆるコンピュータを安全なワークステーションに変えます。あらゆるユーティリティへのアクセスを制御し、学生が無許可のリソースを使用するのを防ぎます。

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
このプロジェクトは osdn.net/projects/mingw に移行中です。引き続きそこでフォローしていただけます。 MinGW: GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) のネイティブ Windows ポートであり、ネイティブ Windows アプリケーションを構築するための自由に配布可能なインポート ライブラリとヘッダー ファイルであり、C99 機能をサポートする MSVC ランタイムの拡張機能が含まれています。すべての MinGW ソフトウェアは 64 ビット Windows プラットフォームで実行できます。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) は、非常に脆弱な PHP/MySQL Web アプリケーションです。その主な目的は、セキュリティ専門家が法的環境でスキルとツールをテストするのに役立ち、Web 開発者が Web アプリケーションを保護するプロセスをより深く理解できるようにし、教師/生徒が教室環境で Web アプリケーションを教え/学習できるようにすることです。安全。 DVWA の目標は、シンプルでわかりやすいインターフェイスを通じて、さまざまな難易度で最も一般的な Web 脆弱性のいくつかを実践することです。このソフトウェアは、

PhpStorm Mac バージョン
最新(2018.2.1)のプロフェッショナル向けPHP統合開発ツール







