ホームページ >Java >&#&チュートリアル >ケーススタディ: 接続された円の問題
ケーススタディ: 接続された円の問題
- PHPzオリジナル
- 2024-08-10 06:52:321098ブラウズ
接続された円の問題は、2 次元平面内のすべての円が接続されているかどうかを判断することです。この問題は、深さ優先トラバーサルを使用して解決できます。 DFS アルゴリズムには多くの用途があります。このセクションでは、DFS アルゴリズムを適用して、接続された円の問題を解決します。
接続された円の問題では、2 次元平面内のすべての円が接続されているかどうかを判断します。すべての円が接続されている場合、下図 (a) に示すように、塗りつぶされた円として描画されます。それ以外の場合は、下図 (b) に示すように、埋められません。
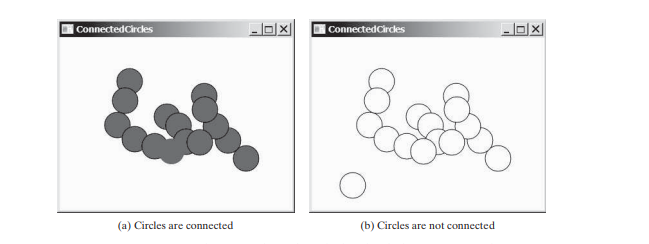
現在円で覆われていない空白の領域でユーザーがマウスをクリックして円を作成できるプログラムを作成します。円を追加すると、円が接続されている場合は塗りつぶされ、そうでない場合は塗りつぶされません。
問題をモデル化するグラフを作成します。各円はグラフの頂点です。 2 つの円が重なると接続されます。グラフに DFS を適用し、深さ優先検索ですべての頂点が見つかった場合、グラフは接続されます。
プログラムは以下のコードで与えられます。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Point2D;
import javafx.scene.Node;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ConnectedCircles extends Application {
@Override // Override the start method in the Application class
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
// Create a scene and place it in the stage
Scene scene = new Scene(new CirclePane(), 450, 350);
primaryStage.setTitle("ConnectedCircles"); // Set the stage title
primaryStage.setScene(scene); // Place the scene in the stage
primaryStage.show(); // Display the stage
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application.launch(args);
}
/** Pane for displaying circles */
class CirclePane extends Pane {
public CirclePane() {
this.setOnMouseClicked(e -> {
if (!isInsideACircle(new Point2D(e.getX(), e.getY()))) {
// Add a new circle
getChildren().add(new Circle(e.getX(), e.getY(), 20));
colorIfConnected();
}
});
}
/** Returns true if the point is inside an existing circle */
private boolean isInsideACircle(Point2D p) {
for (Node circle: this.getChildren())
if (circle.contains(p))
return true;
return false;
}
/** Color all circles if they are connected */
private void colorIfConnected() {
if (getChildren().size() == 0)
return; // No circles in the pane
// Build the edges
java.util.List<AbstractGraph.Edge> edges = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < getChildren().size(); i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < getChildren().size(); j++)
if (overlaps((Circle)(getChildren().get(i)), (Circle)(getChildren().get(j)))) {
edges.add(new AbstractGraph.Edge(i, j));
edges.add(new AbstractGraph.Edge(j, i));
}
// Create a graph with circles as vertices
Graph<Node> graph = new UnweightedGraph<>((java.util.List<Node>)getChildren(), edges);
AbstractGraph<Node>.Tree tree = graph.dfs(0); // a DFS tree
boolean isAllCirclesConnected = getChildren().size() == tree.getNumberOfVerticesFound();
for (Node circle: getChildren()) {
if (isAllCirclesConnected) { // All circles are connected
((Circle)circle).setFill(Color.RED);
}
else {
((Circle)circle).setStroke(Color.BLACK);
((Circle)circle).setFill(Color.WHITE);
}
}
}
}
public static boolean overlaps(Circle circle1, Circle circle2) {
return new Point2D(circle1.getCenterX(), circle1.getCenterY()).distance(circle2.getCenterX(), circle2.getCenterY()) <= circle1.getRadius() + circle2.getRadius();
}
}
JavaFX Circle クラスには、円の中心位置と半径を指定するデータ フィールド x、y、および radius が含まれています。 。また、点が円内にあるかどうかをテストするための contains も定義します。 overlaps メソッド (76 ~ 80 行目) は、2 つの円が重なっているかどうかをチェックします。
ユーザーが既存の円の外側でマウスをクリックすると、マウスポイントを中心に新しい円が作成され、その円がペインに追加されます (行 26)。
円が接続されているかどうかを検出するために、プログラムはグラフを作成します (行 46 ~ 59)。円はグラフの頂点です。エッジは 49 ~ 55 行目で構築されます。 2 つの円の頂点が重なっている場合、それらは接続されます (51 行目)。グラフの DFS はツリーになります (行 60)。ツリーの getNumberOfVerticesFound() は、検索された頂点の数を返します。円の数と等しい場合、すべての円が接続されます (61 ~ 62 行目)。
以上がケーススタディ: 接続された円の問題の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。

