Maison >développement back-end >Tutoriel Python >Vous apprendre étape par étape comment utiliser Flask pour créer un moteur de recherche ES (Pratique)
Vous apprendre étape par étape comment utiliser Flask pour créer un moteur de recherche ES (Pratique)
- Go语言进阶学习avant
- 2023-07-25 17:24:521254parcourir
Commencez à utiliser Flask Build ES Search.

Fichier de configuration
#coding:utf-8
import os
DB_USERNAME = 'root'
DB_PASSWORD = None # 如果没有密码的话
DB_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
DB_PORT = '3306'
DB_NAME = 'flask_es'
class Config:
SECRET_KEY ="随机字符" # 随机 SECRET_KEY
SQLALCHEMY_COMMIT_ON_TEARDOWN = True # 自动提交
SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS = True # 自动sql
DEBUG = True # debug模式
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI = 'mysql+pymysql://%s:%s@%s:%s/%s' % (DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD,DB_HOST, DB_PORT, DB_NAME) #数据库URL
MAIL_SERVER = 'smtp.qq.com'
MAIL_POST = 465
MAIL_USERNAME = '3417947630@qq.com'
MAIL_PASSWORD = '邮箱授权码'
FLASK_MAIL_SUBJECT_PREFIX='M_KEPLER'
FLASK_MAIL_SENDER=MAIL_USERNAME # 默认发送人
# MAIL_USE_SSL = True
MAIL_USE_TLS = False
MAIL_DEBUG = False
ENABLE_THREADS=True
relativement simple. Bien sûr, la connexion à la base de données n'est pas nécessaire pour le projet en cours, j'utilise simplement Mysql à des fins auxiliaires. Pour les bases de données, ES suffit. Ensuite, la notification par e-mail dépendra des besoins personnels.
# coding=utf-8
import os
import logging
import logging.config as log_conf
import datetime
import coloredlogs
coloredlogs.DEFAULT_FIELD_STYLES = {'asctime': {'color': 'green'}, 'hostname': {'color': 'magenta'}, 'levelname': {'color': 'magenta', 'bold': False}, 'name': {'color': 'green'}}
log_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + '/logs'
if not os.path.exists(log_dir):
os.mkdir(log_dir)
today = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
log_path = os.path.join(log_dir, today + ".log")
log_config = {
'version': 1.0,
# 格式输出
'formatters': {
'colored_console': {
'format': "%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s",
'datefmt': '%H:%M:%S'
},
'detail': {
'format': '%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
'datefmt': "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" #时间格式
},
},
'handlers': {
'console': {
'class': 'logging.StreamHandler',
'level': 'DEBUG',
'formatter': 'colored_console'
},
'file': {
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler',
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 1024,
'backupCount': 1,
'filename': log_path,
'level': 'INFO',
'formatter': 'detail', #
'encoding': 'utf-8', # utf8 编码 防止出现编码错误
},
},
'loggers': {
'logger': {
'handlers': ['console'],
'level': 'DEBUG',
},
}
}
log_conf.dictConfig(log_config)
log_v = logging.getLogger('log')
coloredlogs.install(level='DEBUG', logger=log_v)
# # Some examples.
# logger.debug("this is a debugging message")
# logger.info("this is an informational message")
# logger.warning("this is a warning message")
# logger.error("this is an error message")
# logger.critical("this is a critical message") .log
.log 
路由
对于 Flask 项目而言, 蓝图和路由会让整个项目更具观赏性(当然指的是代码的阅读)。
这里我采用两个分支来作为数据支撑,一个是 Math 入口,另一个是 Baike 入口,数据的来源是基于上一篇的百度百科爬虫所得,根据 深度优先 的爬取方式抓取后放入 ES 中。
# coding:utf8 from flask import Flask from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy from app.config.config import Config from flask_mail import Mail from flask_wtf.csrf import CSRFProtect app = Flask(__name__,template_folder='templates',static_folder='static') app.config.from_object(Config) db = SQLAlchemy(app) db.init_app(app) csrf = CSRFProtect(app) mail = Mail(app) # 不要在生成db之前导入注册蓝图。 from app.home.baike import baike as baike_blueprint from app.home.math import math as math_blueprint from app.home.home import home as home_blueprint app.register_blueprint(home_blueprint) app.register_blueprint(math_blueprint,url_prefix="/math") app.register_blueprint(baike_blueprint,url_prefix="/baike")
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from flask import Blueprint
baike = Blueprint("baike", __name__)
from app.home.baike import views# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from flask import Blueprint
math = Blueprint("math", __name__)
from app.home.math import views声明路由并在 __init__ 文件中初始化
下面来看看路由的实现(以Baike为例)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os
from flask_paginate import Pagination, get_page_parameter
from app.Logger.logger import log_v
from app.elasticsearchClass import elasticSearch
from app.home.forms import SearchForm
from app.home.baike import baike
from flask import request, jsonify, render_template, redirect
baike_es = elasticSearch(index_type="baike_data",index_name="baike")
@baike.route("/")
def index():
searchForm = SearchForm()
return render_template('baike/index.html', searchForm=searchForm)
@baike.route("/search", methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def baikeSearch():
search_key = request.args.get("b", default=None)
if search_key:
searchForm = SearchForm()
log_v.error("[+] Search Keyword: " + search_key)
match_data = baike_es.search(search_key,count=30)
# 翻页
PER_PAGE = 10
page = request.args.get(get_page_parameter(), type=int, default=1)
start = (page - 1) * PER_PAGE
end = start + PER_PAGE
total = 30
print("最大数据总量:", total)
pagination = Pagination(page=page, start=start, end=end, total=total)
context = {
'match_data': match_data["hits"]["hits"][start:end],
'pagination': pagination,
'uid_link': "/baike/"
}
return render_template('data.html', q=search_key, searchForm=searchForm, **context)
return redirect('home.index')
@baike.route('/<uid>')
def baikeSd(uid):
base_path = os.path.abspath('app/templates/s_d/')
old_file = os.listdir(base_path)[0]
old_path = os.path.join(base_path, old_file)
file_path = os.path.abspath('app/templates/s_d/{}.html'.format(uid))
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
log_v.debug("[-] File does not exist, renaming !!!")
os.rename(old_path, file_path)
match_data = baike_es.id_get_doc(uid=uid)
return render_template('s_d/{}.html'.format(uid), match_data=match_data)可以看到我们成功的将 elasticSearch 类初始化并且进行了数据搜索。
我们使用了 Flask 的分页插件进行分页并进行了单页数量的限制,根据 Uid 来跳转到详情页中。
细心的小伙伴会发现我这里用了个小技巧
@baike.route('/<uid>')
def baikeSd(uid):
base_path = os.path.abspath('app/templates/s_d/')
old_file = os.listdir(base_path)[0]
old_path = os.path.join(base_path, old_file)
file_path = os.path.abspath('app/templates/s_d/{}.html'.format(uid))
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
log_v.debug("[-] File does not exist, renaming !!!")
os.rename(old_path, file_path)
match_data = baike_es.id_get_doc(uid=uid)
return render_template('s_d/{}.html'.format(uid), match_data=match_data)以此来保证存放详情页面的模板中始终只保留一个 html 文件。

项目启动
一如既往的采用 flask_script 作为项目的启动方案,确实方便。
# coding:utf8
from app import app
from flask_script import Manager, Server
manage = Manager(app)
# 启动命令
manage.add_command("runserver", Server(use_debugger=True))
if __name__ == "__main__":
manage.run()黑窗口键入
python manage.py runserver
就可以启动项目,默认端口 5000,访问 http://127.0.0.1:5000
使用gunicorn启动
pip install gunicorn
#encoding:utf-8 import multiprocessing from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all() # 并行工作进程数 workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 2 + 1 debug = True reload = True # 自动重新加载 loglevel = 'debug' # 指定每个工作者的线程数 threads = 2 # 转发为监听端口8000 bind = '0.0.0.0:5001' # 设置守护进程,将进程交给supervisor管理 daemon = 'false' # 工作模式协程 worker_class = 'gevent' # 设置最大并发量 worker_connections = 2000 # 设置进程文件目录 pidfile = 'log/gunicorn.pid' logfile = 'log/debug.log' # 设置访问日志和错误信息日志路径 accesslog = 'log/gunicorn_acess.log' errorlog = 'log/gunicorn_error.log'
利用配置文件来启动 gunicorn 服务器
gunicorn -c gconfig.py manage:app
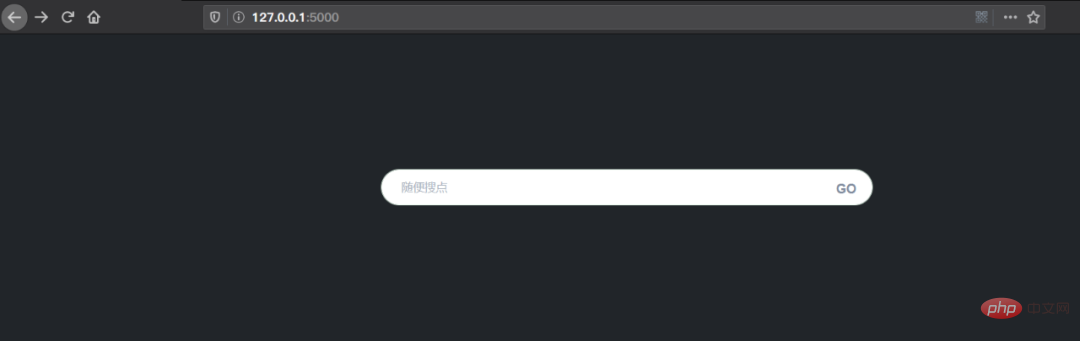
项目截图


Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Flask-Restful : meilleures pratiques pour créer des API RESTful en Python
- Flask-WTF : Ajouter un formulaire à votre application Flask
- Flask-RESTful : créer des API RESTful à l'aide de Python
- Flask-Cors : résoudre les problèmes inter-domaines dans les applications Web Python
- Programmation serveur Python : créer une API RESTful avec Flask
- Programmation serveur Python : utilisation de Flask-Login pour implémenter la connexion utilisateur

