Maison >base de données >tutoriel mysql >Un article pour parler du mécanisme d'implémentation interne du verrouillage Mysql
Un article pour parler du mécanisme d'implémentation interne du verrouillage Mysql
- 青灯夜游avant
- 2022-09-13 19:45:402687parcourir
本篇文章带大家聊聊Mysql锁的内部实现机制,希望对大家有所帮助。

注:所列举代码皆出自Mysql-5.6
虽然现在关系型数据库越来越相似,但其背后的实现机制可能大相径庭。实际使用方面,因为SQL语法规范的存在使得我们熟悉多种关系型数据库并非难事,但是有多少种数据库可能就有多少种锁的实现方法。
Microsoft Sql Server2005之前只提供页锁,直到2005版本才开始支持乐观并发、悲观并发,乐观模式下允许实现行级别锁,在Sql Server的设计中锁是一种稀缺资源,锁的数量越多,开销就越大,为了避免因为锁的数量快速攀升导致性能断崖式下跌,其支持一种称为锁升级的机制,一旦行锁升级为页锁,并发性能就又回到原点。
事实上,即使在同一个数据库,不同的执行引擎对锁这一功能的诠释依然是百家争鸣。对于MyISAM而言仅仅支持表锁,并发读取尚可,并发修改可就捉襟见肘了。Innodb则和Oracle非常相似,提供非锁定一致性读取、行锁支持,与Sql Server明显不同的是随着锁总数的上升,Innodb仅仅只需要付出一点点代价。
行锁结构
Innodb支持行锁,且对于锁的描述并不会存在特别大的开销。因此不需要锁升级这一机制作为大量锁导致性能下降之后的抢救措施。
摘自lock0priv.h文件,Innodb对于行锁的定义如下:
/** Record lock for a page */
struct lock_rec_t {
/* space id */
ulint space;
/* page number */
ulint page_no;
/**
* number of bits in the lock bitmap;
* NOTE: the lock bitmap is placed immediately after the lock struct
*/
ulint n_bits;
};
不难看出虽然并发控制可以细化到行级别,但是锁以页的粒度组织管理。Innodb的设计中通过space id、page number两个必要条件就可以确定唯一一个数据页,n_bits表示描述该页行锁信息需要多少bit位。
同一数据页中每条记录都分配唯一的连续的递增序号:heap_no,若要知道某一行记录是否上锁,则只需要判断位图heap_no位置的数字是否为一即可。由于lock bitmap根据数据页的记录数量进行内存空间分配的,因此没有显式定义,且该页记录可能还会继续增加,因此预留了LOCK_PAGE_BITMAP_MARGIN大小的空间。
/** * Safety margin when creating a new record lock: this many extra records * can be inserted to the page without need to create a lock with * a bigger bitmap */ #define LOCK_PAGE_BITMAP_MARGIN 64
假设space id = 20,page number = 100的数据页目前有160条记录,heap_no为2、3、4的记录已经被锁,则对应的lock_rec_t结构与数据页应该被这样刻画:
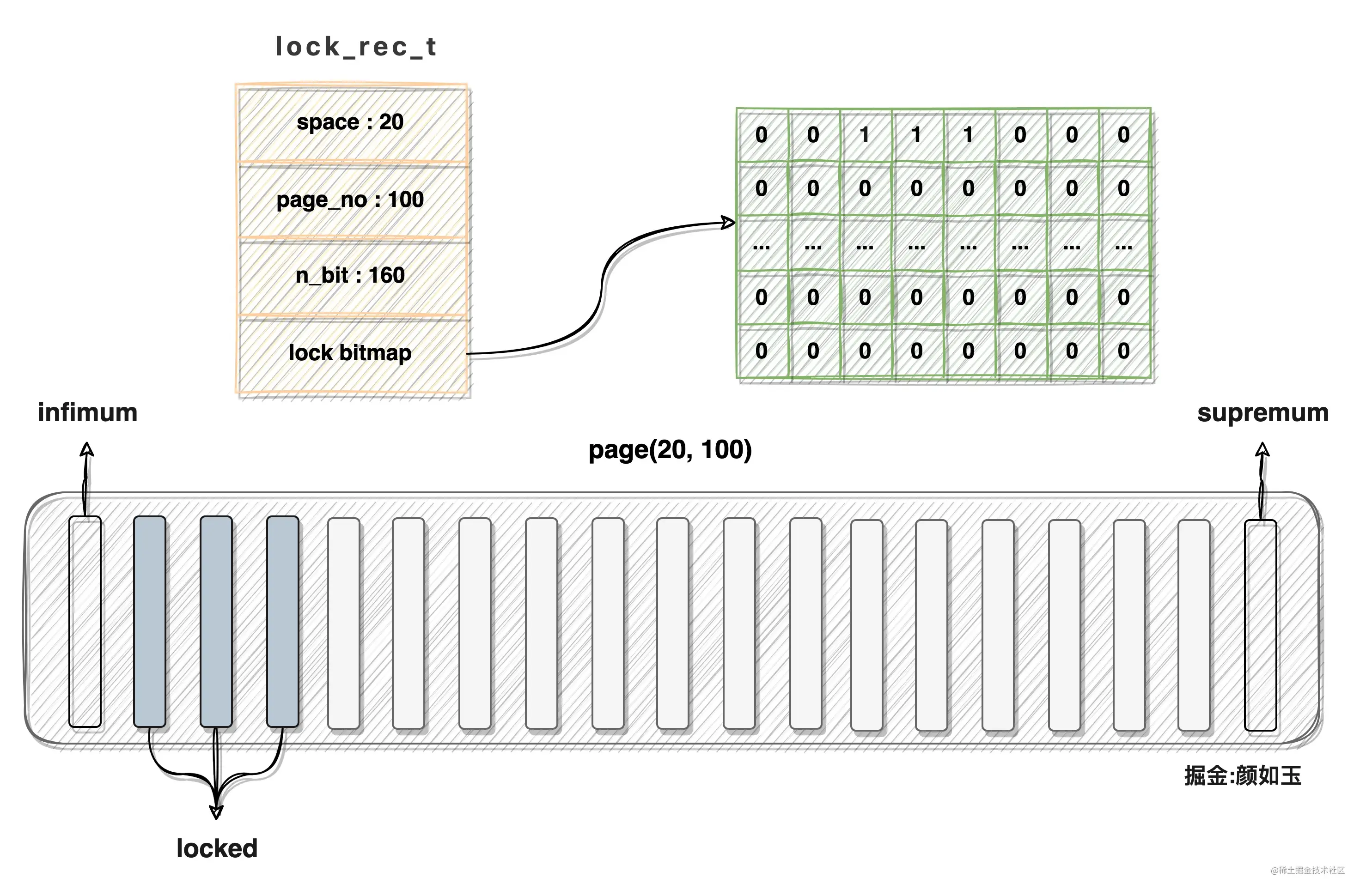
注:
- 内存中的lock bitmap应该是线性分布的,图中所示二维结构是为了方便描述
- bitmap与lock_rec_t结构是一块连续内存,图中引用关系也是绘图需要
可以看到该页对应的bitmap第二三四位置全部置一,描述一个数据页行锁所消耗内存从感官上相当有限,那具体占用多少呢?我们可以计算一下:
160 / 8 + 8 + 1 = 29byte。
- 160条记录对应160bit
- +8是因为需要预留出64bit
- +1是因为源码中还预留了1字节
这里还额外+1,应该是为了避免因为整除导致的结果数值偏小的问题。假如是161条记录如果不+1则计算出来的20byte不够描述所有记录的锁信息(不动用预留位)。
摘自lock0priv.h文件:
/* lock_rec_create函数代码片段 */
n_bits = page_dir_get_n_heap(page) + LOCK_PAGE_BITMAP_MARGIN;
n_bytes = 1 + n_bits / 8;
/* 注意这里是分配的连续内存 */
lock = static_cast<lock_t>(
mem_heap_alloc(trx->lock.lock_heap, sizeof(lock_t) + n_bytes)
);
/**
* Gets the number of records in the heap.
* @return number of user records
*/
UNIV_INLINE ulint page_dir_get_n_heap(const page_t* page)
{
return(page_header_get_field(page, PAGE_N_HEAP) & 0x7fff);
}</lock_t>
表锁结构
Innodb还支持表锁,表锁可分为两大类:意向锁,自增锁其数据结构定义如下:
摘自lock0priv.h文件
struct lock_table_t {
/* database table in dictionary cache */
dict_table_t* table;
/* list of locks on the same table */
UT_LIST_NODE_T(lock_t) locks;
};
摘自ut0lst.h文件
struct ut_list_node {
/* pointer to the previous node, NULL if start of list */
TYPE* prev;
/* pointer to next node, NULL if end of list */
TYPE* next;
};
#define UT_LIST_NODE_T(TYPE) ut_list_node<type></type>
事务中锁的描述
上述lock_rec_t、lock_table_t结构只是单独的定义,锁产生于事务之中,因此每个事务对应的行锁、表锁会有一个相应的锁的结构,其定义如下:
摘自lock0priv.h文件
/** Lock struct; protected by lock_sys->mutex */
struct lock_t {
/* transaction owning the lock */
trx_t* trx;
/* list of the locks of the transaction */
UT_LIST_NODE_T(lock_t) trx_locks;
/**
* lock type, mode, LOCK_GAP or LOCK_REC_NOT_GAP,
* LOCK_INSERT_INTENTION, wait flag, ORed
*/
ulint type_mode;
/* hash chain node for a record lock */
hash_node_t hash;
/*!<p> lock_t是根据每个事务每个页(或表)来定义的,但是一个事务往往涉及到多个页,因此需要链表<strong>trx_locks</strong>串联起一个事务相关的所有锁信息。除了需要根据事务查询到所有锁信息,实际场景还要求系统必须能够快速高效的检测出某个行记录是否已经上锁。因此必须有一个全局变量支持对行记录进行锁信息的查询。Innodb选择了哈希表,其定义如下:</p><p> 摘自<strong>lock0lock.h</strong>文件</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">/** The lock system struct */
struct lock_sys_t {
/* Mutex protecting the locks */
ib_mutex_t mutex;
/* 就是这里: hash table of the record locks */
hash_table_t* rec_hash;
/* Mutex protecting the next two fields */
ib_mutex_t wait_mutex;
/**
* Array of user threads suspended while waiting forlocks within InnoDB,
* protected by the lock_sys->wait_mutex
*/
srv_slot_t* waiting_threads;
/*
* highest slot ever used in the waiting_threads array,
* protected by lock_sys->wait_mutex
*/
srv_slot_t* last_slot;
/**
* TRUE if rollback of all recovered transactions is complete.
* Protected by lock_sys->mutex
*/
ibool rollback_complete;
/* Max wait time */
ulint n_lock_max_wait_time;
/**
* Set to the event that is created in the lock wait monitor thread.
* A value of 0 means the thread is not active
*/
os_event_t timeout_event;
/* True if the timeout thread is running */
bool timeout_thread_active;
};函数lock_sys_create在database start之际负责初始化lock_sys_t结构。rec_hash的hash slot数量由srv_lock_table_size变量决定。rec_hash哈希表的key值通过页的space id,page number计算得出。
摘自lock0lock.ic、ut0rnd.ic 文件
/**
* Calculates the fold value of a page file address: used in inserting or
* searching for a lock in the hash table.
*
* @return folded value
*/
UNIV_INLINE ulint lock_rec_fold(ulint space, ulint page_no)
{
return(ut_fold_ulint_pair(space, page_no));
}
/**
* Folds a pair of ulints.
*
* @return folded value
*/
UNIV_INLINE ulint ut_fold_ulint_pair(ulint n1, ulint n2)
{
return (
(
(((n1 ^ n2 ^ UT_HASH_RANDOM_MASK2) <p> 这将意味着无法提供一个手段使得我们可以直接得知某一行是否上锁。而是应该先通过其所在的页得到space id、page number通过<strong>lock_rec_fold</strong>函数得出key值而后经过hash查询得到lock_rec_t,而后根据heap_no扫描bit map,最终确定锁信息。<strong>lock_rec_get_first</strong>函数实现了上述逻辑:</p><p> 这里返回的其实是<strong>lock_t</strong>对象,摘自<strong>lock0lock.cc</strong>文件</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">/**
* Gets the first explicit lock request on a record.
*
* @param block : block containing the record
* @param heap_no : heap number of the record
*
* @return first lock, NULL if none exists
*/
UNIV_INLINE lock_t* lock_rec_get_first(const buf_block_t* block, ulint heap_no)
{
lock_t* lock;
ut_ad(lock_mutex_own());
for (lock = lock_rec_get_first_on_page(block); lock;
lock = lock_rec_get_next_on_page(lock)
) {
if (lock_rec_get_nth_bit(lock, heap_no)) {
break;
}
}
return(lock);
}锁维护以页的粒度,不是一个最高效直接的方式,明显的时间换空间,这种设计使得锁的开销很小。某一事务对任一行上锁的开销都是一样的,锁数量的上升也不会带来额外的内存消耗。
每个事务都对应一个trx_t的内存对象,其中保存着该事务锁信息链表和正在等待的锁信息。因此存在如下两种途径对锁进行查询:
- 根据事务: 通过trx_t对象的trx_locks链表,再通过lock_t对象中的trx_locks遍历可得某事务持有、等待的所有锁信息。
- 根据记录: 根据记录所在的页,通过space id、page number在lock_sys_t结构中定位到lock_t对象,扫描bitmap找到heap_no对应的bit位。
上述各种数据结构,对其整理关系如下图所示:
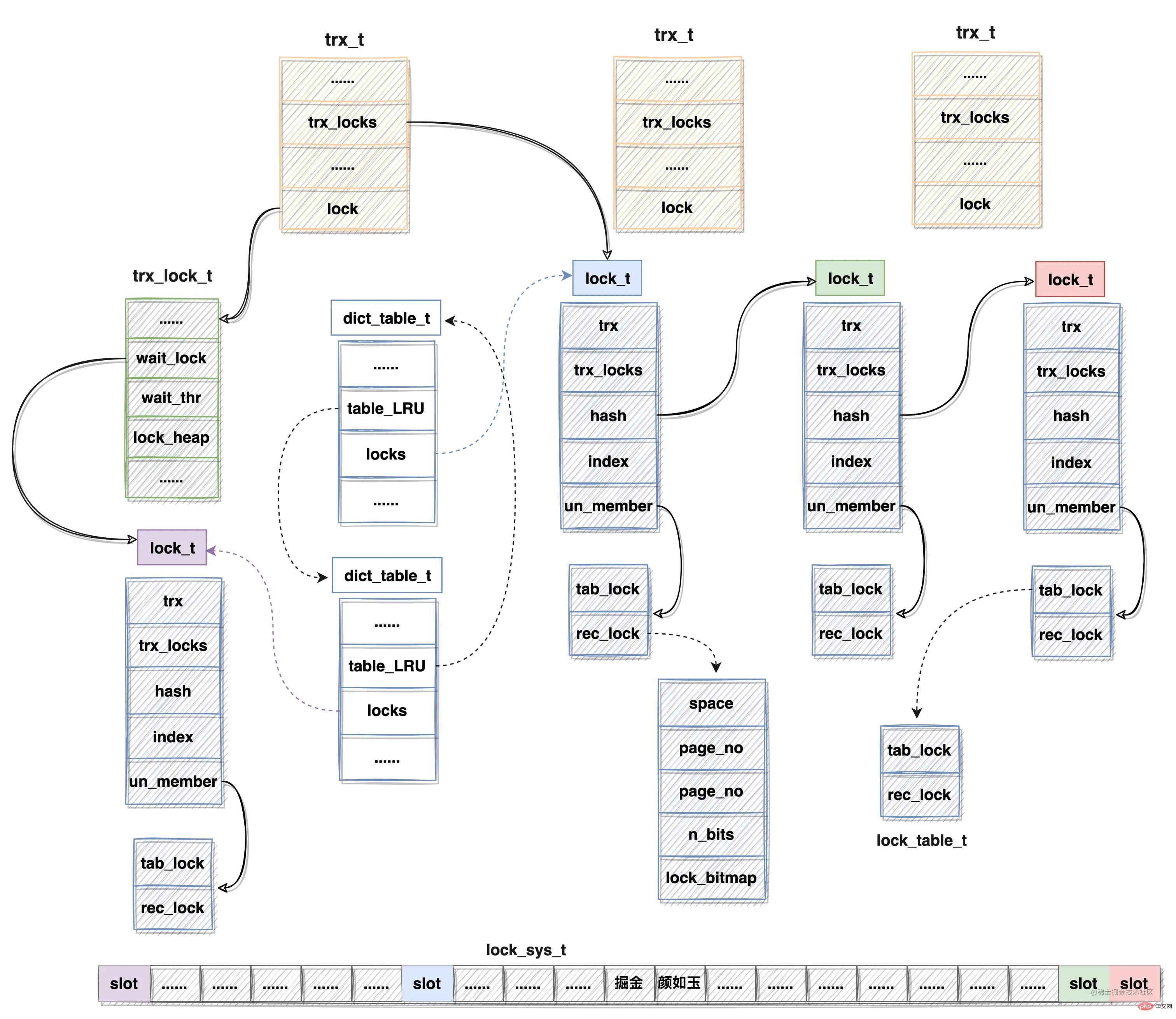
注:
- lock_sys_t中的slot颜色与lock_t颜色相同则表明lock_sys_t slot持有lock_t
指针信息,实在是没法连线,不然图很混乱
【相关推荐:mysql视频教程】
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Parlons de la structure de l'index MySQL
- MySQL explique en termes simples comment utiliser les déclencheurs
- Résumé et partage de la création d'utilisateurs et de la gestion des autorisations dans MySQL
- Comment modifier la structure des tables de la base de données MySQL en ligne
- Exemple détaillé du principe de correspondance de l'index MySQL le plus à gauche
- Implémentation spécifique du verrouillage optimiste et pessimiste MySQL

