Maison >développement back-end >Tutoriel Python >Comprendre l'analyseur de robot Python BeautifulSoup4 dans un article
Comprendre l'analyseur de robot Python BeautifulSoup4 dans un article
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBavant
- 2022-07-12 16:56:552825parcourir
Cet article vous apporte des connaissances pertinentes sur Python, qui organise principalement les problèmes liés à l'analyseur de robots BeautifulSoup4 Beautiful Soup est une bibliothèque Python qui peut extraire des données de fichiers HTML ou XML. Votre convertisseur préféré implémente les méthodes habituelles. de navigation, de recherche et de modification de documents. Jetons-y un coup d'œil, j'espère que cela sera utile à tout le monde.

【Recommandations associées : Tutoriel vidéo Python3】
1. Introduction à la bibliothèque BeautifulSoup4
1. Introduction
Beautiful Soup est une bibliothèque Python qui peut extraire des données à partir de fichiers HTML ou XML. Votre convertisseur préféré implémente vos méthodes préférées pour naviguer, rechercher et modifier des documents. Beautiful Soup vous fera gagner des heures, voire des jours de travail.
BeautifulSoup4 convertit la page web en arborescence DOM : 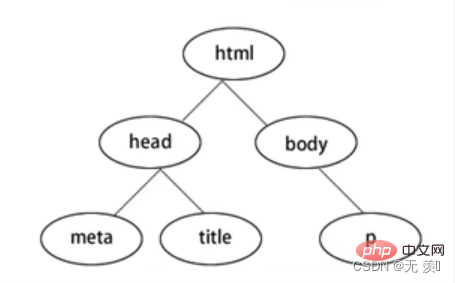
2 Téléchargez le module
1 Sur l'ordinateur Windows, cliquez sur touche win + R et saisissez : . cmdwin键+ R,输入:cmd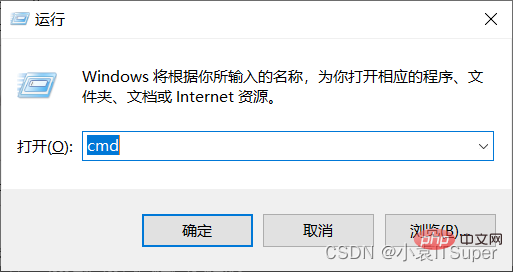
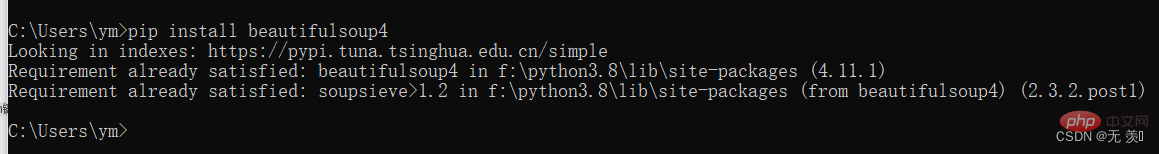
2. 安装beautifulsoup4,输入对应的pip命令:pip install beautifulsoup4 ,我已经安装过了出现版本就安装成功了
3. 导包
form bs4 import BeautifulSoup
3. 解析库
BeautifulSoup在解析时实际上依赖解析器,它除了支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器外,还支持一 些第三方解析器(比如lxml):
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | BeautifulSoup(html,’html.parser’) |
Python的内置标准库、执行速度适中、文档容错能力强 | Python 2.7.3及Python3.2.2之前的版本文档容错能力差 |
| lxml HTML解析库 | BeautifulSoup(html,’lxml’) |
速度快、文档容错能力强 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XML解析库 | BeautifulSoup(html,‘xml' |
速度快、唯一支持XML的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| htm5lib解析库 | BeautifulSoup(html,’htm5llib’) |
2. Installez beautifulsoup4 et entrez la commande pip correspondante : pip install beautifulsoup4 J'ai déjà installé la version et l'installation a réussi | .
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = ''' <p> </p><p> </p><h4>Hello</h4> <p> </p>
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo 百度官网
- Bar
BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser')🎜🎜Bibliothèque standard intégrée de Python, vitesse d'exécution modérée, forte tolérance aux pannes de documents🎜🎜Python 2.7. 3 et les versions antérieures à Python3.2.2 ont une faible tolérance aux pannes de documents🎜🎜BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')🎜🎜Vitesse rapide et forte tolérance aux pannes de documents🎜🎜 Nécessite l'installation de la bibliothèque de langage C🎜🎜BeautifulSoup(html,'xml'🎜🎜rapide, le seul analyseur prenant en charge XML🎜🎜doit installer la bibliothèque de langage C🎜 🎜🎜bibliothèque d'analyse htm5lib🎜🎜BeautifulSoup(html,'htm5llib')🎜🎜La meilleure tolérance aux pannes, analyse de documents dans le navigateur, génération de documents au format HTMLS🎜🎜Vitesse lente, pas facile Fiez-vous aux extensions externes🎜🎜🎜🎜对于我们来说,我们最常使用的解析器是lxml HTML解析器,其次是html5lib.
二、上手操作
1. 基础操作
1. 读取HTML字符串:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = ''' <p> </p><p> </p><h4>Hello</h4> <p> </p>
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo 百度官网
- Bar
2. 读取HTML文件:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(open('index.html'),'lxml')
3. 基本方法
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = ''' <p> </p><p> </p><h4>Hello</h4> <p> </p>
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo 百度官网
- Bar
2. 对象种类
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种: Tag , NavigableString , BeautifulSoup , Comment .
(1)Tag:Tag通俗点讲就是HTML中的一个个标签,例如:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<b>Extremely bold</b>','lxml')
tag = soup.b
print(tag)
print(type(tag))
输出结果:
<b>Extremely bold</b> <class></class>
Tag有很多方法和属性,在 遍历文档树 和 搜索文档树 中有详细解释.现在介绍一下tag中最重要的属性: name和attributes:
name属性:
print(tag.name) # 输出结果:b # 如果改变了tag的name,那将影响所有通过当前Beautiful Soup对象生成的HTML文档: tag.name = "b1" print(tag) # 输出结果:<b1>Extremely bold</b1>
Attributes属性:
# 取clas属性 print(tag['class']) # 直接”点”取属性, 比如: .attrs : print(tag.attrs)
tag 的属性可以被添加、修改和删除:
# 添加 id 属性 tag['id'] = 1 # 修改 class 属性 tag['class'] = 'tl1' # 删除 class 属性 del tag['class']
(2)NavigableString:用.string获取标签内部的文字:
print(soup.b.string)print(type(soup.b.string))
(3)BeautifulSoup:表示的是一个文档的内容,可以获取它的类型,名称,以及属性:
print(type(soup.name)) # <type> print(soup.name) # [document] print(soup.attrs) # 文档本身的属性为空</type>
(4)Comment:是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,其输出的内容不包括注释符号。
print(soup.b) print(soup.b.string) print(type(soup.b.string))
3. 搜索文档树
1.find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, **kwargs)
(1)name 参数:name 参数可以查找所有名字为 name 的tag,字符串对象会被自动忽略掉
-
匹配字符串:查找与字符串完整匹配的内容,用于查找文档中所有的
<a></a>标签a_list = soup.find_all("a")print(a_list) -
匹配正则表达式:如果传入正则表达式作为参数,Beautiful Soup会通过正则表达式的 match() 来匹配内容
# 返回所有表示和<b>标签for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")): print(tag.name)</b> -
匹配列表:如果传入列表参数,Beautiful Soup会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回
# 返回所有所有<p>标签和<a>标签:soup.find_all(["p", "a"])</a></p>
(2)kwargs参数
soup.find_all(id='link2')
(3)text参数:通过 text 参数可以搜搜文档中的字符串内容,与 name 参数的可选值一样, text 参数接受 字符串 , 正则表达式 , 列表
# 匹配字符串
soup.find_all(text="a")
# 匹配正则
soup.find_all(text=re.compile("^b"))
# 匹配列表
soup.find_all(text=["p", "a"])
4. css选择器
我们在使用BeautifulSoup解析库时,经常会结合CSS选择器来提取数据。
注意:以下讲解CSS选择器只选择标签,至于获取属性值和文本内容我们后面再讲。
1. 根据标签名查找:比如写一个 li 就会选择所有li 标签, 不过我们一般不用,因为我们都是精确到标签再提取数据的
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = ''' <p> </p><p> </p><h4>Hello</h4> <p> </p>
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo 百度官网
- Bar
输出结果:
[
2. 根据类名class查找。.1ine, 即一个点加line,这个表达式选的是class= "line "的所有标签,".”代表class
print(soup.select(".panel_body"))
输出结果:
- Foo
- Bar
3. 根据id查找。#box,即一个#和box表示选取id-”box "的所有标签,“#”代表id
print(soup.select("#list-1"))
输出结果:
[
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
4. 根据属性的名字查找。class属性和id属性较为特殊,故单独拿出来定义一个". "和“”来表示他们。
比如:input[ name=“username”]这个表达式查找name= "username "的标签,此处注意和xpath语法的区别
print(soup.select('ul[ name="element"]'))
输出结果:
[
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
5. 标签+类名或id的形式。
# 查找id为list-1的ul标签
print(soup.select('ul#list-1'))
print("-"*20)
# 查找class为list的ul标签
print(soup.select('ul.list'))
输出结果:
[
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo
- Bar
6. 查找直接子元素
# 查找id="list-1"的标签下的直接子标签liprint(soup.select('#list-1>li'))
输出结果:
[
7. 查找子孙标签
# .panel_body和li之间是一个空格,这个表达式查找id=”.panel_body”的标签下的子或孙标签liprint(soup.select('.panel_body li'))
输出结果:
[
8. 取某个标签的属性
# 1. 先取到<p>p = soup.select(".panel_body")[0]# 2. 再去下面的a标签下的href属性print(p.select('a')[0]["href"])</p>
输出结果:
https://www.baidu.com
9. 获取文本内容有四种方式:
(a) string:获得某个标签下的文本内容,强调-一个标签,不含嵌我。 返回-个字符串
# 1. 先取到<p>p = soup.select(".panel_body")[0]# 2. 再去下面的a标签下print(p.select('a')[0].string)</p>
输出结果:
百度官网
(b) strings:获得某个标签下的所有文本内容,可以嵌套。返回-一个生成器,可用list(生成器)转换为列表
print(p.strings)print(list(p.strings))
输出结果:
<generator>['\n', '\n', 'Foo', '\n', 'Bar', '\n', 'Jay', '\n', '\n', '\n', 'Foo', '\n', '百度官网', '\n', 'Bar', '\n', '\n']</generator>
(c)stripped.strings:跟(b)差不多,只不过它会去掉每个字符串头部和尾部的空格和换行符
print(p.stripped_strings)print(list(p.stripped_strings))
输出结果:
<generator>['Foo', 'Bar', 'Jay', 'Foo', '百度官网', 'Bar']</generator>
(d) get.text():获取所有字符串,含嵌套. 不过会把所有字符串拼接为一个,然后返回
注意2:
前3个都是属性,不加括号;最后一个是函数,加括号。
print(p.get_text())
输出结果:
Foo Bar Jay Foo 百度官网 Bar
【相关推荐:Python3视频教程 】
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- Compréhension approfondie des règles d'indentation de code en python
- Explication détaillée des exemples de modèles de forêt aléatoire Python
- Comprendre l'utilisation de Tkinter en python en un seul article
- Parlons de la façon de lire le contenu des fichiers mat (données matlab) à l'aide de python
- Que signifient python et jquery ?

