Maison >interface Web >Tutoriel H5 >Comment dessiner des effets de lignes d'énergie sympas sur un canevas HTML5 (avec code)
Comment dessiner des effets de lignes d'énergie sympas sur un canevas HTML5 (avec code)
- 奋力向前avant
- 2021-07-13 18:30:432835parcourir
Cet article vous expliquera comment utiliser le canevas HTML5 pour dessiner des effets de lignes d'énergie sympas. Il a une certaine valeur de référence. Les amis dans le besoin peuvent s'y référer. J'espère qu'il vous sera utile.
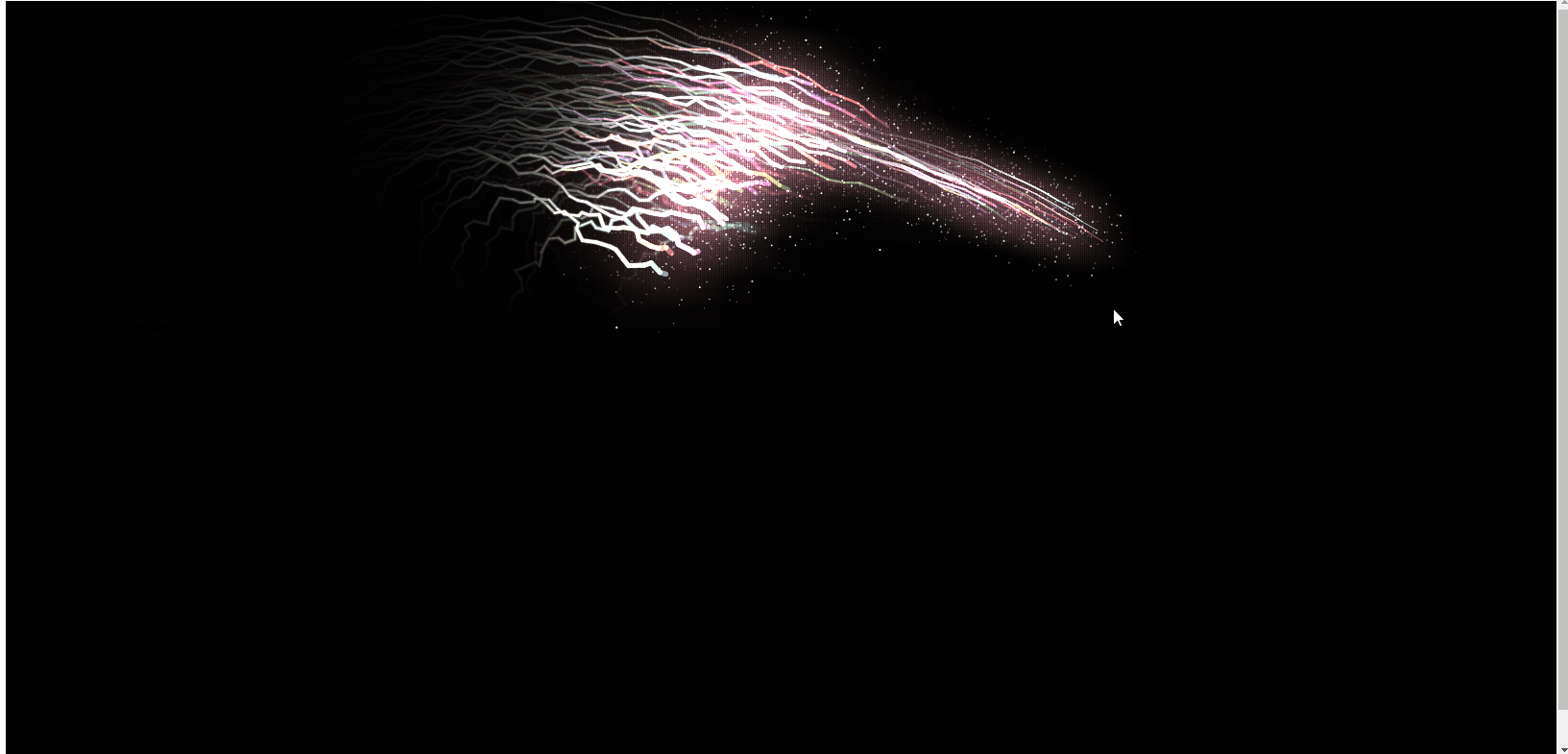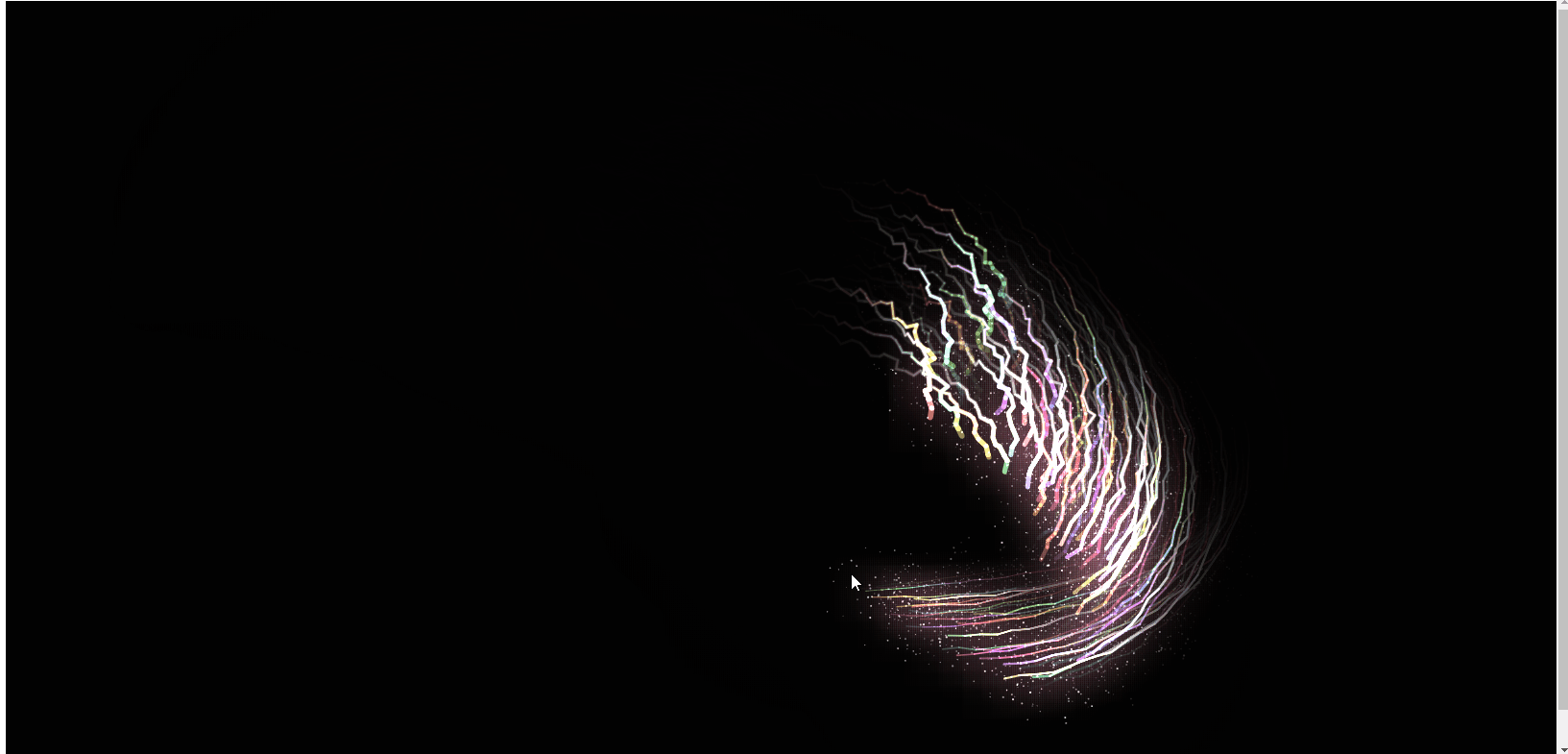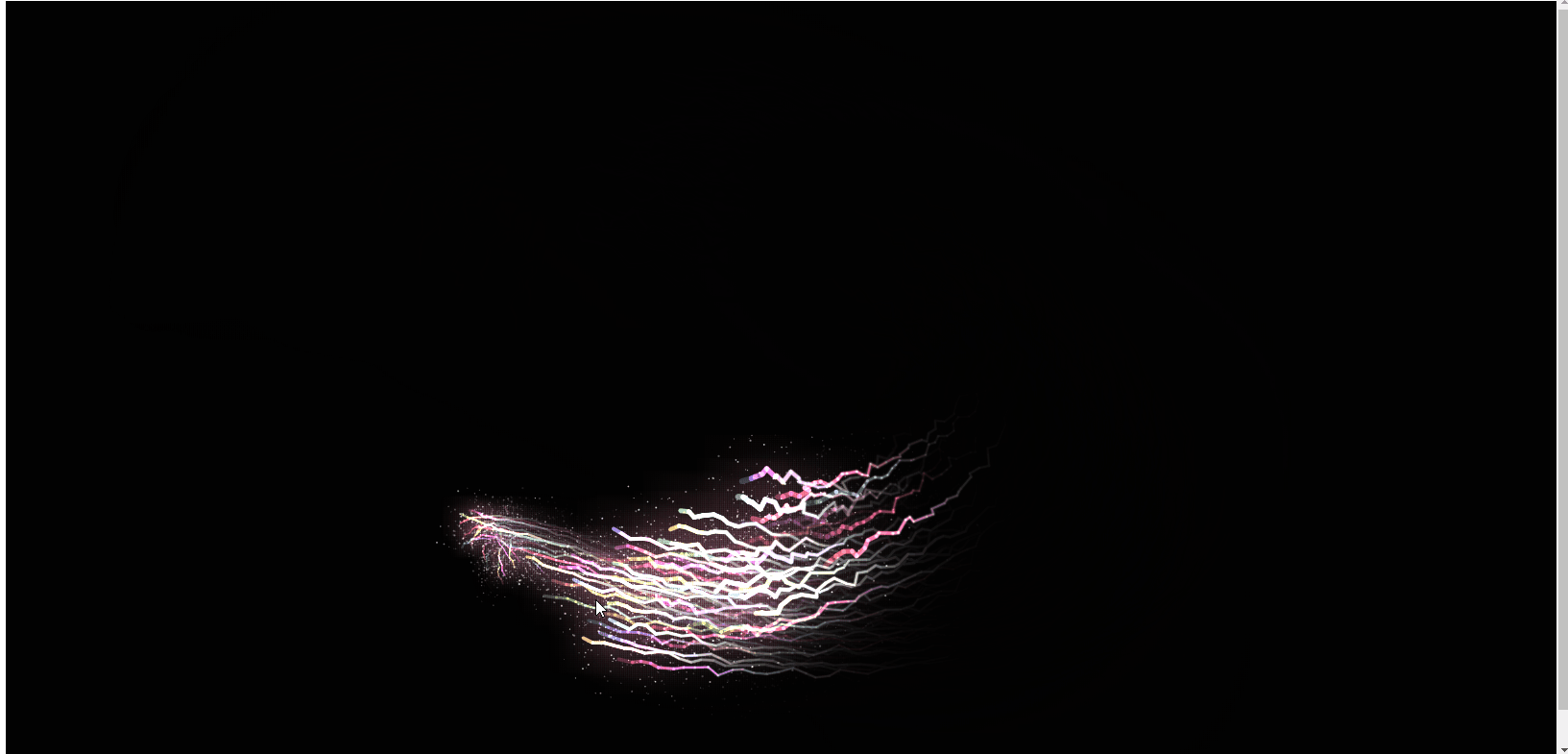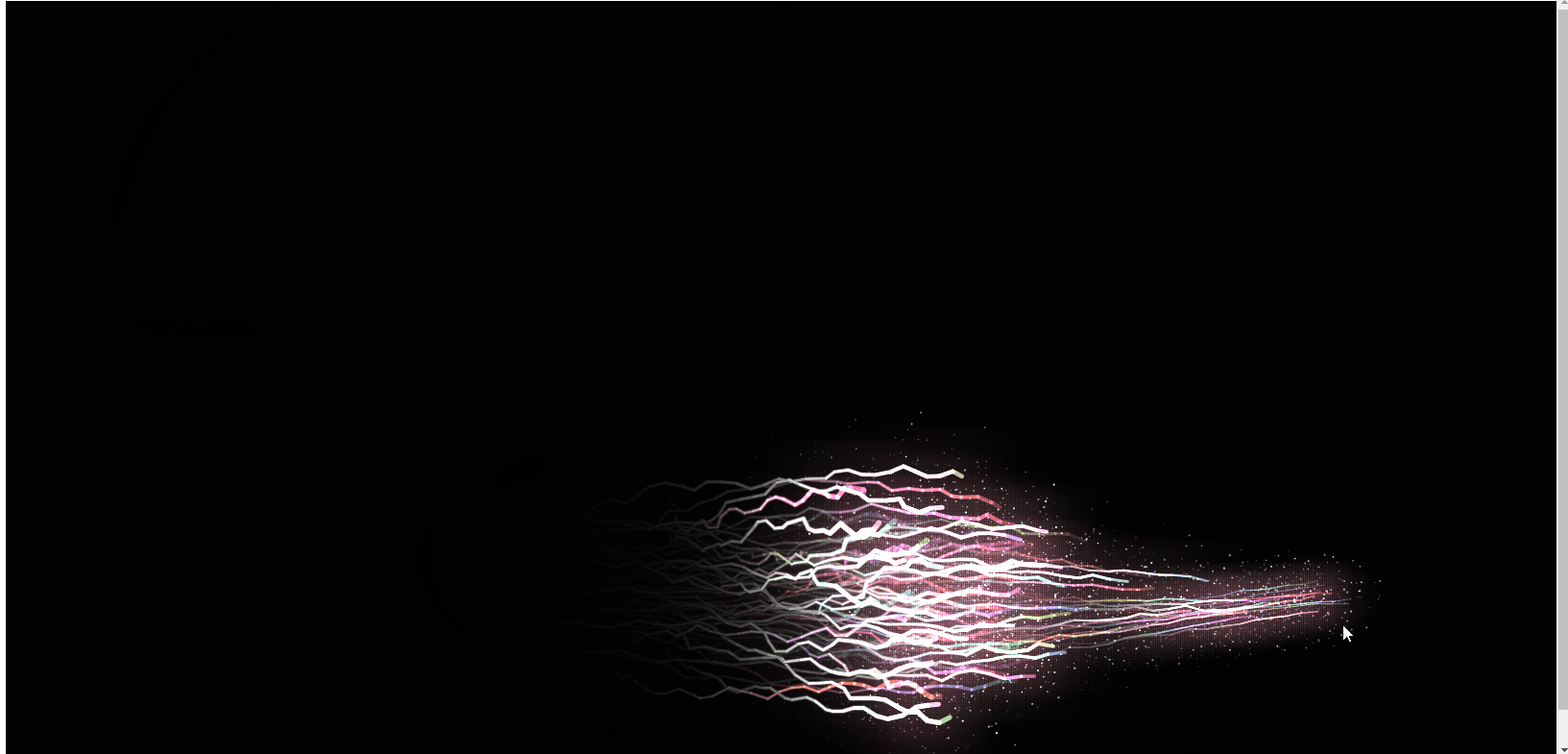
Ce qui précède est le rendu, et le code js est directement joint ci-dessous. J'espère qu'il sera utile à tout le monde ! !
// UTILconst PI = Math.PI,
TWO_PI = Math.PI * 2;const Util = {};Util.timeStamp = function() {
return window.performance.now();};Util.random = function(min, max) {
return min + Math.random() * (max - min);};Util.map = function(a, b, c, d, e) {
return (a - b) / (c - b) * (e - d) + d;};Util.lerp = function(value1, value2, amount) {
return value1 + (value2 - value1) * amount;};Util.clamp = function(value, min, max) {
return Math.max(min, Math.min(max, value));};// Vectorclass Vector {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x || 0;
this.y = y || 0;
}
set(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
reset() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
fromAngle(angle) {
let x = Math.cos(angle),
y = Math.sin(angle);
return new Vector(x, y);
}
add(vector) {
this.x += vector.x;
this.y += vector.y;
}
sub(vector) {
this.x -= vector.x;
this.y -= vector.y;
}
mult(scalar) {
this.x *= scalar;
this.y *= scalar;
}
p(scalar) {
this.x /= scalar;
this.y /= scalar;
}
dot(vector) {
return vector.x * this.x + vector.y * this.y;
}
limit(limit_value) {
if (this.mag() > limit_value) this.setMag(limit_value);
}
mag() {
return Math.hypot(this.x, this.y);
}
setMag(new_mag) {
if (this.mag() > 0) {
this.normalize();
} else {
this.x = 1;
this.y = 0;
}
this.mult(new_mag);
}
normalize() {
let mag = this.mag();
if (mag > 0) {
this.x /= mag;
this.y /= mag;
}
}
heading() {
return Math.atan2(this.y, this.x);
}
setHeading(angle) {
let mag = this.mag();
this.x = Math.cos(angle) * mag;
this.y = Math.sin(angle) * mag;
}
dist(vector) {
return new Vector(this.x - vector.x, this.y - vector.y).mag();
}
angle(vector) {
return Math.atan2(vector.y - this.y, vector.x - this.x);
}
copy() {
return new Vector(this.x, this.y);
}}// Init canvaslet canvas = document.createElement("canvas"),
ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"),
H = (canvas.height = window.innerHeight),
W = (canvas.width = window.innerWidth);document.body.appendChild(canvas);// Mouselet mouse = {
x: W/2,
y: H/2};canvas.onmousemove = function(event) {
mouse.x = event.clientX - canvas.offsetLeft;
mouse.y = event.clientY - canvas.offsetTop;};document.body.onresize = function(event){
H = (canvas.height = window.innerHeight);
W = (canvas.width = window.innerWidth);}// Let's goclass Arrow {
constructor(x, y, target) {
this.position = new Vector(x, y);
this.velocity = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
this.acceleration = new Vector(0, 0);
this.target = target;
this.travelled_distance = 0;
this.min_size = 1;
this.max_size = 6;
this.size = Util.random(this.min_size, this.max_size);
this.zone = this.size * 4;
this.topSpeed = Util.map(this.size,this.min_size,this.max_size,40,10);
let tailLength = Math.floor(Util.map(this.size, this.min_size, this.max_size, 4, 16));
this.tail = [];
for (let i = 0; i < tailLength; i++) {
this.tail.push({
x: this.position.x,
y: this.position.y });
}
this.wiggle_speed = Util.map(this.size, this.min_size, this.max_size, 2 , 1.2);
this.blink_offset = Util.random(0, 100);
this.alpha = Util.random(0.1,1)
}
render() {
this.update();
this.draw();
}
update() {
let old_position = this.position.copy();
// Focus on target
let t = new Vector(this.target.x, this.target.y),
angle = this.position.angle(t);
let d_f_target = t.dist(this.position);
let f = new Vector().fromAngle(angle);
f.setMag(Util.map(Util.clamp(d_f_target,0,400), 0, 400, 0, this.topSpeed * 0.1));
this.addForce(f);
// Update position and velocity
this.velocity.add(this.acceleration);
if(d_f_target < 800){
this.velocity.limit(Util.map(Util.clamp(d_f_target,0,800), 0, 800, this.topSpeed*0.4, this.topSpeed));
}else{
this.velocity.limit(this.topSpeed);
}
this.position.add(this.velocity);
// Reset acceleration for the next loop
this.acceleration.mult(0);
this.travelled_distance += old_position.dist(this.position);
let wiggle =
Math.sin(frame * this.wiggle_speed) *
Util.map(this.velocity.mag(), 0, this.topSpeed, 0, this.size);
let w_a = this.velocity.heading() + Math.PI / 2;
let w_x = this.position.x + Math.cos(w_a) * wiggle,
w_y = this.position.y + Math.sin(w_a) * wiggle;
this.travelled_distance = 0;
let from = this.tail.length - 1,
to = 0;
let n = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
n.setMag(Math.random()*this.size);
var tail = { x: w_x+ n.x, y: w_y + n.y};
this.tail.splice(from, 1);
this.tail.splice(to, 0, tail);
}
draw() {
let energy = Util.map(this.velocity.mag(),0,this.topSpeed,0.1,1);
let color =
"hsl("+Math.sin((frame + this.blink_offset) * 0.1) * 360+",50%,"+
Util.map(this.velocity.mag(),0,this.topSpeed,40,100) * this.alpha
+"%)";
ctx.globalAlpha = this.alpha;
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
for (let i = 0; i < this.tail.length - 1; i++) {
let t = this.tail[i],
next_t = this.tail[i + 1];
ctx.lineWidth = Util.map(i, 0, this.tail.length - 1, this.size, 1);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(t.x, t.y);
ctx.lineTo(next_t.x, next_t.y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.stroke();
}
let gradient_size = 140 * energy;var grd = ctx.createRadialGradient(
this.position.x,this.position.y , 5,
this.position.x,this.position.y, gradient_size);grd.addColorStop(0, "rgba(255,255,255,0.01)");grd.addColorStop(0.1, "rgba(255,120,200,0.02)");grd.addColorStop(0.9, "rgba(255,255,120,0)");grd.addColorStop(1, "rgba(0,0,0,0)");// Fill with gradientctx.fillStyle = grd;ctx.fillRect(this.position.x - gradient_size / 2 ,this.position.y - gradient_size / 2 , gradient_size, gradient_size);
ctx.globalAlpha = energy+0.2;
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
for(let i = 0; i < 4; i++){
let n = new Vector().fromAngle(Util.random(0,TWO_PI));
n.setMag(Math.random()*energy*100);
n.add(this.position);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(n.x,n.y,Math.random(),0,TWO_PI)
ctx.fill();
}
}
addForce(vector) {
this.acceleration.add(vector);
}
avoid(others) {
others.forEach(other => {
if (other !== this) {
let dist = this.position.dist(other.position),
max_dist = this.zone + other.size;
if (max_dist - dist >= 0) {
let angle = other.position.angle(this.position);
let force = new Vector().fromAngle(angle);
force.setMag(Util.map(dist, 0, max_dist, 2, 0));
this.addForce(force);
}
}
});
}}let arrows = [];for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
arrows.push(new Arrow(W / 2, H / 2, mouse));}let frame = 0;ctx.strokeStyle = "white";function loop() {
ctx.fillStyle="black";
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "source-over";
ctx.globalAlpha = 0.2;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, W, H);
ctx.globalAlpha = 1;
ctx.globalCompositeOperation = "lighter";
arrows.forEach(a => {
a.avoid(arrows);
});
arrows.forEach(a => {
a.render();
});
frame += 1;
requestAnimationFrame(loop);}ctx.lineCap = "round";ctx.lineJoin = "round";loop();Apprentissage recommandé : Tutoriel vidéo HTML5
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Déclaration:
Cet article est reproduit dans:. en cas de violation, veuillez contacter admin@php.cn Supprimer
Article précédent:Quel est le concept de HTML5Article suivant:Quel est le concept de HTML5

