Maison >interface Web >js tutoriel >22 questions d'entretien avancées sur React
22 questions d'entretien avancées sur React
- 青灯夜游avant
- 2020-08-04 10:00:149775parcourir

[Recommandations de sujets connexes : réagir aux questions d'entretien (2021)]
Q1 : Qu'est-ce que le DOM virtuel ?
Difficulté : ⭐
DOM virtuel (VDOM) C'est une représentation mémoire du vrai DOM, un concept de programmation et un modèle. Il sera synchronisé avec le vrai DOM, par exemple via une bibliothèque telle que ReactDOM. Ce processus de synchronisation est appelé réconciliation.
Le DOM virtuel est plus un modèle qu'une technologie spécifique.
Source : https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
Référence : https://www.javascriptcn com/. read-65385.html
Q2 : Quelle est la différence entre les composants de classe et les composants de fonction ?
Difficulté : ⭐⭐
-
Composants de classe(Composants de classe)
-
Qu'un composant soit déclaré à l'aide d'une fonction ou d'une classe, il ne doit pas modifier le sien
props.- Tous les composants React doivent être des fonctions pures et ne sont pas autorisés à se modifier
props.
- Tous les composants React doivent être des fonctions pures et ne sont pas autorisés à se modifier
-
React est un flux de données unique. Si le composant parent modifie ses propriétés, la vue du composant enfant sera mise à jour.
- Les attributs
propssont transmis du monde extérieur et le statutstateappartient au composant lui-même. Le statut peut être modifié arbitrairement dans le composant. les attributs et l'état du composant mettront à jour la vue.
- Les attributs
class Welcome extends React.Component { render() { return ( <h1>Welcome { this.props.name }</h1> ); } } ReactDOM.render(<Welcome name='react' />, document.getElementById('root')); -
- Composant fonctionnel
Fonction Le composant reçoit une un seul
- objet et renvoie un élément React
-
propsfunction Welcome (props) { return <h1>Welcome {props.name}</h1> } ReactDOM.render(<Welcome name='react' />, document.getElementById('root'));
-
bien sûr Il y a une différence, et le les performances des composants de fonction sont supérieures à celles des composants de classe, car les composants de classe doivent être instanciés lorsqu'ils sont utilisés, tandis que les composants de fonction peuvent exécuter directement la fonction et obtenir le résultat de retour. Pour améliorer les performances, essayez d'utiliser des composants fonctionnels.
| Différence | Composant de fonction | Composant de classe |
|---|---|---|
Y a-t-il ce
|
Non | Oui |
| Existe-t-il un cycle de vie | Non | Oui |
| Y a-t-il un état | Non | td>Oui |
资料来源:https://github.com/Pau1fitz/react-interview
参考资料:https://overreacted.io/how-are-function-components-different-from-classes/
Q3:React中的refs作用是什么?
难度:⭐⭐
Refs 是 React 提供给我们的安全访问 DOM 元素或者某个组件实例的句柄。
我们可以为元素添加 ref 属性然后在回调函数中接受该元素在 DOM 树中的句柄,该值会作为回调函数的第一个参数返回:
class UnControlledForm extends Component {
handleSubmit = () => {
console.log("Input Value: ", this.input.value)
}
render () {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<input
type='text'
ref={(input) => this.input = input} />
<button type='submit'>Submit</button>
</form>
)
}
}上述代码中的 input 域包含了一个 ref 属性,该属性声明的回调函数会接收 input 对应的 DOM 元素,我们将其绑定到 this 指针以便在其他的类函数中使用。
另外值得一提的是,refs 并不是类组件的专属,函数式组件同样能够利用闭包暂存其值:
function CustomForm ({handleSubmit}) {
let inputElement
return (
<form onSubmit={() => handleSubmit(inputElement.value)}>
<input
type='text'
ref={(input) => inputElement = input} />
<button type='submit'>Submit</button>
</form>
)
}资料来源:https://github.com/Pau1fitz/react-interview
参考资料:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29503213/use-state-or-refs-in-react-js-form-components
Q4:描述React事件处理。
难度:⭐⭐
为了解决跨浏览器兼容性问题,React中的事件处理程序将传递SyntheticEvent实例,该实例是React跨浏览器本机事件的跨浏览器包装器。这些综合事件具有与您惯用的本机事件相同的界面,除了它们在所有浏览器中的工作方式相同。
有点有趣的是,React实际上并未将事件附加到子节点本身。React将使用单个事件侦听器在顶层侦听所有事件。这对性能有好处,也意味着React在更新DOM时无需担心跟踪事件监听器。
资料来源:https://tylermcginnis.com/react-interview-questions/
参考资料:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiangming25/p/6430461.html
Q5:state 和 props有什么区别?
难度:⭐⭐
state 和 props都是普通的JavaScript对象。尽管它们两者都具有影响渲染输出的信息,但它们在组件方面的功能不同。即
-
props是一个从外部传进组件的参数,主要作为就是从父组件向子组件传递数据,它具有可读性和不变性,只能通过外部组件主动传入新的props来重新渲染子组件,否则子组件的props以及展现形式不会改变。 -
state的主要作用是用于组件保存、控制以及修改自己的状态,它只能在constructor中初始化,它算是组件的私有属性,不可通过外部访问和修改,只能通过组件内部的this.setState来修改,修改state属性会导致组件的重新渲染。
资料来源: https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
参考资料:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27991366/what-is-the-difference-between-state-and-props-in-react
Q6:如何创建refs?
难度:⭐⭐
Refs 是使用 React.createRef() 方法创建的,并通过 ref 属性添加到 React 元素上。为了在整个组件中使用refs,只需将 ref 分配给构造函数中的实例属性
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.myRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return <p ref={this.myRef} />;
}
}和:
class UserForm extends Component {
handleSubmit = () => {
console.log("Input Value is: ", this.input.value)
}
render () {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<input
type='text'
ref={(input) => this.input = input} /> // Access DOM input in handle submit
<button type='submit'>Submit</button>
</form>
)
}
}我们还可以借助闭包在功能组件中使用它。
资料来源: https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
参考资料:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000015113359
Q7:什么是高阶组件?
难度:⭐⭐
高阶组件就是一个函数,且该函数接受一个组件作为参数,并返回一个新的组件。基本上,这是从React的组成性质派生的一种模式,我们称它们为“纯”组件, 因为它们可以接受任何动态提供的子组件,但它们不会修改或复制其输入组件的任何行为。
const EnhancedComponent = higherOrderComponent(WrappedComponent);
- 高阶组件(HOC)是 React 中用于复用组件逻辑的一种高级技巧
- 高阶组件的参数为一个组件返回一个新的组件
- 组件是将 props 转换为 UI,而高阶组件是将组件转换为另一个组件
资料来源: https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
参考资料:https://css-tricks.com/what-are-higher-order-components-in-react/
Q8:constructor中super与props参数一起使用的目的是什么?
难度:⭐⭐
在调用方法之前,子类构造函数无法使用this引用super()。
在ES6中,在子类的constructor中必须先调用super才能引用this。
在constructor中可以使用this.props
使用props:
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log(this.props); // Prints { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 }
}
}不使用props:
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super();
console.log(this.props); // Prints undefined
// But Props parameter is still available
console.log(props); // Prints { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 }
}
render() {
// No difference outside constructor
console.log(this.props) // Prints { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 }
}
}上面的代码片段揭示了this.props行为仅在构造函数中有所不同。外部构造函数相同。
资料来源:
https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
https://www.fullstack.cafe/React)
Q9:什么是受控组件?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
在HTML当中,像<input>,<textarea></textarea>, 和 <select></select>这类表单元素会维持自身状态,并根据用户输入进行更新。但在React中,可变的状态通常保存在组件的状态属性中,并且只能用 setState() 方法进行更新。
非受控组件
非受控组件,即组件的状态不受React控制的组件,例如下边这个
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class Demo1 extends Component {
render() {
return (
<input />
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo1/>, document.getElementById('content'))在这个最简单的输入框组件里,我们并没有干涉input中的value展示,即用户输入的内容都会展示在上面。如果我们通过props给组件设置一个初始默认值,defaultValue属性是React内部实现的一个属性,目的类似于input的placeholder属性。
ps: 此处如果使用value代替defaultValue,会发现输入框的值无法改变
受控组件
同样的,受控组件就是组件的状态受React控制。上面提到过,既然通过设置input的value属性, 无法改变输入框值,那么我们把它和state结合在一起,再绑定onChange事件,实时更新value值就行了。
class Demo1 extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
value: props.value
}
}
handleChange(e) {
this.setState({
value: e.target.value
})
}
render() {
return (
<input value={this.state.value} onChange={e => this.handleChange(e)}/>
)
}
}资料来源:https://github.com/Pau1fitz/react-interview
参考资料:https://www.php.cn/js-tutorial-382697.html
Q10:以下使用React.createElement的等价项是什么?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
问题:
const element = (
<h1 className="greeting">
Hello, world!
</h1>
);以下等同于什么使用React.createElement?
答:
const element = React.createElement(
'h1',
{className: 'greeting'},
'Hello, world!'
);资料来源:https://github.com/Pau1fitz/react-interview
Q11:什么是JSX?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
JSX即JavaScript XML。一种在React组件内部构建标签的类XML语法。JSX为react.js开发的一套语法糖,也是react.js的使用基础。React在不使用JSX的情况下一样可以工作,然而使用JSX可以提高组件的可读性,因此推荐使用JSX。
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
let props = this.props;
return (
<p className="my-component">
<a href={props.url}>{props.name}</a>
</p>
);
}
}优点:
1.允许使用熟悉的语法来定义 HTML 元素树;
2.提供更加语义化且移动的标签;
3.程序结构更容易被直观化;
4.抽象了 React Element 的创建过程;
5.可以随时掌控 HTML 标签以及生成这些标签的代码;
6.是原生的 JavaScript。
资料来源: https://www.codementor.io/blog/5-essential-reactjs-interview-questions-du1084ym1
参考资料:http://facebook.github.io/jsx/
Q12:为什么不直接更新state状态?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
如果进行如下方式更新状态,那么它将不会重新渲染组件。
//Wrong
This.state.message =”Hello world”;而是使用setState()方法。它计划对组件状态对象的更新。状态改变时,组件通过重新渲染做出响应
//Correct
This.setState({message: ‘Hello World’});注意:可以分配状态的唯一位置是构造函数。
资料来源:https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
Q13:ReactJS生命周期有哪些不同阶段?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
React组件的生命周期分为四个不同阶段:
- 初始化:在此阶段,react组件准备设置初始状态和默认道具。
- 挂载: react组件已准备好挂载在浏览器DOM中。此阶段涵盖componentWillMount和componentDidMount生命周期方法。
- 更新:在此阶段,组件以两种方式进行更新,即发送新道具和更新状态。此阶段涵盖了shouldComponentUpdate,componentWillUpdate和componentDidUpdate生命周期方法。
- 卸载:在最后一个阶段,不需要该组件,并且可以从浏览器DOM上卸载该组件。此阶段包括componentWillUnmount生命周期方法。
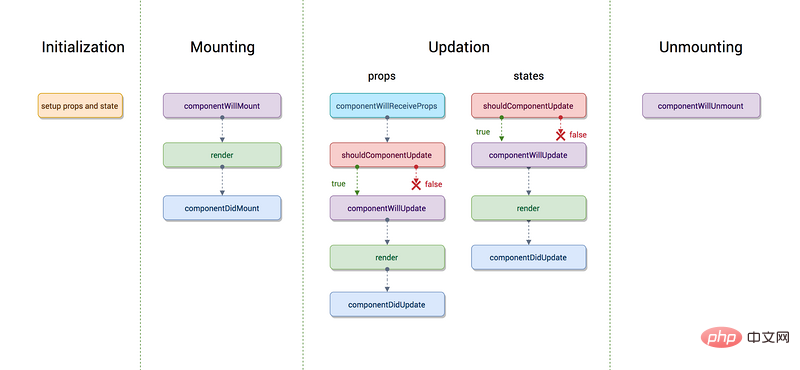
资料来源: https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
Q14:ReactJS的生命周期方法是什么?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
- componentWillMount:在渲染之前执行,用于根组件中的应用程序级别配置。
-
componentDidMount:仅在客户端的第一次渲染之后执行。 这是AJAX请求和DOM或状态更新应该发生的地方。此方法也用于与其他JavaScript框架以及任何延迟执行的函数(如
setTimeout或setInterval)进行集成,在这里使用它来更新状态,以便我们可以触发其他生命周期方法。 -
componentWillReceiveProps:只要在另一个渲染被调用之前更新
props就被调用。 当我们更新状态时,从setNewNumber触发它。 - shouldComponentUpdate:确定是否将更新组件。默认情况下,它返回true。如果您确定组件在状态或道具更新后不需要渲染,则可以返回false值。这是提高性能的好地方,因为如果组件收到新的道具,它可以防止重新渲染。
- componentWillUpdate:在由shouldComponentUpdate确认返回正值的优点和状态更改时,在重新渲染组件之前执行。
- componentDidUpdate:通常用于更新DOM以响应属性或状态更改。
- componentWillUnmount:它将用于取消任何传出的网络请求,或删除与该组件关联的所有事件侦听器。
资料来源:
https://github.com/sudheerj/reactjs-interview-questions
https://www.fullstack.cafe/React)
Q15:React中的这三个点(...)是做什么的?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
...在此React(使用JSX)代码中做什么?它叫什么?
<Modal {...this.props} title='Modal heading' animation={false}>扩展传值符号。它是在ES2018中添加的(数组/可迭代对象的传播较早,ES2015)。
例如,如果this.props包含a:1和b:2,则
<Modal {...this.props} title='Modal heading' animation={false}>与以下内容相同:
<Modal a={this.props.a} b={this.props.b} title='Modal heading' animation={false}>扩展符号不仅适用于该用例,而且对于创建具有现有对象的大多数(或全部)属性的新对象非常方便-在更新状态时会遇到很多问题,因为您无法修改状态直:
this.setState(prevState => {
return {foo: {...prevState.foo, a: "updated"}};
});资料来源: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31048953/what-do-these-three-dots-in-react-do
Q16:使用React Hooks有什么优势?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
hooks 是react 16.8 引入的特性,他允许你在不写class的情况下操作state 和react的其他特性。
hooks 只是多了一种写组件的方法,使编写一个组件更简单更方便,同时可以自定义hook把公共的逻辑提取出来,让逻辑在多个组件之间共享。
Hook 是什么
Hook 是什么? Hook 是一个特殊的函数,它可以让你“钩入” React 的特性。例如,useState 是允许你在 React 函数组件中添加 state 的 Hook。稍后我们将学习其他 Hook。
什么时候我会用 Hook? 如果你在编写函数组件并意识到需要向其添加一些 state,以前的做法是必须将其它转化为 class。现在你可以在现有的函数组件中使用 Hook。
ReactHooks的优点
- 无需复杂的DOM结构
- 简洁易懂
资料来源: https://hackernoon.com/react-hooks-usestate-using-the-state-hook-89ec55b84f8c
Q17:React中的useState?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
案例:
import { useState } from 'react';
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<p>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Click me
</button>
</p>
)
}语法:
function useState<S>(initialState: S | (() => S)): [S, Dispatch<SetStateAction<S>>];
其中 state 是他的值, setState 是用来设置值的函数, initialState 是初始值
useState-initialState
该初始值可以接受任何参数,但是记得当他接受为一个函数时,就变成了Lazy initialization (延迟初始化)
该函数返回值即为initialState
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [count, setCount] = useState(()=>0);
// 这两种初始化方式 是相等的,但是在函数为初始值时会被执行一次
const [count, setCount] = useState(()=>{
console.log('这里只会在初始化的时候执行')
// class 中的 constructor 的操作都可以移植到这里
return 0
});
// 当第一次执行完毕后 就和另一句的代码是相同的效果了useState-setState
也许很多人 在使用 class 的 setState 时候,会经常使用他的回调函数,
但是这里很遗憾,他只接受新的值,如果想要对应的回调,可以使用useEffect,这个问题等会会提供一个跳转链接
Q18:React中的StrictMode是什么?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
React的StrictMode是一种帮助程序组件,可以帮助您编写更好的react组件,您可以使用包装一些组件,<strictmode></strictmode>并且基本上可以:
- 验证内部组件是否遵循某些推荐做法,如果不在控制台中,则会发出警告。
- 验证不赞成使用的方法,如果使用了严格模式,则会在控制台中警告您。
- 通过识别潜在风险来帮助您预防某些副作用。
参考资料:http://react.html.cn/docs/strict-mode.html
Q19:为什么类方法需要绑定?
难度:⭐⭐⭐
在JavaScript中,this的值取决于当前上下文。在React类的组件方法中,开发人员通常希望它引用组件的当前实例,因此有必要将这些方法绑定到该实例。通常,这是在构造函数中完成的,例如:
class SubmitButton extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
isFormSubmitted: false
};
this.handleSubmit = this.handleSubmit.bind(this);
}
handleSubmit() {
this.setState({
isFormSubmitted: true
});
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleSubmit}>Submit</button>
)
}
}资料来源: https://www.toptal.com/react/interview-questions
Q20:描述Flux与MVC?
难度:⭐⭐⭐⭐
传统的MVC模式在分离数据(模型),UI(视图)和逻辑(控制器)的关注方面效果很好,但是MVC架构经常遇到两个主要问题:
- 数据流定义不佳:跨视图进行的级联更新通常会导致纠结的事件网,难以调试。
- 缺乏数据完整性:可以从任何地方对模型数据进行突变,从而在整个UI上产生不可预测的结果。
使用Flux模式,复杂的UI不再受到级联更新的困扰。任何给定的React组件都将能够根据商店提供的数据重建其状态。Flux模式还通过限制对共享数据的直接访问来增强数据完整性。
资料来源:
https://www.codementor.io/blog/5-essential-reactjs-interview-questions-du1084ym1
https://www.fullstack.cafe/React)
Q21:React context是什么?
难度:⭐⭐⭐⭐
React文档官网并未对Context给出“是什么”的定义,更多是描述使用的Context的场景,以及如何使用Context。
官网对于使用Context的场景是这样描述的:
In Some Cases, you want to pass data through the component tree without having to pass the props down manuallys at every level. you can do this directly in React with the powerful "context" API.
简单说就是,当你不想在组件树中通过逐层传递props或者state的方式来传递数据时,可以使用Context来实现跨层级的组件数据传递。
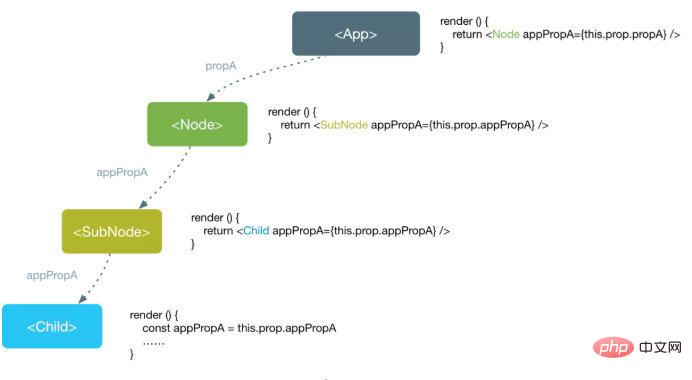
使用props或者state传递数据,数据自顶下流。
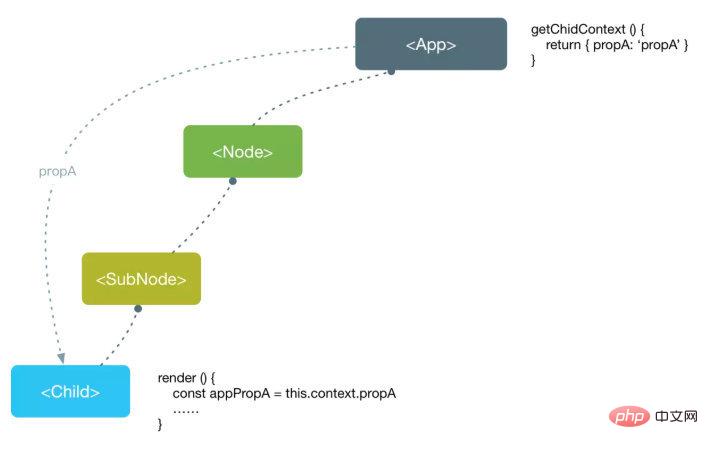
使用Context,可以跨越组件进行数据传递。
资料来源: https://github.com/WebPredict/react-interview-questions
Q22:React Fiber是什么?
难度:⭐⭐⭐⭐
React Fiber 并不是所谓的纤程(微线程、协程),而是一种基于浏览器的单线程调度算法,背后的支持 API 是大名鼎鼎的:requestIdleCallback。
Fiberl是一种将 recocilation (递归 diff),拆分成无数个小任务的算法;它随时能够停止,恢复。停止恢复的时机取决于当前的一帧(16ms)内,还有没有足够的时间允许计算。
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
Articles Liés
Voir plus- SublimeText3 configure la vérification de la syntaxe de réaction
- 4 conseils pratiques pour développer des applications React
- Compilation de points de connaissances pour démarrer avec React
- Une brève discussion sur les méthodes d'obtention de données dans React et leurs avantages et inconvénients
- 35 questions d'entretien que vous devez connaître et maîtriser React
- 50 questions d'entretien React incontournables

