Maison >développement back-end >tutoriel php >PHP implémente un algorithme de tri par tas (exemple de code)
PHP implémente un algorithme de tri par tas (exemple de code)
- 藏色散人original
- 2019-03-04 11:15:193111parcourir
En informatique, le tri par tas (inventé par J. W. J. Williams en 1964) est un algorithme de tri basé sur la comparaison. Heapsort peut être considéré comme un tri de sélection amélioré : similaire à cet algorithme, il divise l'entrée en zone triée et zone non triée, et extrait le maximum d'éléments et les déplace vers la zone triée. pour réduire de manière interactive la zone non triée. Les améliorations incluent l'utilisation d'une structure de données en tas au lieu d'une recherche temporelle linéaire pour trouver le maximum.
Bien qu'il s'exécute en fait un peu plus lentement qu'un tri rapide bien implémenté sur la plupart des machines, il a l'avantage d'être un runtime O(n dans le pire des cas log n) est plus avantageux. Le tri par tas est un algorithme de tri sur place, mais ce n'est pas un tri stable.
L'algorithme de tri en tas trie un ensemble de valeurs disposées de manière aléatoire. Dans la première phase de l'algorithme, les éléments du tableau sont réorganisés pour satisfaire les propriétés du tas. Avant de procéder au tri proprement dit, la structure arborescente du tas est brièvement présentée à titre d'illustration.
Diagramme schématique de l'idée d'algorithme de tri de tas PHP :
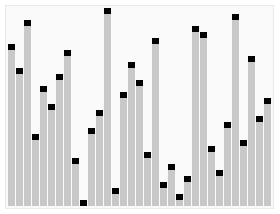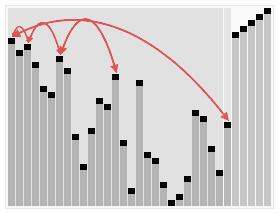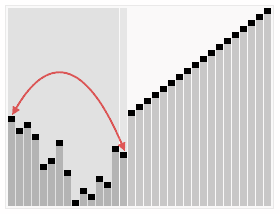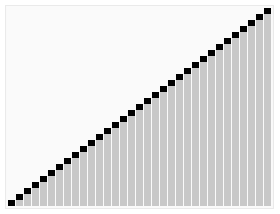
Le code d'implémentation du tri de tas PHP est le suivant :
<?php
class Node
{
private $_i;
public function __construct($key)
{
$this->_i = $key;
}
public function getKey()
{
return $this->_i;
}
}
class Heap
{
private $heap_Array;
private $_current_Size;
public function __construct()
{
$heap_Array = array();
$this->_current_Size = 0;
}
public function remove()
{
$root = $this->heap_Array[0];
$this->heap_Array[0] = $this->heap_Array[--$this->_current_Size];
$this->bubbleDown(0);
return $root;
}
public function bubbleDown($index)
{
$larger_Child = null;
$top = $this->heap_Array[$index];
while ($index < (int)($this->_current_Size/2)) {
$leftChild = 2 * $index + 1;
$rightChild = $leftChild + 1;
if ($rightChild < $this->_current_Size
&& $this->heap_Array[$leftChild] < $this->heap_Array[$rightChild])
{
$larger_Child = $rightChild;
} else {
$larger_Child = $leftChild;
}
if ($top->getKey() >= $this->heap_Array[$larger_Child]->getKey()) {
break;
}
$this->heap_Array[$index] = $this->heap_Array[$larger_Child];
$index = $larger_Child;
}
$this->heap_Array[$index] = $top;
}
public function insertAt($index, Node $newNode)
{
$this->heap_Array[$index] = $newNode;
}
public function incrementSize()
{
$this->_current_Size++;
}
public function getSize()
{
return $this->_current_Size;
}
public function asArray()
{
$arr = array();
for ($j = 0; $j < sizeof($this->heap_Array); $j++) {
$arr[] = $this->heap_Array[$j]->getKey();
}
return $arr;
}
}
function heapsort(Heap $Heap)
{
$size = $Heap->getSize();
for ($j = (int)($size/2) - 1; $j >= 0; $j--)
{
$Heap->bubbleDown($j);
}
for ($j = $size-1; $j >= 0; $j--) {
$BiggestNode = $Heap->remove();
$Heap->insertAt($j, $BiggestNode);
}
return $Heap->asArray();
}
$arr = array(3, 0, 2, 5, -1, 4, 1);
echo "原始数组 : ";
echo implode(', ',$arr );
$Heap = new Heap();
foreach ($arr as $key => $val) {
$Node = new Node($val);
$Heap->insertAt($key, $Node);
$Heap->incrementSize();
}
$result = heapsort($Heap);
echo "\n排序后数组 : ";
echo implode(', ',$result)."\n";Sortie :
原始数组 : 3, 0, 2, 5, -1, 4, 1 排序后数组 : -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Cet article est une introduction au tri de tas PHP. J'espère qu'il sera utile aux amis qui en ont besoin !
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

