Today we will create a multi-step form with animation using AngularJs and the great UI Router and the Angular ngAnimate module. This technique can be used on large forms where you want to simplify user operations.
We have seen that this technology has been applied to many web pages. Things like shopping carts, registration forms, onboarding flows, and many multi-step forms make it easier for users to fill out forms online.
Here we will build it:
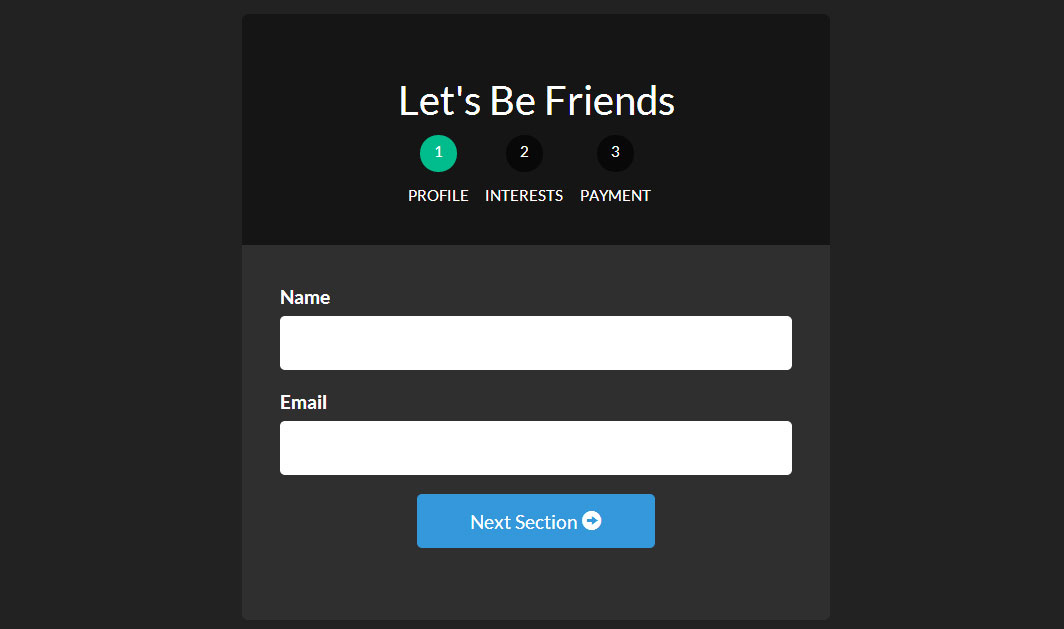
Using UI Router, which can embed states and display different views for each state, we can make multi-step forms quite easy.
Let’s get down to business and start creating our best form yet!
Create project
Creating a project has a template structure. It requires a layout file, a view file for each form, a format file, and a JavaScript file.
The following is the file list, create them first, and then fill in the content
- - index.html
- - form.html
- - form-profile.html
- - form-interests.html
- - form-payment.html
- - app.js
- - style.css
Each form-____.html represents an html file in a hierarchical structure. These structures ultimately create our form structure.
Our layout/template file index.html
We start our project by creating a main file to introduce all the resources we need. Here we use the index.html file as the main file
Now, we load the resources we need (AngularJS, ngAnimate, Ui Router, and other scripts and stylesheets) and set up a ui-view to tell the UI Router where our view needs to be displayed. Here we use Bootstrap to quickly apply styles.
<!-- index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<!-- CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="//netdna.bootstrapcdn.com/bootswatch/3.1.1/darkly/bootstrap.min.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<!-- JS -->
<!-- load angular, nganimate, and ui-router -->
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.2.16/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/angular-ui-router/0.2.10/angular-ui-router.min.js"></script>
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.2.16/angular-animate.min.js"></script>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</head>
<!-- apply our angular app -->
<body ng-app="formApp">
<div class="container">
<!-- views will be injected here -->
<div ui-view></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
After completing the introduction of all files, let us enter app.js to start creating the Angular application and the most basic routing configuration. Notice how we applied the Angular App (formApp) to the body.
Create our Angular App app.js
Now let’s create the application and routes. In a large application, you would definitely want to distribute your Angular applications, routes, and controllers into their own modules, but for our simple use case, we will put them all into the happy family of app.js middle.
// app.js
// create our angular app and inject ngAnimate and ui-router
// =============================================================================
angular.module('formApp', ['ngAnimate', 'ui.router'])
// configuring our routes
// =============================================================================
.config(function($stateProvider, $urlRouterProvider) {
$stateProvider
// route to show our basic form (/form)
.state('form', {
url: '/form',
templateUrl: 'form.html',
controller: 'formController'
})
// nested states
// each of these sections will have their own view
// url will be nested (/form/profile)
.state('form.profile', {
url: '/profile',
templateUrl: 'form-profile.html'
})
// url will be /form/interests
.state('form.interests', {
url: '/interests',
templateUrl: 'form-interests.html'
})
// url will be /form/payment
.state('form.payment', {
url: '/payment',
templateUrl: 'form-payment.html'
});
// catch all route
// send users to the form page
$urlRouterProvider.otherwise('/form/profile');
})
// our controller for the form
// =============================================================================
.controller('formController', function($scope) {
// we will store all of our form data in this object
$scope.formData = {};
// function to process the form
$scope.processForm = function() {
alert('awesome!');
};
});
Now we have an application with ngAnimate and ui.router injected. We also established corresponding routes. Notice how we define the url, view file (templateUrl) and controller for each view area.
The form will be our main view area. It also has a subview area form.profile separated by . This idea can be realized when the application state changes (Translator: it may be routing, queryString, etc.), the subview will be displayed in the main view area. (Translator: And it can only update the subview area changes and record the subview area status).
We will demonstrate this in the next section. Now we need to create views for the form and its subview areas.
Form template view form.html
Let’s start by creating a new form.html. This file will serve as a template for the rest of our form view files, just as index.html is used as the overall template for the entire project. All we have to do is include ui-view in this file so that the nested declarations know where to inject their views.
<!-- form.html -->
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-2">
<div id="form-container">
<div class="page-header text-center">
<h2 id="Let-s-Be-Friends">Let's Be Friends</h2>
<!-- the links to our nested states using relative paths -->
<!-- add the active class if the state matches our ui-sref -->
<div id="status-buttons" class="text-center">
<a ui-sref-active="active" ui-sref=".profile"><span>1</span> Profile</a>
<a ui-sref-active="active" ui-sref=".interests"><span>2</span> Interests</a>
<a ui-sref-active="active" ui-sref=".payment"><span>3</span> Payment</a>
</div>
</div>
<!-- use ng-submit to catch the form submission and use our Angular function -->
<form id="signup-form" ng-submit="processForm()">
<!-- our nested state views will be injected here -->
<div id="form-views" ui-view></div>
</form>
</div>
<!-- show our formData as it is being typed -->
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">
{{ formData }}
注意我们是如何第二次在项目中使用ui-view的。这就是UI Router伟大的地方:我们可以嵌套声明和视图。这能够在我们开发应用时提供给我们非常多的灵活性。关于UI Router视图的内容,请参见官方文档。
添加基于状态的激活类
我们希望每一个状态按钮能够在他们被激活时展示。为了达到这个效果,我们将会使用UI Router提供的ui-sref-active。如果ui-sref和当前状态一致,则会添加我们指定的类。
现在,你可能想知道我们的表单究竟看起来是什么样子。让我们打开浏览器看一眼。
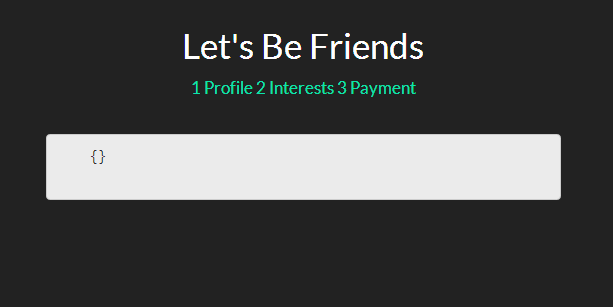
目前为止,我们并没有完全按照希望的那样得到所有的内容,但是这是一系列伟大事情的开端。让我们继续前进,添加一点样式,之后会添加一些嵌入视图和注释。
基础Stylingstyle.css
我们将设计我们的form-container和status-buttons来是我们的表单看起来更好。
/* style.css */
/* BASIC STYLINGS
============================================================================= */
body { padding-top:20px; }
/* form styling */
#form-container { background:#2f2f2f; margin-bottom:20px;
border-radius:5px; }
#form-container .page-header { background:#151515; margin:0; padding:30px;
border-top-left-radius:5px; border-top-right-radius:5px; }
/* numbered buttons */
#status-buttons { }
#status-buttons a { color:#FFF; display:inline-block; font-size:12px; margin-right:10px; text-align:center; text-transform:uppercase; }
#status-buttons a:hover { text-decoration:none; }
/* we will style the span as the circled number */
#status-buttons span { background:#080808; display:block; height:30px; margin:0 auto 10px; padding-top:5px; width:30px;
border-radius:50%; }
/* active buttons turn light green-blue*/
#status-buttons a.active span { background:#00BC8C; }
现在我们的按钮更好看了并且更符合我们想要的了,接下来我们看下嵌套视图。
嵌套视图form-profile.html, form-interests.html, form-payment.html
这部分会比较简单。我们将定义不同的带有我们需要的输入框的视图。并且将他们绑定到formData对象以便我们能看到输入的数据。
下面是我们用于嵌套视图的视图文件:
表单概要视图
<!-- form-profile.html --> <div class="form-group"> <label for="name">Name</label> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="name" ng-model="formData.name"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="email">Email</label> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="email" ng-model="formData.email"> </div> <div class="form-group row"> <div class="col-xs-6 col-xs-offset-3"> <a ui-sref="form.interests" class="btn btn-block btn-info"> Next Section <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-circle-arrow-right"></span> </a> </div> </div>
表单兴趣视图
<!-- form-interests.html -->
<label>What's Your Console of Choice?</label>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="radio">
<label>
<input type="radio" ng-model="formData.type" value="xbox" checked>
I like XBOX
</label>
</div>
<div class="radio">
<label>
<input type="radio" ng-model="formData.type" value="ps">
I like PS4
</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="col-xs-6 col-xs-offset-3">
<a ui-sref="form.payment" class="btn btn-block btn-info">
Next Section <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-circle-arrow-right"></span>
</a>
</div>
</div>
表单支付视图
<!-- form-payment.html --> <div class="text-center"> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-heart"></span> <h3 id="Thanks-For-Your-Money">Thanks For Your Money!</h3> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-danger">Submit</button> </div>
既然我们已经定义了这些视图,那么当我们浏览表单时,他们就会显示出来。同样我们用下一个按钮和ui-sref来连接每一个新视图.
当使用ui-sref时,你要连接到你路由中定义的state而不是URL。然后Angular会使用这个来为你构建href。
下面是我们表单目前的每一个页面。
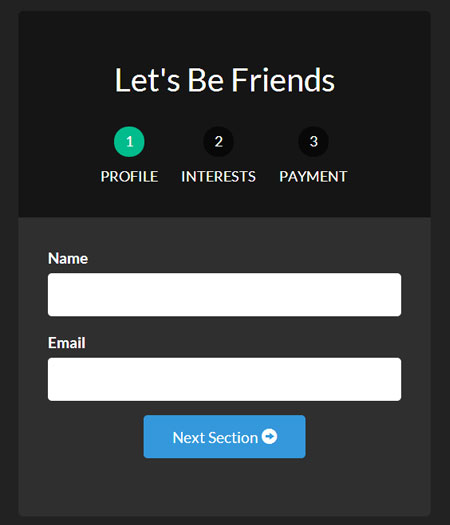
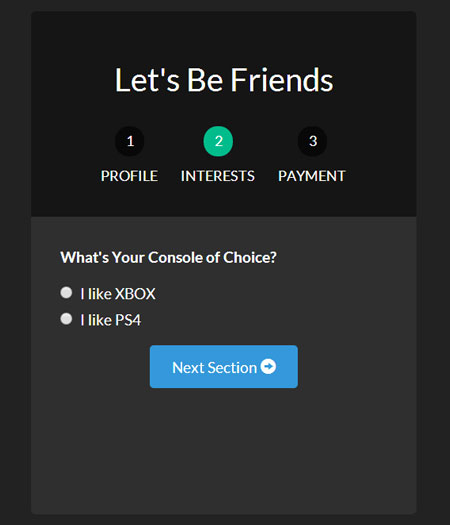
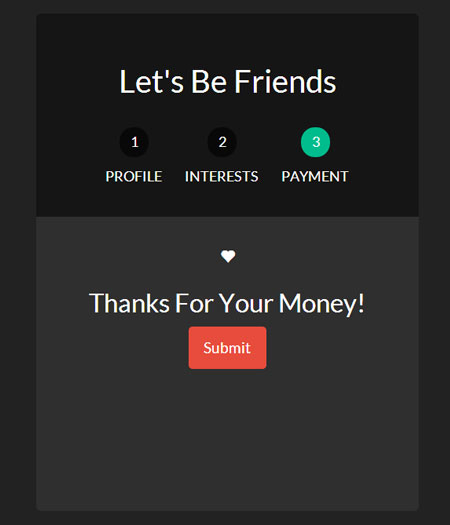
为了让我们的页面不同寻常,让我们加上动画效果。
让我们的表单产生动画效果
因为在项目开始的时候,我们已经加载了ngAnimate,它已经添加到需要动画的的类上了。当视图进入或退出的时候,它将自动添加类ng-enter和ng-leave。
现在我们所有做的就是通过样式形成我们最终的表单。为了理解Angular动画,这篇文章是一个很好的起点。
让我们进去css文件,将动画,并应用到我们的表单上
/* style.css */
/* ANIMATION STYLINGS
============================================================================= */
#signup-form { position:relative; min-height:300px; overflow:hidden; padding:30px; }
#form-views { width:auto; }
/* basic styling for entering and leaving */
/* left and right added to ensure full width */
#form-views.ng-enter,
#form-views.ng-leave { position:absolute; left:30px; right:30px;
transition:0.5s all ease; -moz-transition:0.5s all ease; -webkit-transition:0.5s all ease;
}
/* enter animation */
#form-views.ng-enter {
-webkit-animation:slideInRight 0.5s both ease;
-moz-animation:slideInRight 0.5s both ease;
animation:slideInRight 0.5s both ease;
}
/* leave animation */
#form-views.ng-leave {
-webkit-animation:slideOutLeft 0.5s both ease;
-moz-animation:slideOutLeft 0.5s both ease;
animation:slideOutLeft 0.5s both ease;
}
/* ANIMATIONS
============================================================================= */
/* slide out to the left */
@keyframes slideOutLeft {
to { transform: translateX(-200%); }
}
@-moz-keyframes slideOutLeft {
to { -moz-transform: translateX(-200%); }
}
@-webkit-keyframes slideOutLeft {
to { -webkit-transform: translateX(-200%); }
}
/* slide in from the right */
@keyframes slideInRight {
from { transform:translateX(200%); }
to { transform: translateX(0); }
}
@-moz-keyframes slideInRight {
from { -moz-transform:translateX(200%); }
to { -moz-transform: translateX(0); }
}
@-webkit-keyframes slideInRight {
from { -webkit-transform:translateX(200%); }
to { -webkit-transform: translateX(0); }
}
首先,确定视图离开或进去时,表单的样式,他们是绝对定位的。需要确认当视图进入的时候一个视图不会放到另一个视图的下面。
其次,应用我们的动画到.ng-enter和.ng-leave类
第三,用@keyframes定义动画。所有这些部分组合到一起,我们的表单就有了Angular动画,基于状态的UI Router和Angular数据绑定。
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),







