 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI When Sora detonated the video generation, Meta began to use Agent to automatically cut the video, led by Chinese authors
When Sora detonated the video generation, Meta began to use Agent to automatically cut the video, led by Chinese authorsWhen Sora detonated the video generation, Meta began to use Agent to automatically cut the video, led by Chinese authors
Recently, the field of AI video technology has attracted much attention, especially the Sora video generation large model launched by OpenAI, which has caused widespread discussion. At the same time, in the field of video editing, large-scale AI models such as Agent have also shown strong strength.
Although natural language is used to handle video editing tasks, users can directly express their intentions without manual operations. However, most current video editing tools still require a lot of manual operations and lack personalized contextual support. This results in users needing to solve complex video editing problems on their own.
The key is how to design a video editing tool that can act as a collaborator and continuously assist users during the editing process? In this article, researchers from the University of Toronto, Meta (Reality Labs Research), and the University of California, San Diego propose to use the multi-functional language capabilities of large language models (LLM) for video editing, and explore the future video editing paradigm, thereby Reduce frustration with the manual video editing process.

- Paper title: LAVE: LLM-Powered Agent Assistance and Language Augmentation for Video Editing
- Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.10294.pdf
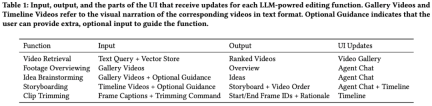
The researcher developed a video editing tool called LAVE, which integrates Multiple language enhancements provided by LLM. LAVE introduces an intelligent planning and execution system based on LLM, which can interpret the user's free-form language instructions, plan and execute related operations to achieve the user's video editing goals. This intelligent system provides conceptual assistance, such as creative brainstorming and video footage overviews, as well as operational assistance, including semantic-based video retrieval, storyboarding, and clip trimming.
In order to smoothly operate these agents, LAVE uses a visual language model (VLM) to automatically generate a language description of video visual effects. These visual narratives allow LLM to understand the video content and use their language capabilities to assist users in editing. In addition, LAVE provides two modes of interactive video editing, namely agent assistance and direct operation. This dual mode provides users with greater flexibility to improve the agent's operation as needed.
As for the editing effect of LAVE? The researchers conducted a user study with 8 participants, including novice and experienced editors, and the results showed that participants could use LAVE to create satisfactory AI collaborative videos.
It is worth noting that 5 of the six authors of this study are Chinese, including the first author, Bryan Wang, a doctoral student in computer science at the University of Toronto, Meta research scientists Yuliang Li, Zhaoyang Lv and Yan Xu and Haijun Xia, assistant professor at the University of California, San Diego.
LAVE User Interface (UI)
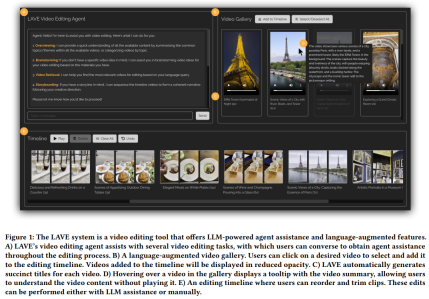
Let’s first look at the system design of LAVE, as shown in Figure 1 below.
LAVE's user interface consists of three main components, as follows:
- Language enhanced video library, displayed with automatic generation Video clips described in the language;
- Video clipping timeline, including the main timeline for editing;
- Video clipping agent, Enables users to interact with a conversational agent and get help.
#The design logic is this: when the user interacts with the agent, the message exchange will be displayed in the chat UI. When doing so, the agent makes changes to the video library and clip timeline. In addition, users can directly operate the video library and timeline using the cursor, similar to traditional editing interfaces.
Language enhancement video library
The functions of the language enhancement video library are as follows As shown in Figure 3.
Like traditional tools, this feature allows clip playback but provides visual narrative, i.e. automatically generated text descriptions for each video, including semantic titles and summaries. The titles help understand and index the clips, and the summaries provide an overview of each clip's visual content, helping users form the storyline of their editing project. A title and duration appear below each video.
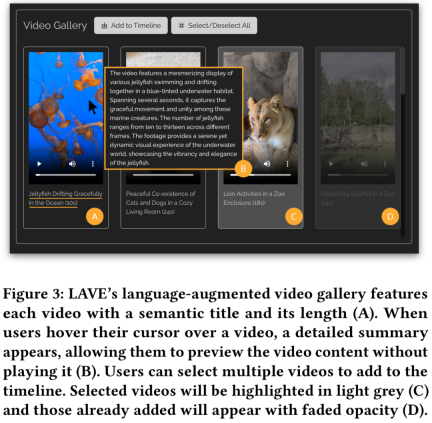
Additionally, LAVE enables users to search for videos using semantic language queries, and the retrieved videos are displayed in a video library and sorted by relevance. This function must be performed by the Clip Agent.
Video Clip Timeline
After selecting a video from the video library and adding it to the Clip Timeline , they will be displayed on the video clip timeline at the bottom of the interface, as shown in Figure 2 below. Each clip on the timeline is represented by a box and displays three thumbnail frames: the start frame, the middle frame, and the end frame.
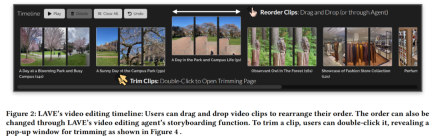
In the LAVE system, each thumbnail frame represents one second of material in the clip. As with the video gallery, a title and description are provided for each clip. The clip timeline in LAVE has two key features, clip sorting and trimming.
Sequencing clips on the timeline is a common task in video editing and is important for creating a coherent narrative. LAVE supports two sorting methods. One is LLM-based sorting, which uses the storyboard function of the video clip agent. The other is manual sorting, which is sorted by direct user operation. Drag and drop each video box to set the order in which clips appear.
Trimming is also important in video editing to highlight key segments and remove excess content. While trimming, the user double-clicks on the clip in the timeline, which opens a pop-up window showing one-second frames, as shown in Figure 4 below.

Video Clip Agent
LAVE The Video Clip Agent is a chat-based component that facilitates interaction between users and LLM-based agents. Unlike command line tools, users can interact with agents using free-form language. The agent leverages LLM's linguistic intelligence to provide video editing assistance and provide specific responses to guide and assist the user throughout the editing process. LAVE's agent assistance functionality is provided through agent operations, each of which involves performing a system-supported editing function.
Overall, LAVE offers features that cover the entire workflow from ideation and pre-planning to actual editing operations, but the system does not mandate a strict workflow. Users have the flexibility to leverage subsets of functionality that match their editing goals. For example, users with a clear editorial vision and a clear storyline may bypass the ideation phase and jump straight into editing.
Back-end system
This study uses OpenAI’s GPT-4 to illustrate the design of the LAVE back-end system, which mainly includes agent design, Implement two aspects of editing functions driven by LLM.
Agent Design
This research leverages the multi-language capabilities of LLM (i.e. GPT-4) (including Reasoning, planning, and storytelling) builds the LAVE agent.
LAVE agent has two states: planning and execution. This setup has two main benefits:
- Allows the user to set high-level goals that contain multiple actions, eliminating the need to detail each individual action like traditional command line tools .
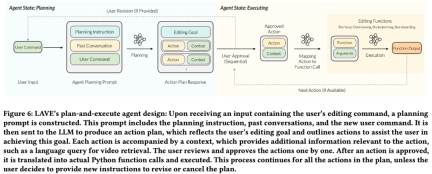
- Before execution, the agent will present the plan to the user, providing opportunities for modification and ensuring that the user has full control over the operation of the agent. The research team designed a back-end pipeline to complete the planning and execution process.
#As shown in Figure 6 below, the pipeline first creates an action plan based on user input. The plan is then converted from a textual description into function calls, and the corresponding functions are then executed.
Implement LLM driven editing function
In order to help users complete the video For editing tasks, LAVE mainly supports five functions driven by LLM, including:
- Material Overview
- Creative Brainstorming
- Video Retrieval
- Storyboard
- Clip Trim
The first four of them can be accessed through the agent (Figure 5), while the clip The trim feature is available by double-clicking on a clip in the timeline, which opens a pop-up window showing one-second frames (Figure 4).

Among them, language-based video retrieval is implemented through the vector storage database, and the rest is implemented through LLM prompt engineering. All features are built on automatically generated verbal descriptions of the original footage, including titles and summaries for each clip in the video library (Figure 3). The research team calls the text descriptions of these videos visual narration.

Interested readers can read the original text of the paper to learn more about the research content.
The above is the detailed content of When Sora detonated the video generation, Meta began to use Agent to automatically cut the video, led by Chinese authors. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!






