JQ command usage examples in Linux
JSON is a data representation format used to store and transfer data between different layers of an application; it stores data in key:value pairs. In this article, we will learn to use JQ commands to manipulate and process JSON data in the shell.
How to install JQ command
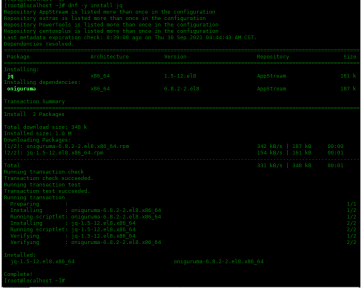
Use the following command to install jq in Centos8:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -y install jq
grammar
Now we can start using the JQ command since it has been successfully installed on our system, but first, let’s take a look at the syntax of the JQ command:
jq [options] [file...] jq [options] --args [strings...] jq [options] --jsonargs [JSON_TEXTS...]
The JQ command can be used in a number of different ways; it can be used directly on JSON files or combined with several other commands to interpret JSON data. JQ commands can be used with different filters such as ".", "|", "," or ".[]" filters to organize JSON data.
The JQ command also takes different options as arguments, such as –tab, –stream, –indent n, –unbuffered and the -L directory option. The syntax of JQ commands may seem complicated at first, but you'll become familiar with it after reading the entire article.
How to use JQ commands to organize JSON data
The simplest and most commonly used feature of JQ command filter. They are used to organize and beautify JSON data when printing it to standard output.
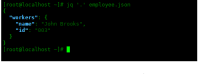
In this example, we have a JSON file named employee.json and we need to output the data to standard output:
{"workers":{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"}}
We can use the cat command to display data:
[root@localhost ~]# cat employee.json
{"workers":{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"}}

The data printed to standard output using the cat command is unorganized and confusing. We can use JQ commands and "." to organize this data, and use . to filter:
[root@localhost ~]# jq '.' employee.json
{
"workers": {
"name": "John Brooks",
"id": "003"
}
}
Now the data is more organized, colorful and easier to understand. This filter is especially needed when accessing data from an API; the data stored in the API can be very unorganized and confusing.
How to use JQ commands to access properties
.FieldsFilters and JQ commands can be used to access object properties in the shell.
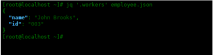
If we only want to access a single property and print it to standard output, then we can use the .field operator. For example, to access a worker's properties we can use the following command:
[root@localhost ~]# jq '.workers' employee.json
{
"name": "John Brooks",
"id": "003"
}
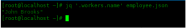
We can also access the items present in the attribute using the .field operator. To access the name item in the worker attribute we will use:
[root@localhost ~]# jq '.workers.name' employee.json "John Brooks"
How to use JQ commands to access array items
We can also access and output the elements present in the array in the JSON file using the .[] operator. For this example, we will modify our JSON file and add the following:
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]
Check the employee.json file:
[root@localhost ~]# cat employee.json
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]

要输出 JSON 文件中存在的所有数组,我们将运行以下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# jq '.[]' employee.json
{
"name": "John Brooks",
"id": "003"
}
{
"name": "Randy Park",
"id": "053"
}
{
"name": "Todd Gray",
"id": "009"
}

要仅输出第二个数组,我们可以通过以下方式修改上述命令:
[root@localhost ~]# jq '.[1]' employee.json
{
"name": "Randy Park",
"id": "053"
}

请记住,数组从索引 0 开始的。
我们还可以使用 .字段 运算符访问数组中存在的属性。例如,如果我们想访问第三个数组中的 name 属性,那么我们将运行以下命令:
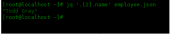
[root@localhost ~]# jq '.[2].name' employee.json "Todd Gray"
类似地,要访问数组中的所有名称属性,我们可以执行以下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# jq '.[].name' employee.json "John Brooks" "Randy Park" "Todd Gray"

总 结
JQ 命令用于将 JSON 数据转换为更易读的格式并将其打印到 Linux 上的标准输出。JQ 命令是围绕过滤器构建的,过滤器用于从 JSON 文件中仅查找和打印所需的数据。
The above is the detailed content of JQ command usage examples in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Does the internet run on Linux?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Does the internet run on Linux?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AMThe Internet does not rely on a single operating system, but Linux plays an important role in it. Linux is widely used in servers and network devices and is popular for its stability, security and scalability.
 What are Linux operations?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What are Linux operations?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AMThe core of the Linux operating system is its command line interface, which can perform various operations through the command line. 1. File and directory operations use ls, cd, mkdir, rm and other commands to manage files and directories. 2. User and permission management ensures system security and resource allocation through useradd, passwd, chmod and other commands. 3. Process management uses ps, kill and other commands to monitor and control system processes. 4. Network operations include ping, ifconfig, ssh and other commands to configure and manage network connections. 5. System monitoring and maintenance use commands such as top, df, du to understand the system's operating status and resource usage.
 Boost Productivity with Custom Command Shortcuts Using Linux AliasesApr 12, 2025 am 11:43 AM
Boost Productivity with Custom Command Shortcuts Using Linux AliasesApr 12, 2025 am 11:43 AMIntroduction Linux is a powerful operating system favored by developers, system administrators, and power users due to its flexibility and efficiency. However, frequently using long and complex commands can be tedious and er
 What is Linux actually good for?Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What is Linux actually good for?Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AMLinux is suitable for servers, development environments, and embedded systems. 1. As a server operating system, Linux is stable and efficient, and is often used to deploy high-concurrency applications. 2. As a development environment, Linux provides efficient command line tools and package management systems to improve development efficiency. 3. In embedded systems, Linux is lightweight and customizable, suitable for environments with limited resources.
 Essential Tools and Frameworks for Mastering Ethical Hacking on LinuxApr 11, 2025 am 09:11 AM
Essential Tools and Frameworks for Mastering Ethical Hacking on LinuxApr 11, 2025 am 09:11 AMIntroduction: Securing the Digital Frontier with Linux-Based Ethical Hacking In our increasingly interconnected world, cybersecurity is paramount. Ethical hacking and penetration testing are vital for proactively identifying and mitigating vulnerabi
 How to learn Linux basics?Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AM
How to learn Linux basics?Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AMThe methods for basic Linux learning from scratch include: 1. Understand the file system and command line interface, 2. Master basic commands such as ls, cd, mkdir, 3. Learn file operations, such as creating and editing files, 4. Explore advanced usage such as pipelines and grep commands, 5. Master debugging skills and performance optimization, 6. Continuously improve skills through practice and exploration.
 What is the most use of Linux?Apr 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM
What is the most use of Linux?Apr 09, 2025 am 12:02 AMLinux is widely used in servers, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In the server field, Linux has become an ideal choice for hosting websites, databases and applications due to its stability and security. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is popular for its high customization and efficiency. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides a variety of desktop environments to meet the needs of different users.
 What are the disadvantages of Linux?Apr 08, 2025 am 12:01 AM
What are the disadvantages of Linux?Apr 08, 2025 am 12:01 AMThe disadvantages of Linux include user experience, software compatibility, hardware support, and learning curve. 1. The user experience is not as friendly as Windows or macOS, and it relies on the command line interface. 2. The software compatibility is not as good as other systems and lacks native versions of many commercial software. 3. Hardware support is not as comprehensive as Windows, and drivers may be compiled manually. 4. The learning curve is steep, and mastering command line operations requires time and patience.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






