 Software Tutorial
Software Tutorial Office Software
Office Software The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL
The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCELThe difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL

The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL
The so-called absolute references and relative references are for cells. For example, $A$1 is an absolute reference and A1 is a relative reference ($A1 and A$1 are mixed references)
Assume A1=1,A2=2,A3=3,....
If you enter the formula =$A$1*2 in b1, and then drag it down to fill, the formula in each cell in column B is =$A$1*2, and its values are B1=2, B2 respectively. =2,B3=2,......
If you enter the formula =A1*2 in b1, and then drag down to fill, the formulas in the cells in column B are (B1)=A1*2, (B2)=A2*2, (B3)= A3*2,...their values are B1=2,B2=4,B3=6,...
Do you understand this clearly? For a formula that absolutely references a cell, the referenced cell will remain unchanged no matter where the formula is copied; for a formula that refers to a relative cell, the referenced cell will change depending on where the formula is copied.
How to achieve relative reference to rows when copying cells in Excel tables and absolute reference to rows when pulling down
1. The cell address can be written as $B1
2. Whoever $ precedes will definitely be quoted
A1 is a relative reference
$A1 absolute reference column is a mixed reference
A$1 absolute reference line is a mixed reference
$A$1 absolute reference row and column are absolute references
F4 is a shortcut key for switching between four types of references (press the F4 function key when entering a formula in the edit bar to switch)
three,
A1 (relative reference) will become references A2, A3, A4... when you pull down and drag the reference. When you drag it to the right, the reference will become B1, C1, D1....;
A$1 (Mixed Reference) When you want to ensure that only cell A1 is referenced when you pull down and copy, A1 must add a $ sign to become A$1, so that you can ensure a relative reference to the first row of column A when you pull down. (That is, keeping the line number unchanged when referencing);
$A1 (Mixed Reference) When you pull right to copy and want to ensure that only the A1 cell is referenced, A1 must add the $ symbol to become $A1, so that when you pull right to copy, you can ensure that the first row of column A is referenced. Relative reference (that is, keeping the column label unchanged when referencing);
$A$1 (absolute reference) When you want to ensure that only the A1 cell is referenced when copying in pull-down and right pull-down, A1 must add the $ symbol to become $A$1, so that it can be guaranteed in pull-down and right pull-down. An absolute reference to the first row of column A (that is, keeping the row number column label unchanged during the reference).
When to use relative references and absolute references in Excel functions
For example, the ranking function RANK.
If you want to get the ranking of column B data and only calculate cell B2, you can enter =RANK(B2,B2:B18) in cell C2, and the result is correct
B2 here is a relative reference cell, and B2:B18 is a relative reference area.
But if you copy the ranking formula of cell C2 downward, the result will be wrong,
Because in cell C3, the formula becomes =RANK(B3,B3:B19);
In cell C4, the formula becomes =RANK(B4,B4:B20);
Obviously, the relative reference of the previous cell is correct, but the later reference area has been changing, causing errors in the ranking results.
Therefore, when filling downwards, the subsequent reference area should be modified to an absolute reference or a relative-absolute mixed reference to ensure that the reference area will not change with copying or filling
The formula in cell C2 becomes
=RANK(B2,$B$2:$B$18)
or=RANK(B2,B$2:B$18)
I hope this example can help you improve your understanding of relative references and absolute references.
The above is the detailed content of The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
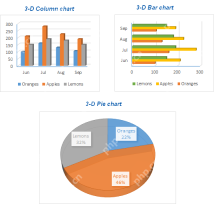 How to make a chart (graph) in Excel and save it as templateApr 28, 2025 am 09:31 AM
How to make a chart (graph) in Excel and save it as templateApr 28, 2025 am 09:31 AMThis Excel charting tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to creating and customizing graphs within Microsoft Excel. Learn to visualize data effectively, from basic chart creation to advanced techniques. Everyone uses Excel charts to visualize dat
 Excel charts: add title, customize chart axis, legend and data labelsApr 28, 2025 am 09:18 AM
Excel charts: add title, customize chart axis, legend and data labelsApr 28, 2025 am 09:18 AMAfter you have created a chart in Excel, what's the first thing you usually want to do with it? Make the graph look exactly the way you've pictured it in your mind! In modern versions of Excel, customizing charts is easy and fun. Microsof
 Using Excel REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE functions - formula examplesApr 28, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Using Excel REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE functions - formula examplesApr 28, 2025 am 09:16 AMThis tutorial demonstrates the Excel REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE functions with practical examples. Learn how to use REPLACE with text, numbers, and dates, and how to nest multiple REPLACE or SUBSTITUTE functions within a single formula. Last week, we ex
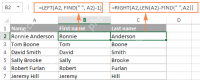 Excel FIND and SEARCH functions with formula examplesApr 28, 2025 am 09:09 AM
Excel FIND and SEARCH functions with formula examplesApr 28, 2025 am 09:09 AMThis tutorial details the syntax and advanced applications of Excel's FIND and SEARCH functions. Previous articles covered the basic Find and Replace dialog; this expands on using Excel to automatically locate and extract data based on specified cri
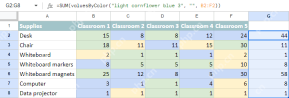 Count & sum cells by color in Google SheetsApr 28, 2025 am 09:04 AM
Count & sum cells by color in Google SheetsApr 28, 2025 am 09:04 AMGoogle Sheets lacks built-in functions for summarizing data based on cell color. To overcome this, custom functions are provided that consider both font and background colors for basic calculations, enabling color-based summing and counting. These
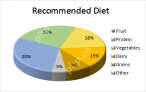 How to make a pie chart in ExcelApr 27, 2025 am 09:37 AM
How to make a pie chart in ExcelApr 27, 2025 am 09:37 AMThis Excel pie chart tutorial guides you through creating and customizing pie charts. Learn to build effective pie charts, avoiding common pitfalls. Pie charts, also called circular graphs, visually represent proportions of a whole. Each slice repr
 How to create a chart in Excel from multiple sheetsApr 27, 2025 am 09:22 AM
How to create a chart in Excel from multiple sheetsApr 27, 2025 am 09:22 AMThis tutorial shows how to create and modify Excel charts from data across multiple worksheets. Previously, we covered basic charting; this expands on that by addressing the common question of combining data from different sheets. Creating Charts fr
 Why use $ in Excel formula: relative & absolute cell referenceApr 27, 2025 am 09:13 AM
Why use $ in Excel formula: relative & absolute cell referenceApr 27, 2025 am 09:13 AMThe dollar sign ($) in cell references in Excel formulas often confuses users, but its principle is simple. The dollar sign has only one function in Excel cell references: it tells Excel whether to change the reference when copying a formula to another cell. This tutorial will explain this feature in detail. The importance of Excel cell reference cannot be overemphasized. Understand the difference between absolute, relative, and mixed citations, and you've mastered half of the power of Excel formulas and functions. You may have seen the dollar sign ($) in the Excel formula and want to know what it is. In fact, you can refer to the same cell in four different ways, such as A1, $A


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.





