 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Application scenarios and examples: Application of directed acyclic graph (DAG) in the shortest path problem
Application scenarios and examples: Application of directed acyclic graph (DAG) in the shortest path problemApplication scenarios and examples: Application of directed acyclic graph (DAG) in the shortest path problem

有向无环图(DAG)在最短路径问题中可以优化算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度。在任务调度、时间管理等实际应用中,DAG可方便确定任务执行顺序,通过拓扑排序简化动态规划计算,提高算法效率。本文将详细介绍DAG在最短路径问题中的应用,并通过代码示例说明实现方式。
一、DAG介绍
DAG是一种有向图,它没有环。这意味着从任何一个顶点出发,都不可能回到该顶点。因此,DAG可以用来表示具有特定约束关系的任务调度问题,例如某些任务必须在其他任务完成之后才能开始。DAG的特性使得它在计算机科学和工程领域有着广泛的应用,例如编译器优化、并行计算和数据流分析等。通过合理的任务调度和依赖关系管理,DAG可以提高系统的效率和性能,有效地解决复杂的任务调度问题。
二、最短路径问题
最短路径问题涉及从起点到终点的路径,目标是找到边权值和最小的路径。在有向无环图中,可以通过拓扑排序和动态规划来解决。
拓扑排序是一种用于确定有向无环图(DAG)中节点相对顺序的方法,它对应于动态规划中递推公式的正确计算。在拓扑排序过程中,节点的入度起着关键作用。首先,从入度为0的节点开始,将其加入拓扑序列,并将其邻接节点的入度减1。然后,重复这个过程,直到所有节点都被加入拓扑序列,或者发现DAG中存在环。通过拓扑排序,我们可以获得DAG中节点的相对顺序,从而确保动态规划的递推公式的正确性。
动态规划的递推公式如下:
设dist表示从起点到节点i的最短路径长度,则有:
dist=min{dist[j]+w(j,i)},其中j是i的前驱节点,w(j,i)是从j到i的边权值。
为了方便起见,可以使用一个数组d来存储dist的值,初始时所有节点的d值设置为无穷大,起点的d值设置为0。然后,按照拓扑序列的顺序,依次更新每个节点的d值,直到更新完所有节点。具体而言,对于每个节点i,遍历其所有邻接节点j,如果d[j]+w(j,i)
这个过程可以用代码来实现,示例代码如下:
def shortest_path(graph, start):
# 初始化d数组,起点d值为0,其他节点d值为无穷大
d = {node: float('inf') for node in graph}
d[start] = 0
# 拓扑排序,确定节点的相对顺序
topo_order = []
in_degree = {node: 0 for node in graph}
for node in graph:
for neighbor in graph[node]:
in_degree[neighbor] += 1
queue = [node for node in graph if in_degree[node] == 0]
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
topo_order.append(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
in_degree[neighbor] -= 1
if in_degree[neighbor] == 0:
queue.append(neighbor)
# 动态规划,依次更新每个节点的d值
for node in topo_order:
for neighbor in graph[node]:
new_distance = d[node] + graph[node][neighbor]
if new_distance < d[neighbor]:
d[neighbor] = new_distance
return d三、有向无环图在最短路径问题中的应用示例
假设有一个任务调度问题,有7个任务需要完成,它们之间有一些依赖关系,其中,设红色节点表示起点,绿色节点表示终点。每个节点的标签表示该任务的耗时。任务之间的边表示依赖关系,比如节点1和2之间的边表示任务2必须在任务1完成后才能开始。
现在,我们需要找到一种最短的方式来完成所有任务,即使得完成所有任务的总时间最小。这个问题可以转化为一个最短路径问题,其中每个节点表示一个任务,节点之间的边表示依赖关系,边权值表示完成前一个任务所需要的时间。
根据上面的动态规划递推公式,我们可以使用拓扑排序和动态规划来解决这个问题。代码如下:
graph = {
1: {2: 2, 3: 1},
2: {4: 2, 5: 3},
3: {4: 1, 5: 2},
4: {6: 4},
5: {6: 2},
6: {}
}
start = 1
dist = shortest_path(graph, start)
print(dist[6]) # 输出最短路径长度,即完成所有任务的最小时间输出结果为:9,表示完成所有任务的最小时间为9个时间单位。
The above is the detailed content of Application scenarios and examples: Application of directed acyclic graph (DAG) in the shortest path problem. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
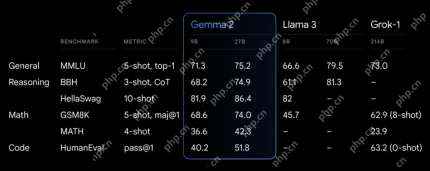 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,
 What are the TCL Commands in SQL? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
What are the TCL Commands in SQL? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:07 AMIntroduction Transaction Control Language (TCL) commands are essential in SQL for managing changes made by Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. These commands allow database administrators and users to control transaction processes, thereby


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor





