 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Google MIT's latest research shows: Obtaining high-quality data is not difficult, large models are the solution
Google MIT's latest research shows: Obtaining high-quality data is not difficult, large models are the solutionGoogle MIT's latest research shows: Obtaining high-quality data is not difficult, large models are the solution
Получение высококачественных данных стало основным узким местом в современном обучении больших моделей.
Несколько дней назад газета New York Times подала в суд на OpenAI и потребовала миллиарды долларов компенсации. В жалобе перечислены многочисленные доказательства плагиата со стороны GPT-4.
Даже New York Times призывала к уничтожению почти всех крупных моделей, таких как GPT.

Многие громкие имена в индустрии искусственного интеллекта уже давно полагают, что «синтетические данные» могут быть лучшим решением этой проблемы.

Ранее команда Google также предложила RLAIF, метод, который использует LLM для замены предпочтений человека в отношении маркировки, и эффект даже не уступает люди.

Теперь исследователи из Google и MIT обнаружили, что обучение на больших моделях может привести к представлениям лучших моделей, обученных с использованием реальных данных.
Этот последний метод называется SynCLR и представляет собой метод изучения виртуальных представлений полностью на основе синтетических изображений и синтетических описаний без каких-либо реальных данных.

Адрес статьи: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.17742
Результаты эксперимента показывают, что представление, полученное с помощью метода SynCLR, может быть таким же хорошим, как эффект передачи CLIP OpenAI в ImageNet.

Обучение на генеративных моделях
#Наиболее эффективные методы обучения «визуального представления» в настоящее время основаны на крупномасштабных реальных наборах данных. Однако при сборе реальных данных возникает много трудностей.
Чтобы снизить затраты на сбор данных, исследователи в этой статье задаются вопросом:
Выборка из готовых материалов генеративные модели Являются ли синтетические данные жизнеспособным путем к созданию масштабных наборов данных для обучения современным визуальным представлениям?

## В отличие от обучения непосредственно на данных, исследователи Google называют эту модель «обучением на модели». В качестве источника данных для создания крупномасштабных обучающих наборов модели имеют несколько преимуществ:
- Предоставляют новые методы управления данными через скрытые переменные, условные переменные и гиперпараметры.
— моделями также легче делиться и хранить (поскольку модели легче сжимать, чем данные), и они могут создавать неограниченное количество образцов данных.
Все большее количество литературы исследует эти свойства, а также другие преимущества и недостатки генеративных моделей как источника данных для обучения последующих моделей.
Некоторые из этих методов используют гибридную модель, т. е. смешивают реальные и синтетические наборы данных или требуют, чтобы один реальный набор данных генерировал другой синтетический набор данных.
Другие методы пытаются изучить представления на основе чисто «синтетических данных», но сильно отстают от наиболее эффективных моделей.
В статье последний метод, предложенный исследователями, использует генеративную модель для переопределения степени детализации классов визуализации.
Как показано на рисунке 2, четыре изображения были созданы с использованием двух подсказок: «Золотистый ретривер в солнцезащитных очках и пляжной шляпе едет на велосипеде» и «Милый золотистый ретривер». Собака сидит. в доме из суши».

Traditional self-supervised methods (such as Sim-CLR) will treat these images as different classes, and the embeddings of different images will be separated, without explicitly considering the shared semantics between images.
At the other extreme, supervised learning methods (i.e. SupCE) treat all these images as a single class (such as "golden retriever"). This ignores semantic nuances in the images, such as a dog riding a bicycle in one pair of images and a dog sitting in a sushi house in another.
In contrast, the SynCLR approach treats descriptions as classes, i.e. one visual class per description.
In this way, we can group the pictures according to the two concepts of "riding a bicycle" and "sitting in a sushi restaurant".
This kind of granularity is difficult to mine in real data because collecting multiple images by a given description is not trivial, especially when the number of descriptions increases.
However, the text-to-image diffusion model fundamentally has this capability.
By simply conditioning on the same description and using different noise inputs, a text-to-image diffusion model can generate different images that match the same description.
Specifically, the authors study the problem of learning visual encoders without real image or text data.
Latest methods rely on the utilization of 3 key resources: a language generative model (g1), a text-to-image generative model (g2), and a curated list of visual concepts ( c).
Pre-processing includes three steps:
(1) Use (g1) to synthesize a comprehensive set of image descriptions T, which covers Various visual concepts in C;
(2) For each title in T, use (g2) to generate multiple images, ultimately generating an extensive synthetic image dataset X ;
(3) Train on X to obtain the visual representation encoder f.
Then, use llama-27b and Stable Diffusion 1.5 as (g1) and (g2) respectively because of their fast inference speed.
Synthetic description
To take advantage of the power of powerful text-to-image models to generate large amounts of training image data Set, first requires a set of descriptions that not only accurately describe the image but also exhibit diversity to encompass a wide range of visual concepts.
In response, the authors developed a scalable method to create such a large set of descriptions, leveraging the contextual learning capabilities of large models.
The following shows three examples of synthetic templates.

The following is a context description generated using Llama-2. The researchers randomly sampled three context examples in each inference run.

Synthetic Image
For each text description, the researchers The back-diffusion process is started with different random noises, resulting in various images.
In this process, the classifier-free bootstrapping (CFG) ratio is a key factor.
The higher the CFG scale, the better the quality of the samples and the consistency between text and images, while the lower the scale, the greater the diversity of the samples, that is The closer it is to the original conditional distribution of the image based on the given text.

Representation learning
In the paper, the representation learning method is based on Based on StableRep.
The key component of the method proposed by the authors is the multi-positive contrast learning loss, which works by aligning (in embedding space) images generated from the same description.
In addition, various techniques from other self-supervised learning methods were also combined in the study.
Comparable to OpenAI’s CLIP
In the experimental evaluation, the researchers first conducted an ablation study to evaluate the effectiveness of various designs and modules within the pipeline, and then continued to expand the amount of synthetic data.
The following figure is a comparison of different description synthesis strategies.
The researchers report the ImageNet linear evaluation accuracy and average accuracy on 9 fine-grained datasets. Each item here includes 10 million descriptions and 4 pictures per description.

The following table is a comparison of ImageNet linear evaluation and fine-grained classification.
Despite using only synthetic data, SynCLR achieved comparable results to OpenAI’s CLIP and DINO v2 models.

The following table compares SynCLR and CLIP on the same synthetic data. It can be seen that SynCLR is significantly better than CLIP.
The specific setting is to generate 4 images per title. SynCaps-150M provides better representation for SynCLR and CLIP.

PCA visualization is as follows. Following DINO v2, the researchers calculated PCA between patches of the same set of images and colored them based on their first 3 components.
Compared with DINO v2, SynCLR is more accurate for drawings of cars and airplanes, but slightly worse for drawings that can be drawn.

Figure 6 and Figure 7 respectively show the linear accuracy of ImageNet under different training scales and the fine classification under different training parameter scales. .

Why learn from generative models?
One compelling reason is that generative models can operate on hundreds of data sets simultaneously, providing a convenient and efficient way to curate training data.
In summary, the latest paper investigates a new paradigm of visual representation learning - learning from generative models.
Without using any actual data, SynCLR learns visual representations that are comparable to those learned by state-of-the-art general-purpose visual representation learners.
The above is the detailed content of Google MIT's latest research shows: Obtaining high-quality data is not difficult, large models are the solution. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
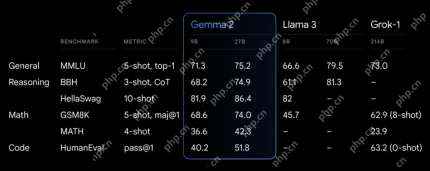 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools





