 Web Front-end
Web Front-end H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial HTML5 Guide-5. Use web storage to store key-value pair data_html5 tutorial tips
HTML5 Guide-5. Use web storage to store key-value pair data_html5 tutorial tipsHTML5 Guide-5. Use web storage to store key-value pair data_html5 tutorial tips
The content of this lesson is to introduce web storage, which is used to store key-value pair data in the browser. It functions like the previous cookies, but it is better and can store larger data. There are two types of web storage: local storage and session storage. They use the same implementation mechanism, but have different visibility and life cycles. There are items There are items
1. Use local storage
We use the localStorage object to access local storage. It returns the Storage object. Storage is used to store key-value pair data. It has the following properties and methods:
clear(): Clear the stored key-value pair data;
getItem(
key(
length: Returns the number of key-value pairs;
removeItem(
setItem(
[
Storage object allows us to store key-value pair data in the form of strings. The key is unique, which means that when we use the setItem method to add a key-value pair, if the key value already exists, it will be updated. operation. Let’s look at the following example:
> ;
Item Count: -
<script> <br />displayData(); <br />var buttons = document.getElementsByTagName('button'); <br />for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i ) { <br />buttons[i].onclick = handleButtonPress; <br />} <br />function handleButtonPress(e) { <br />switch (e.target.id) { <br />case 'add': <br />var key = document.getElementById('key').value; <br />var value = document.getElementById('value').value; <br />localStorage.setItem(key, value); <br />break; <br />case 'clear': <br />localStorage.clear(); <br />break; <br />} <br />displayData(); <br />} <br />function displayData() { <br />var tableElement = document.getElementById ('data'); <br />tableElement.innerHTML = ''; <br />var itemCount = localStorage.length; <br />document.getElementById('count').innerHTML = itemCount; <br />for (var i = 0; i < itemCount; i ) { <br />var key = localStorage.key(i); <br />var val = localStorage.getItem(key); <br />tableElement.innerHTML = '<tr>< th>' key ':<td>' val ''; <br />} <br />} <br /></script>
< ;/body>
Let’s take a look at the running results:
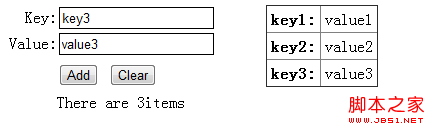
The browser cannot delete the data we created through localStorage unless the user deletes it.
2. Listen to Storage events
Data stored through local storage is visible to documents from the same source. For example, if you open two chrome browsers to access the same URL address, on any page The local storage created on the page is also visible to another page. However, if you use another browser (such as Firefox) to open the same URL address, the local storage will not be visible because they have different sources. The Storage event is used to monitor changes in the storage content. Let’s see what attributes it contains:
key: Returns the changed key value;
oldValue: Returns the value before the key value was changed;
newValue: Returns the new value of the changed key value;
url: The changed url address;
storageArea: Returns the changed Storage object (whether it is local storage or session storage).
Let’s look at an example below:
key oldValue newValue
url storageArea
<script> <br />var tableElement = document.getElementById('data'); <br />window.onstorage = function (e) { <br />var row = '<tr>'; <br />row = '<td>' e.key '< ;/td>'; <br />row = '<td>' e.oleValue ''; <br />row = '<td>' e.newValue ''; <br />row = '<td>' e.url ''; <br />row = '<td>' (e.storageArea == localStorage) ' tr>'; <br />tableElement.innerHTML = row; <br />} <br /></script>
The data we added, deleted, and modified storage in Example 1 will be displayed on the Example 2 page. Example 2 runs normally in Chrome browser, but Firefox does not respond. Other browsers have not been tested.
Run result:

3. Use session storage
Session storage is used the same as local storage, except that its accessibility is limited to the current page, and it will disappear after the page is closed. We access it through sessionStorage.
Item Count: -
<script> <br />displayData(); <br />var buttons = document.getElementsByTagName("button"); <br />for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i ) { <br />buttons[i].onclick = handleButtonPress; <br />} <br />function handleButtonPress(e) { <br />switch (e.target.id) { <br />case 'add': <br />var key = document.getElementById("key").value; <br />var value = document.getElementById("value").value; <br />sessionStorage.setItem(key, value); <br />break; <br />case 'clear': <br />sessionStorage.clear(); <br />break; <br />} <br />displayData(); <br />} <br />function displayData() { <br />var tableElement = document.getElementById('data'); <br />tableElement.innerHTML = ''; <br />var itemCount = sessionStorage.length; <br />document.getElementById('count').innerHTML = itemCount; <br />for (var i = 0; i < itemCount; i ) { <br />var key = sessionStorage.key(i); <br />var val = sessionStorage.getItem(key); <br />tableElement.innerHTML = "<tr><th>" key ":<td>" val ""; <br />} <br />} <br /></script>
运行效果:

你在例3中做任何修改,例2的页面不会发生任何改变。
总结:
sessionStorage用于本地存储一个会话(session)中的数据,这些数据只有在同一个会话中的页面才能访问并且当会话结束后数据也随之销毁。因此sessionStorage不是一种持久化的本地存储,仅仅是会话级别的存储。
localStorage用于持久化的本地存储,除非主动删除数据,否则数据是永远不会过期的。
web storage和cookie的区别:Web Storage的概念和cookie相似,区别是它是为了更大容量存储设计的。Cookie的大小是受限的,并且每次你请求一个新的页面的时候Cookie都会被发送过去,这样无形中浪费了带宽,另外cookie还需要指定作用域,不可以跨域调用。除此之外,Web Storage拥有setItem,getItem,removeItem,clear等方法,不像cookie需要前端开发者自己封装setCookie,getCookie。还有,web storage每个域(包括子域)有独立的存储空间,各个存储空间是完全独立的,因此不会造成数据混乱。
但是Cookie也是不可以或缺的:Cookie的作用是与服务器进行交互,作为HTTP规范的一部分而存在 ,而Web Storage仅仅是为了在本地“存储”数据而生。
源码下载
 HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AMThere is no difference between HTML5 and H5, which is the abbreviation of HTML5. 1.HTML5 is the fifth version of HTML, which enhances the multimedia and interactive functions of web pages. 2.H5 is often used to refer to HTML5-based mobile web pages or applications, and is suitable for various mobile devices.
 HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AMHTML5 is the latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language, standardized by W3C. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, multimedia support and form enhancements, improving web structure, user experience and SEO effects. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, such as, ,, etc., to make the web page structure clearer and the SEO effect better. HTML5 supports multimedia elements and no third-party plug-ins are required, improving user experience and loading speed. HTML5 enhances form functions and introduces new input types such as, etc., which improves user experience and form verification efficiency.
 H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AM
H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AMHow to write clean and efficient HTML5 code? The answer is to avoid common mistakes by semanticizing tags, structured code, performance optimization and avoiding common mistakes. 1. Use semantic tags such as, etc. to improve code readability and SEO effect. 2. Keep the code structured and readable, using appropriate indentation and comments. 3. Optimize performance by reducing unnecessary tags, using CDN and compressing code. 4. Avoid common mistakes, such as the tag not closed, and ensure the validity of the code.
 H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AMH5 improves web user experience with multimedia support, offline storage and performance optimization. 1) Multimedia support: H5 and elements simplify development and improve user experience. 2) Offline storage: WebStorage and IndexedDB allow offline use to improve the experience. 3) Performance optimization: WebWorkers and elements optimize performance to reduce bandwidth consumption.
 Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AMHTML5 code consists of tags, elements and attributes: 1. The tag defines the content type and is surrounded by angle brackets, such as. 2. Elements are composed of start tags, contents and end tags, such as contents. 3. Attributes define key-value pairs in the start tag, enhance functions, such as. These are the basic units for building web structure.
 Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AMHTML5 is a key technology for building modern web pages, providing many new elements and features. 1. HTML5 introduces semantic elements such as, , etc., which enhances web page structure and SEO. 2. Support multimedia elements and embed media without plug-ins. 3. Forms enhance new input types and verification properties, simplifying the verification process. 4. Offer offline and local storage functions to improve web page performance and user experience.
 H5 Code: Best Practices for Web DevelopersApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
H5 Code: Best Practices for Web DevelopersApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AMBest practices for H5 code include: 1. Use correct DOCTYPE declarations and character encoding; 2. Use semantic tags; 3. Reduce HTTP requests; 4. Use asynchronous loading; 5. Optimize images. These practices can improve the efficiency, maintainability and user experience of web pages.
 H5: The Evolution of Web Standards and TechnologiesApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AM
H5: The Evolution of Web Standards and TechnologiesApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AMWeb standards and technologies have evolved from HTML4, CSS2 and simple JavaScript to date and have undergone significant developments. 1) HTML5 introduces APIs such as Canvas and WebStorage, which enhances the complexity and interactivity of web applications. 2) CSS3 adds animation and transition functions to make the page more effective. 3) JavaScript improves development efficiency and code readability through modern syntax of Node.js and ES6, such as arrow functions and classes. These changes have promoted the development of performance optimization and best practices of web applications.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools




