Home >Technology peripherals >AI >OpenAI strengthens security team, empowering them to veto dangerous AI
OpenAI strengthens security team, empowering them to veto dangerous AI
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-12-19 17:30:411384browse
Models in production are managed by the "Security Systems" team. Leading edge models in development have “readiness” teams that identify and quantify risks before the model is released. Then there's the "Super Alignment" team, who are working on theoretical guidelines for "super intelligence" models
Reorganize the security advisory group to sit above the technical team to make recommendations to leadership and give the board veto power
OpenAI announced that in order to defend against the threat of harmful artificial intelligence, they are strengthening their internal security processes. They will create a new department called the "Security Advisory Group," which will sit above the technology team and provide advice to leadership and be given board veto power. This decision was announced on December 18, local time
The update is causing concern mainly because OpenAI CEO Sam Altman was fired by the board of directors, which appears to be related to security issues with large models. Two "slowdown" members of OpenAI's board of directors, Ilya Sutskvi and Helen Toner, lost their board seats following a high-level shakeup
In this post, OpenAI discusses their latest “Preparedness Framework,” how OpenAI tracks, assesses, predicts, and protects against catastrophic risks posed by increasingly powerful models. What is the definition of catastrophic risk? OpenAI explained, “What we call catastrophic risks refers to risks that may result in hundreds of billions of dollars in economic losses or cause serious injury or death to many people. This also includes but is not limited to existential risks.”
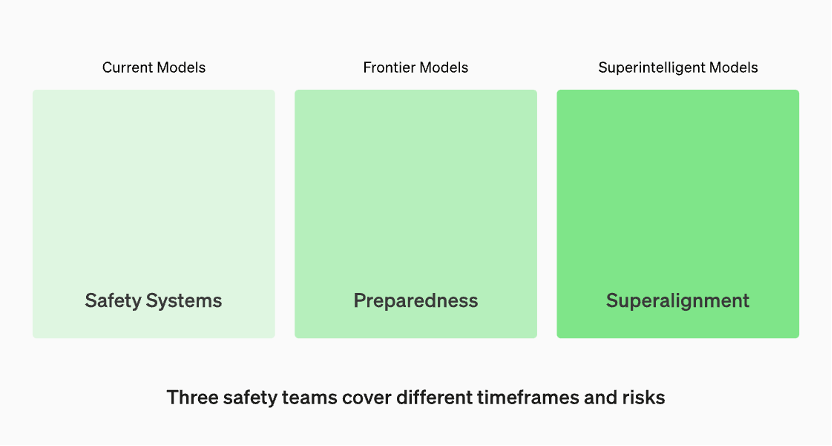
There are three groups of security teams covering different time frames and risks
According to the information on the OpenAI official website, the models in production are managed by the "Security System" team. During the development phase, there is a team called “preparation” who identify and assess risks before the model is released. In addition, there is a team called "superalignment" who are working on theoretical guidelines for "superintelligent" models
The OpenAI team will rate each model according to four risk categories: cybersecurity, persuasiveness (such as disinformation), model autonomy (the ability to act autonomously), and CBRN (chemical, biological , radioactive and nuclear threats, such as the ability to create new pathogens)
OpenAI considers various mitigations in its assumptions: for example, the model maintains reasonable reservations about describing the process of making napalm or pipe bombs. If a model is still assessed as having a "high" risk after taking into account known mitigations, it will not be deployed, and if a model presents any "critical" risks, it will not be developed further
Not everyone who makes a model is the best person to evaluate the model and make recommendations. For this reason, OpenAI is setting up a team called the "Cross-Functional Security Advisory Group," which will review the researchers' reports from a technical level and make recommendations from a higher perspective, hoping to uncover some of the "unknown unknowns." ”
This process requires that these recommendations be sent to both the board and leadership, who will decide whether to continue or cease operations, but the board has the authority to reverse those decisions. This prevents high-risk products or processes from being approved without the board’s knowledge
However, the outside world is still concerned that if the expert panel makes recommendations and the CEO makes decisions based on this information, does OpenAI’s board of directors really have the right to refute and take action? If they did, would the public hear about it? Currently, aside from OpenAI's promise to solicit independent third-party audits, their transparency issues have not actually been truly addressed
OpenAI’s “Readiness Framework” contains the following five key elements:
1. Evaluation and scoring
We will evaluate our models and update our "scorecard" on an ongoing basis. We will evaluate all state-of-the-art models, including tripling the effective computation during training. We will push the limits of the model. These findings will help us assess the risks of the latest models and measure the effectiveness of any proposed mitigation measures. Our goal is to detect edge-specific insecurities to effectively mitigate risks. To track the safety level of our models, we will produce risk "scorecards" and detailed reports
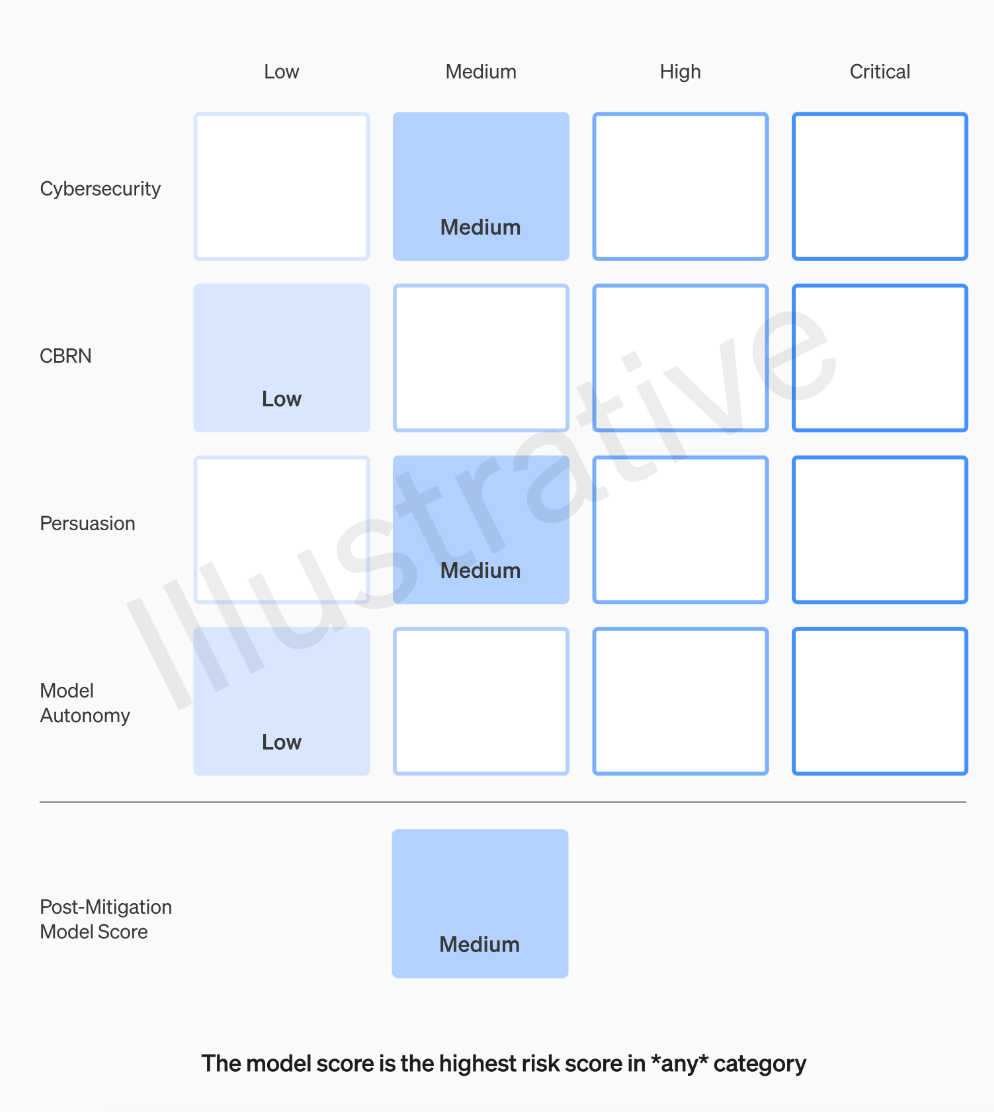
To evaluate all cutting-edge models, a "scorecard" is required
The purpose of setting risk thresholds is to have a clear boundary when making decisions and managing risks. Risk threshold refers to the maximum level of risk that an organization or individual is willing to bear under specific circumstances. By setting risk thresholds, you can help an organization or individual identify when action is needed to mitigate or avoid a risk. The setting of risk thresholds should be based on the results of risk assessment, relevant regulations and policies, and the risk tolerance of the organization or individual. When setting risk thresholds, the characteristics and impact of different risk types need to be taken into account to ensure the effectiveness and applicability of risk management measures. Finally, the risk thresholds set should be regularly evaluated and adjusted to remain consistent with the organization's or individual's risk management objectives
We will set risk thresholds that trigger security measures. We set thresholds for risk levels based on the following preliminary tracking categories: cybersecurity, CBRN (chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear threats), persuasion, and model autonomy. We specify four security risk levels, and only models with a post-mitigation score of "medium" or below can be deployed; only models with a post-mitigation score of "high" or below can be further developed. For models with high or critical risk (pre-mitigation), we will also implement additional security measures
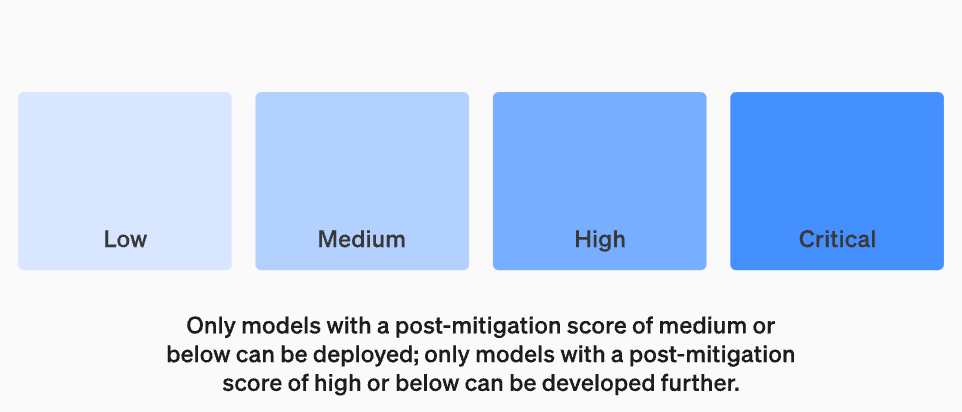
Danger Level
Reset the operational structure for overseeing technical work and safety decision-making
We will establish a dedicated team to oversee the technical work and operational structure of security decisions. The readiness team will drive technical work to examine the limits of capabilities of cutting-edge models and conduct assessments and comprehensive reporting. This technical work is critical to the development and deployment decisions of OpenAI security models. We are creating a cross-functional security advisory group to review all reports and send them to both leadership and the board of directors. Although leadership is the decision maker, the board of directors has the power to overturn decisions
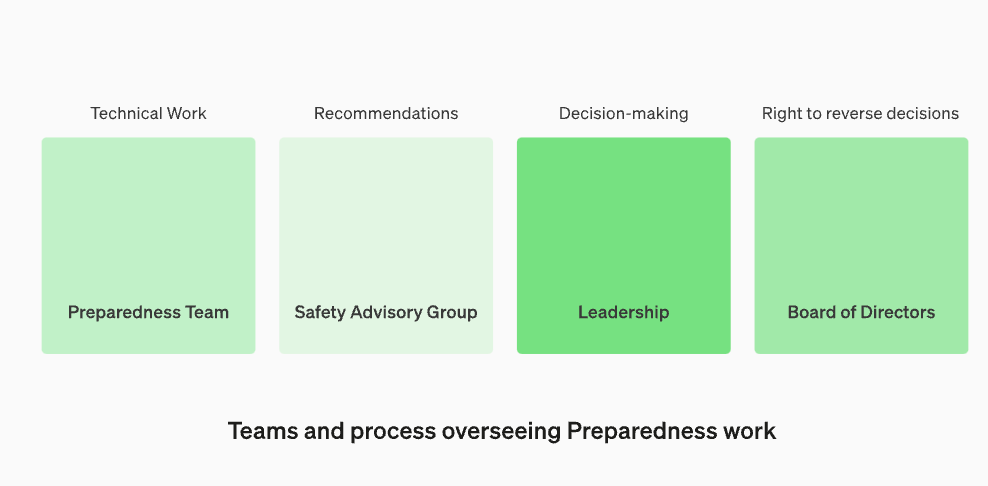
New changes in the operational structure for overseeing technical work and security decision-making
Enhancing security and strengthening external accountability
We will develop protocols to improve safety and external accountability. We will conduct regular security drills to stress-test our business and our own culture. Some security issues can arise quickly, so we have the ability to flag urgent issues for quick response. We believe it is helpful to get feedback from people outside OpenAI and have it reviewed by a qualified, independent third party. We will continue to have others form red teams and evaluate our models, and plan to share updates externally
Reduce other known and unknown security risks:
We will assist in mitigating other known and unknown security risks. We will work closely with external parties as well as internally with teams such as security systems to track real-world abuse. We will also work with Super Alignment to track urgent misalignment risks. We are also pioneering new research to measure how risk evolves as models scale and help predict risk ahead of time, similar to our earlier success with the Law of Scale. Finally, we will engage in a continuous process to try to resolve any emerging "unknown unknowns"
The above is the detailed content of OpenAI strengthens security team, empowering them to veto dangerous AI. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- OpenAI President: GPT-4 is not perfect but it is definitely different
- It's really not Versailles! ChatGPT is so successful, even OpenAI doesn't understand it
- Introduction to OpenAI and Microsoft Sentinel
- OpenAI wins ChatGPT competition and makes Time cover headlines
- OpenAI launches first generative artificial intelligence mobile application ChatGPT, opening a new era of intelligent communication

