 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI A team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences uses AI large model training technology to process massive synchrotron radiation data
A team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences uses AI large model training technology to process massive synchrotron radiation data
Without changing the original meaning, the sentence that needs to be rewritten into Chinese is: Edit| It is a coherent diffraction imaging technology that can theoretically achieve diffraction-limited resolution and has been widely used in research in various scientific fields such as materials, life, semiconductors, and energy.
The new generation of synchrotron radiation light source can provide high coherence and high brightness X-rays, promoting the development of coherent imaging technology in the direction of high-throughput and multi-dimensional, making ptychography useful in fine structure research and functional characterization of large-volume samples It has excellent application prospects. However, new experimental models and application scenarios have brought technical challenges to the online analysis of massive data. The amount of original diffraction pattern data for a single experiment can reach the PB level, becoming one of the largest data sources for scientific experiments on the fourth-generation synchrotron radiation light source. one. In addition, its phase recovery problem is also one of the most difficult problems in the field of synchrotron radiation data processing.
As a powerful tool for big data analysis and processing, artificial intelligence methods maintain the advantages of traditional algorithms and highlight their capabilities in online analysis of massive experimental data.
As a relatively time-consuming scanning imaging technology, one of the main goals of ptychography is to enable real-time analysis. However, it is difficult for the current traditional ptychography reconstruction algorithm to meet the needs of online reconstruction. Based on the convolutional neural network, the research team proposed a grouped convolutional neural network decoder structure, which makes the network training and reconstruction faster and the reconstruction effect better. Neural networks can learn to map from diffraction patterns to real objects. Thanks to the further improvement in the volume and quality of light source data in the future, the network scale, parameter volume, and training data volume will further increase, which will improve the performance and generalization capabilities of the network. The High Energy Synchrotron Radiation Source (HEPS) beamline software team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a convolutional neural network framework called PtyNet to recover objects from X-ray Ptychography experimental data accurate projection. With the support of powerful computing clusters, PtyNet can quickly obtain data from synchrotron radiation light sources for training, and quickly reconstruct images of users’ experimental data
 Figure 1
Figure 1
The research is titled "Efficient ptychography reconstruction strategy by fine-tuning large pre-trained deep learning models" and was published in iScience magazine on November 9, 2023
 Paper link:
Paper link:
Since the target objects recovered by different experimental data are different, the team also introduced a fine-tuning strategy Further optimize network parameters. The unsupervised fine-tuning strategy enables the network to have stronger generalization ability and higher reconstruction resolution. Synchrotron radiation sources can provide the network with sufficient data to obtain a more powerful pre-trained model. Even for a new sample that does not appear within the network, the network can be successfully reconstructed (Figure 2).
 What needs to be rewritten is: The second picture
What needs to be rewritten is: The second picture
In the future, the team will continue to apply convolutional neural networks to X-ray coherence imaging research in the field. Using fine-tuning and large model strategies, a large model of coherent imaging was developed. The model itself can identify different imaging tasks and give recovery results. Users only need to input a few line station parameters for real-time reconstruction.
Facing the challenge of EB-scale data in the future, HEPS is actively promoting the innovative scientific research paradigm of "Large-scale scientific software framework AI for Science" and has established a professional scientific software team to carry out experimental control, large-scale Cross-field research such as data collection and processing, artificial intelligence, cutting-edge subject algorithms, multi-scale image processing and data mining has laid the foundation for the construction of "smart light sources".
The above is the detailed content of A team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences uses AI large model training technology to process massive synchrotron radiation data. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The Hidden Dangers Of AI Internal Deployment: Governance Gaps And Catastrophic RisksApr 28, 2025 am 11:12 AM
The Hidden Dangers Of AI Internal Deployment: Governance Gaps And Catastrophic RisksApr 28, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe unchecked internal deployment of advanced AI systems poses significant risks, according to a new report from Apollo Research. This lack of oversight, prevalent among major AI firms, allows for potential catastrophic outcomes, ranging from uncont
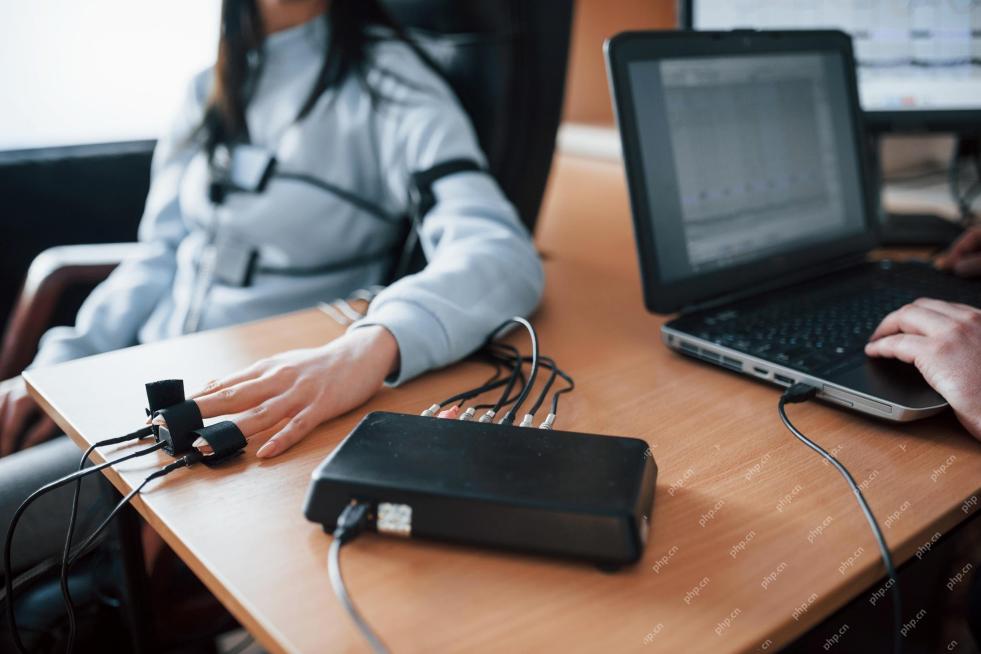 Building The AI PolygraphApr 28, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Building The AI PolygraphApr 28, 2025 am 11:11 AMTraditional lie detectors are outdated. Relying on the pointer connected by the wristband, a lie detector that prints out the subject's vital signs and physical reactions is not accurate in identifying lies. This is why lie detection results are not usually adopted by the court, although it has led to many innocent people being jailed. In contrast, artificial intelligence is a powerful data engine, and its working principle is to observe all aspects. This means that scientists can apply artificial intelligence to applications seeking truth through a variety of ways. One approach is to analyze the vital sign responses of the person being interrogated like a lie detector, but with a more detailed and precise comparative analysis. Another approach is to use linguistic markup to analyze what people actually say and use logic and reasoning. As the saying goes, one lie breeds another lie, and eventually
 Is AI Cleared For Takeoff In The Aerospace Industry?Apr 28, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Is AI Cleared For Takeoff In The Aerospace Industry?Apr 28, 2025 am 11:10 AMThe aerospace industry, a pioneer of innovation, is leveraging AI to tackle its most intricate challenges. Modern aviation's increasing complexity necessitates AI's automation and real-time intelligence capabilities for enhanced safety, reduced oper
 Watching Beijing's Spring Robot RaceApr 28, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Watching Beijing's Spring Robot RaceApr 28, 2025 am 11:09 AMThe rapid development of robotics has brought us a fascinating case study. The N2 robot from Noetix weighs over 40 pounds and is 3 feet tall and is said to be able to backflip. Unitree's G1 robot weighs about twice the size of the N2 and is about 4 feet tall. There are also many smaller humanoid robots participating in the competition, and there is even a robot that is driven forward by a fan. Data interpretation The half marathon attracted more than 12,000 spectators, but only 21 humanoid robots participated. Although the government pointed out that the participating robots conducted "intensive training" before the competition, not all robots completed the entire competition. Champion - Tiangong Ult developed by Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center
 The Mirror Trap: AI Ethics And The Collapse Of Human ImaginationApr 28, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Mirror Trap: AI Ethics And The Collapse Of Human ImaginationApr 28, 2025 am 11:08 AMArtificial intelligence, in its current form, isn't truly intelligent; it's adept at mimicking and refining existing data. We're not creating artificial intelligence, but rather artificial inference—machines that process information, while humans su
 New Google Leak Reveals Handy Google Photos Feature UpdateApr 28, 2025 am 11:07 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Handy Google Photos Feature UpdateApr 28, 2025 am 11:07 AMA report found that an updated interface was hidden in the code for Google Photos Android version 7.26, and each time you view a photo, a row of newly detected face thumbnails are displayed at the bottom of the screen. The new facial thumbnails are missing name tags, so I suspect you need to click on them individually to see more information about each detected person. For now, this feature provides no information other than those people that Google Photos has found in your images. This feature is not available yet, so we don't know how Google will use it accurately. Google can use thumbnails to speed up finding more photos of selected people, or may be used for other purposes, such as selecting the individual to edit. Let's wait and see. As for now
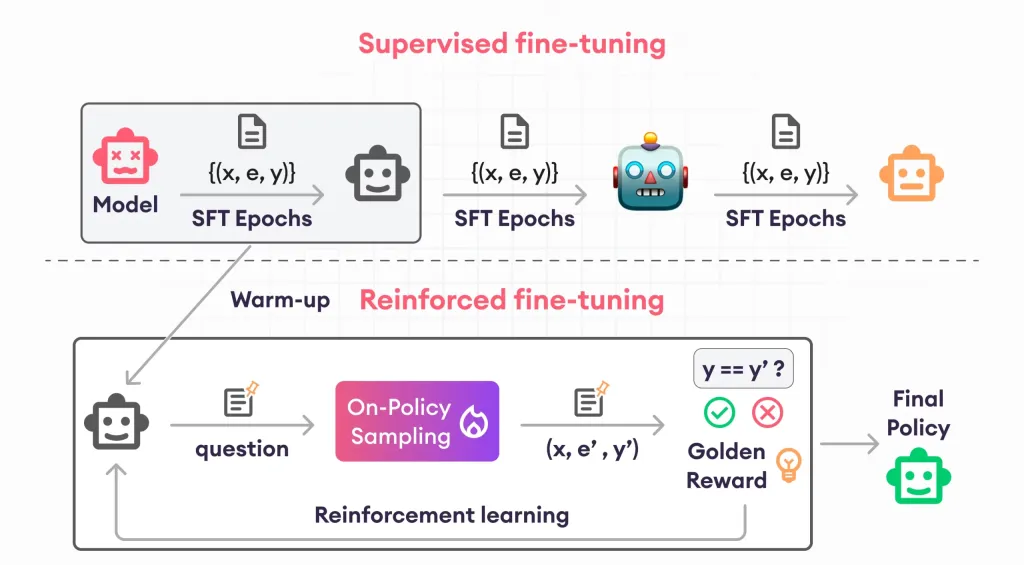 Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AM
Guide to Reinforcement Finetuning - Analytics VidhyaApr 28, 2025 am 09:30 AMReinforcement finetuning has shaken up AI development by teaching models to adjust based on human feedback. It blends supervised learning foundations with reward-based updates to make them safer, more accurate, and genuinely help
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!





