 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI The Chinese team won the best paper and best system paper awards, and the CoRL research results were announced.
The Chinese team won the best paper and best system paper awards, and the CoRL research results were announced.The Chinese team won the best paper and best system paper awards, and the CoRL research results were announced.
Since it was first held in 2017, CoRL has become one of the world's top academic conferences in the intersection of robotics and machine learning. CoRL is a single-theme conference for robot learning research, covering multiple topics such as robotics, machine learning and control, including theory and application
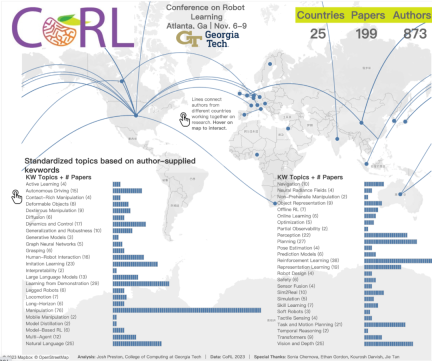
The 2023 CoRL Conference will be held in November It will be held in Atlanta, USA from the 6th to the 9th. According to official data, 199 papers from 25 countries were selected for CoRL this year. Popular topics include operations, reinforcement learning, and more. Although CoRL is smaller in scale than large AI academic conferences such as AAAI and CVPR, as the popularity of concepts such as large models, embodied intelligence, and humanoid robots increases this year, relevant research worthy of attention will also be presented at the CoRL conference.
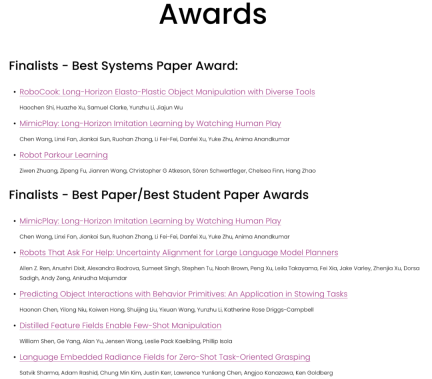
Currently, CoRL 2023 officials have announced the Best Paper Award, Best Student Paper Award, Best System Paper Award and other awards. Next, we will introduce these award-winning papers to you.
Best Paper

- ##Thesis: Distilled Feature Fields Enable Few-Shot Language- Guided Manipulation
- Authors: William Shen, Ge Yang, Alan Yu, Jensen Wong, Leslie Pack Kaelbling, Phillip Isola
- Institution: MIT CSAIL , IAIFI
- Paper address: https://openreview.net/forum?id=Rb0nGIt_kh5
Research Overview: Currently, self-supervised learning and language supervised learning in image models have incorporated rich global knowledge, which is very critical to the generalization ability of the model. However, image features only contain two-dimensional information. We learned that in robotics tasks it is very important to have an understanding of the geometry of three-dimensional objects in the real world
By using Distilled Feature Field (DFF), This research combines precise 3D geometry with rich semantics from a 2D base model to enable robots to leverage rich visual and language priors in the 2D base model to complete language-guided operations
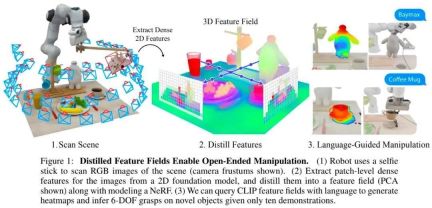
Specifically, this study proposes a few-shot learning method for 6-DOF grabbing and placing, and leverages strong spatial and semantic priors Generalize to unseen objects. Using features extracted from the vision-language model CLIP, this study proposes an open-ended natural language instruction to operate on new objects and demonstrates the ability of this method to generalize to unseen expressions and novel objects. .
The two co-authors of this paper are William Shen and Yang Ge, members of the CSAIL "Embodied Intelligence" team. Yang Ge is a co-author of the 2023 CSAIL Embodied Intelligence Symposium. Organizer.
I learned that "Heart of the Machine" has introduced this research in detail, please read "How powerful are robots supported by large models? MIT CSAIL&IAIFI uses natural language to guide robots to grasp objects 》
Best Student Paper
- Paper: Robots That Ask For Help: Uncertainty Alignment for Large Language Model Planners
- Author: Allen Z. Ren, Anushri Dixit, Alexandra Bodrova, Sumeet Singh, Stephen Tu, Noah Brown, Peng Xu, Leila Takayama, Fei Xia, Jake Varley, Zhenjia Xu, Dorsa Sadigh, Andy Zeng, Anirudha Majumdar
- Institution: Princeton University, Google DeepMind
- Paper address: https://openreview.net/forum ?id=4ZK8ODNyFXx
Large language model (LLM) is a technology with broad application prospects, especially in the field of robotics. However, although LLM shows great potential in step-by-step planning and common-sense reasoning, it also suffers from some illusion problems
Based on this, this study proposes a new framework—— KnowNo, for measuring and aligning uncertainty in LLM-based planners. It enables the LLM to realize what information is unknown and to ask for help when needed.

KnowNo is based on conformal prediction theory, which provides statistical guarantees of task completion and can minimize human intervention in multi-step planning tasks
This study tested KnowNo with various modes of uncertain tasks (including spatial uncertainty, numerical uncertainty, etc.) in various simulated and real robot experiments. Experimental results show that KnowNo performs well in improving efficiency and autonomy, outperforms baselines, and is safe and trustworthy. KnowNo can be used directly in LLM without model fine-tuning, providing an effective lightweight solution to model uncertainty and complementing the increasing capabilities of the underlying model.
Best System Paper

- ##Paper: RoboCook: Long-Horizon Elasto-Plastic Object Manipulation with Diverse Tools
- Authors: Haochen Shi, Huazhe Xu, Samuel Clarke, Yunzhu Li, Jiajun Wu
- Institution: Stanford University, UIUC ##Paper address:
- https://openreview.net/forum?id=69y5fzvaAT

The study shows that with just 20 minutes of real-world interaction data per tool, RoboCook can learn and manipulate the robotic arm to complete some complex, long-term elastic-plastic behaviors Object manipulation tasks, such as making dumplings, alphabet cookies, etc.
According to experimental results, RoboCook's performance is significantly better than the existing SOTA method, and it can still show stability in the face of severe external interference and adapt to different materials. The ability is also better
It is worth mentioning that the co-authors of this paper are Haochen Shi, a doctoral student from Stanford University, a former postdoctoral researcher at Stanford University, and a current cross-disciplinary researcher at Tsinghua University. Huazhe Xu, assistant professor at the Institute of Information Science, and one of the authors of the paper is Wu Jiajun, an alumnus of Yao Class and assistant professor at Stanford University.
The above is the detailed content of The Chinese team won the best paper and best system paper awards, and the CoRL research results were announced.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What are the TCL Commands in SQL? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
What are the TCL Commands in SQL? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:07 AMIntroduction Transaction Control Language (TCL) commands are essential in SQL for managing changes made by Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. These commands allow database administrators and users to control transaction processes, thereby
 How to Make Custom ChatGPT? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:06 AM
How to Make Custom ChatGPT? - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:06 AMHarness the power of ChatGPT to create personalized AI assistants! This tutorial shows you how to build your own custom GPTs in five simple steps, even without coding skills. Key Features of Custom GPTs: Create personalized AI models for specific t
 Difference Between Method Overloading and OverridingApr 22, 2025 am 10:55 AM
Difference Between Method Overloading and OverridingApr 22, 2025 am 10:55 AMIntroduction Method overloading and overriding are core object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts crucial for writing flexible and efficient code, particularly in data-intensive fields like data science and AI. While similar in name, their mechanis
 Difference Between SQL Commit and SQL RollbackApr 22, 2025 am 10:49 AM
Difference Between SQL Commit and SQL RollbackApr 22, 2025 am 10:49 AMIntroduction Efficient database management hinges on skillful transaction handling. Structured Query Language (SQL) provides powerful tools for this, offering commands to maintain data integrity and consistency. COMMIT and ROLLBACK are central to t
 PySimpleGUI: Simplifying GUI Development in Python - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 10:46 AM
PySimpleGUI: Simplifying GUI Development in Python - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 10:46 AMPython GUI Development Simplified with PySimpleGUI Developing user-friendly graphical interfaces (GUIs) in Python can be challenging. However, PySimpleGUI offers a streamlined and accessible solution. This article explores PySimpleGUI's core functio
 8 Mind-blowing Use Cases of Claude 3.5 Sonnet - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 10:40 AM
8 Mind-blowing Use Cases of Claude 3.5 Sonnet - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 10:40 AMIntroduction Large language models (LLMs) rapidly transform how we interact with information and complete tasks. Among these, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, developed by Anthropic AI, stands out for its exceptional capabilities. Experts o
 How LLM Agents are Leading the Charge with Iterative Workflows?Apr 22, 2025 am 10:36 AM
How LLM Agents are Leading the Charge with Iterative Workflows?Apr 22, 2025 am 10:36 AMIntroduction Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides in natural language processing and generation. However, the typical zero-shot approach, producing output in a single pass without refinement, has limitations. A key challenge i
 Functional Programming vs Object-Oriented ProgrammingApr 22, 2025 am 10:24 AM
Functional Programming vs Object-Oriented ProgrammingApr 22, 2025 am 10:24 AMFunctional vs. Object-Oriented Programming: A Detailed Comparison Object-oriented programming (OOP) and functional programming (FP) are the most prevalent programming paradigms, offering diverse approaches to software development. Understanding thei


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





