 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Robot achieves 'semi-autonomous navigation' within living lung tissue while avoiding key structures such as tiny airways and blood vessels
Robot achieves 'semi-autonomous navigation' within living lung tissue while avoiding key structures such as tiny airways and blood vesselsRobot achieves 'semi-autonomous navigation' within living lung tissue while avoiding key structures such as tiny airways and blood vessels

3 stages of semi-autonomous medical robot lungs. Image source: KUNTZ et al/University of North Carolina
Some tumors are so small that they are hidden deep in the lung tissue, making it difficult for doctors to reach them. To address this challenge, researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Vanderbilt University have been working on an extremely flexible but strong robot that can travel through lung tissue. In a recent paper published in the journal Science Robotics, they showed that the new robot can autonomously travel from "point A" to "point B" while avoiding important structures in living laboratory models, such as tiny Airways and blood vessels.
Researchers pointed out that this technology can achieve goals that robotic bronchoscopy cannot. It can provide an extra few centimeters or even millimeters of distance, which is very helpful for tracking small targets in the lungs
The robot consists of several independent components. The principle of the mechanical control assembly is to utilize a needle that provides controlled thrust forward and backward, and the needle design allows steering along a curved path. The needle is made of nickel-titanium alloy and is laser-etched to increase its flexibility, allowing it to move easily through tissue.
The etching on the needle allows it to easily maneuver around obstacles as it moves forward. Other accessories such as catheters can be used with the needle to perform procedures such as lung biopsies.
In order to move through tissue, the needle needs to know where it is going. The research team used CT scans of the subjects' chests and artificial intelligence to create a three-dimensional model of the lungs, including airways, blood vessels and selected targets. Using this 3D model, once the needle is set on target, the AI-driven software instructs it to automatically move from "point A" to "point B" while avoiding important structures.
It is similar to a self-driving car, but it can navigate through lung tissue, avoiding obstacles such as vital blood vessels when reaching its destination, researchers say.
The content that needs to be rewritten is: the editor-in-chief’s selection and modification
When talking about robots working in the human body, people always hope that it will be small, flexible, intelligent, flexible and strong. They hope that this kind of robot can assist human hands and eyes to go to places that are difficult for human hands to reach and see clearly. Lesions that are indistinguishable to the human eye. This time, a brand new robot was born. Not only can it reach its set destination, it can also flexibly avoid some small but important structures. You know, the human body is so complex, and there are many little obstacles that need to be bypassed on the way to your goal. Researchers must work hard on the structure, materials and robot movement mode so that it can move forward and backward freely, and smoothly carry out disease treatment and treatment work
(Source: Science and Technology Daily)
The above is the detailed content of Robot achieves 'semi-autonomous navigation' within living lung tissue while avoiding key structures such as tiny airways and blood vessels. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to Run LLM Locally Using LM Studio? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:38 AM
How to Run LLM Locally Using LM Studio? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:38 AMRunning large language models at home with ease: LM Studio User Guide In recent years, advances in software and hardware have made it possible to run large language models (LLMs) on personal computers. LM Studio is an excellent tool to make this process easy and convenient. This article will dive into how to run LLM locally using LM Studio, covering key steps, potential challenges, and the benefits of having LLM locally. Whether you are a tech enthusiast or are curious about the latest AI technologies, this guide will provide valuable insights and practical tips. Let's get started! Overview Understand the basic requirements for running LLM locally. Set up LM Studi on your computer
 Guy Peri Helps Flavor McCormick's Future Through Data TransformationApr 19, 2025 am 11:35 AM
Guy Peri Helps Flavor McCormick's Future Through Data TransformationApr 19, 2025 am 11:35 AMGuy Peri is McCormick’s Chief Information and Digital Officer. Though only seven months into his role, Peri is rapidly advancing a comprehensive transformation of the company’s digital capabilities. His career-long focus on data and analytics informs
 What is the Chain of Emotion in Prompt Engineering? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:33 AM
What is the Chain of Emotion in Prompt Engineering? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:33 AMIntroduction Artificial intelligence (AI) is evolving to understand not just words, but also emotions, responding with a human touch. This sophisticated interaction is crucial in the rapidly advancing field of AI and natural language processing. Th
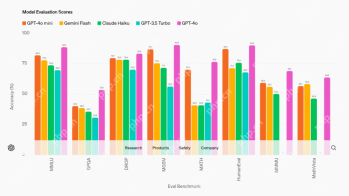
 12 Best AI Tools for Data Science Workflow - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:31 AM
12 Best AI Tools for Data Science Workflow - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:31 AMIntroduction In today's data-centric world, leveraging advanced AI technologies is crucial for businesses seeking a competitive edge and enhanced efficiency. A range of powerful tools empowers data scientists, analysts, and developers to build, depl
 AV Byte: OpenAI's GPT-4o Mini and Other AI InnovationsApr 19, 2025 am 11:30 AM
AV Byte: OpenAI's GPT-4o Mini and Other AI InnovationsApr 19, 2025 am 11:30 AMThis week's AI landscape exploded with groundbreaking releases from industry giants like OpenAI, Mistral AI, NVIDIA, DeepSeek, and Hugging Face. These new models promise increased power, affordability, and accessibility, fueled by advancements in tr
 Perplexity's Android App Is Infested With Security Flaws, Report FindsApr 19, 2025 am 11:24 AM
Perplexity's Android App Is Infested With Security Flaws, Report FindsApr 19, 2025 am 11:24 AMBut the company’s Android app, which offers not only search capabilities but also acts as an AI assistant, is riddled with a host of security issues that could expose its users to data theft, account takeovers and impersonation attacks from malicious
 Everyone's Getting Better At Using AI: Thoughts On Vibe CodingApr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Everyone's Getting Better At Using AI: Thoughts On Vibe CodingApr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AMYou can look at what’s happening in conferences and at trade shows. You can ask engineers what they’re doing, or consult with a CEO. Everywhere you look, things are changing at breakneck speed. Engineers, and Non-Engineers What’s the difference be
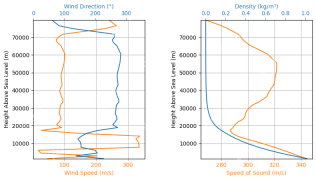 Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AMSimulate Rocket Launches with RocketPy: A Comprehensive Guide This article guides you through simulating high-power rocket launches using RocketPy, a powerful Python library. We'll cover everything from defining rocket components to analyzing simula


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool




