While businesses and consumers alike are excited about the potential of artificial intelligence to transform daily life, privacy concerns arising from widespread use of artificial intelligence remain a major concern. Clearly, as more and more personal data is fed into AI models, many consumers are rightfully concerned about their privacy and how their data is being used.

#This article is intended to help these consumers build a deeper knowledge base about the privacy capabilities of artificial intelligence. Additionally, it provides guidance for business owners and leaders on how to better understand customer concerns and how to use AI in a way that protects privacy without sacrificing functionality.
Artificial Intelligence and Privacy Issues
Copyright and Intellectual Property Laws Are Rarely Respected
AI models pull training data from all corners of the web. Unfortunately, many AI vendors are either unaware or don’t care when they use others’ copyrighted artwork, content, or other intellectual property without their consent.
As models are trained, retrained, and fine-tuned using this data, the problem is getting worse, and many of today’s AI models are so complex that even their builders can’t confidently say information, what data is being used and who has access to it.
Unauthorized merging of user data
When users of an artificial intelligence model enter their own data in the form of a query, this data has the potential to become part of the model's future training data set. When this happens, this data may be displayed as output to other users' queries, which is a particularly big problem if users have entered sensitive data into the system.
Limited regulatory agencies and safeguards
Currently, some countries and regulatory agencies are developing artificial intelligence regulations and safe use policies, but there is no unified standard to require artificial intelligence suppliers to build it And use AI tools responsibly
In the past, many AI vendors have been criticized for violating intellectual property rights and opaque training and data collection processes. As it stands, however, most AI vendors have the right to determine their own data storage, cybersecurity and user rules without interference
Unauthorized use of biometric data
More and more personal devices are using facial recognition, fingerprints, voice recognition and other biometric data to replace traditional authentication methods. At the same time, public surveillance equipment often uses artificial intelligence to scan biometric data to more quickly identify individuals. Although these new biometric security tools are very convenient, it is difficult for artificial intelligence companies to collect this data after collecting it. There is limited regulation of how this data is used. In many cases, individuals are not even aware that their biometric data has been collected, let alone that it is stored and used for other purposes.
Stealth Metadata Collection Practices
When a user interacts with an ad, social media video, or virtually any web property, metadata from that interaction can be stored along with the user's search history and interests, For more precise content targeting in the future
This method of metadata collection has been going on for years, but with the help of artificial intelligence, more data can be collected and interpreted at scale, making it possible for tech companies to target users without them. Target them further with information on how they work. While most user sites have policies that mention these data collection practices, they are only mentioned briefly in other policy text, so most users don’t realize what they have agreed to and place all content on themselves and their mobile devices placed under review.
AI models have limited built-in security features
While some AI vendors may choose to build in basic cybersecurity features and protections, many AI models do not have native cybersecurity capabilities Safety precautions. This makes it very easy for unauthorized users and malicious actors to access and use other users’ data, including personally identifiable information (PII)
Extended data storage period
Few artificial intelligence supplies Providers are able to disclose when, where and why they store user data, and transparent providers often store data for long periods of time.
For example, OpenAI’s policy states that it can store user input and output data for up to 30 days in order to identify abuse. However, it's unclear when or how the company took a more granular look at users' personal data without their knowledge
Privacy and Artificial Intelligence Data Collection
Web scraping and Web crawling
Artificial intelligence tools often rely on web scraping and web crawling to build training datasets because they do not require special permissions and also enable vendors to collect large amounts of different data
Content is scraped from public sources on the Internet, including third-party websites, Wikipedia, digital libraries, etc. In recent years, user metadata has also become the majority of content collected through web scraping and crawling. This metadata often comes from marketing and advertising data sets, as well as websites that contain your target audience and the content they care about most.
User Queries in Artificial Intelligence Models
When users enter questions or other data into an AI model, most AI models will store this data for at least a few days. Although this data may never be used for other purposes, research shows that many artificial intelligence tools not only collect this data, but also retain it for future training.
Biometric Technology
Surveillance devices, such as security cameras, facial and fingerprint scanners, and microphones capable of detecting human voices, can be used to collect biometric data and identify humans without their knowledge or consent
Many businesses have increasingly strict rules on how transparent they need to be when using such technology. But in most cases, they can collect, store and use this data without asking customers for permission.
IoT Sensors and Devices
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and edge computing systems collect large amounts of real-time data and process it nearby to complete larger, faster computing tasks. Artificial intelligence software usually utilizes the database of the IoT system and collects relevant data through methods such as data learning, data ingestion, secure IoT protocols and gateways, and APIs
API
API provides different Type commercial software interface that enables users to easily collect and integrate various data for artificial intelligence analysis and training. With the right API and setup, users can collect data from CRMs, databases, data warehouses, and cloud-based and on-premises systems
Public records
Public records are typically collected and incorporated manually Smart training sets, whether they are already digital or not. Information about publicly traded businesses, current and historical events, criminal and immigration records, and other public information may be collected without prior authorization
USER SURVEYS AND QUESTIONNAIRE
While this data Collection methods are somewhat outdated, but surveys and questionnaires are still a reliable way for AI vendors to collect data from users. Users can answer questions about what they are most interested in, what they need help with, and what they have recently learned about the product. or how the experience with the service was, or any other questions that can give the AI a better idea of how to personalize interactions with that person in the future. After rewrite: Users can answer questions about what they are most interested in, what they need help with, what their recent experience with the product or service was like, or any other questions. These questions can help AI better understand how to personalize interactions with users in the future
Solutions to Artificial Intelligence and Privacy Questions
With some best practices, tools, and other resources, Enterprises can use AI solutions effectively without sacrificing user privacy. To protect your most sensitive data at all stages of AI use, follow these tips:
Create an appropriate usage policy for AI: Internal users should know what data they can use, and when using it How and when this data should be used when using artificial intelligence tools is especially important for businesses that handle sensitive customer data.- Invest in data governance and security tools: Some of the best solutions for protecting AI tools and other attack surfaces include Extended Detection and Response (XDR), data loss prevention, and threat intelligence and monitoring software. There are also a number of data governance-specific tools that can help protect data and ensure that all data is used in compliance with relevant regulations.
- Read the fine print: AI vendors typically provide some kind of documentation that covers how their products work and the basics of training. Read these documents carefully to look for any red flags, and if there’s anything you’re not sure about or something is unclear in their policy documents, contact their representative for clarification.
- Use Only Non-Sensitive Data: As a general rule, don’t enter your business or customer’s most sensitive data into any AI tool, even if it’s a custom or fine-tuned solution that feels private. If you want to pursue a specific use case involving sensitive data, investigate whether there is a way to do it securely using digital twins, data anonymization, or synthetic data.
- Summary
Artificial intelligence tools bring many new conveniences to businesses and everyday consumers, including task automation, guided Q&A, and product design and programming. However, while these tools can simplify our lives, they also run the risk of invading personal privacy, which can damage provider reputations and consumer trust, while also posing a threat to cybersecurity and regulatory compliance.
Using AI responsibly to protect user privacy requires extra effort, but it’s well worth it when you consider how privacy violations can impact a business’s public image. Especially as this technology matures and becomes more prevalent in our daily lives, following the passage of AI laws and developing more specific AI that is consistent with corporate culture and customer privacy expectations, using best practices will become crucial.
The above is the detailed content of How to protect artificial intelligence privacy?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
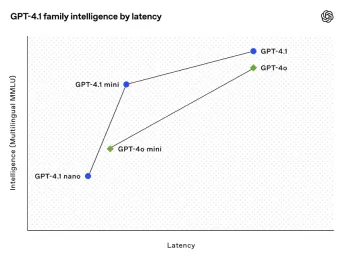 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!







