Home >Technology peripherals >AI >To help the Internet of Things, Sony develops an energy harvesting module that uses electromagnetic wave noise to efficiently generate electricity.
To help the Internet of Things, Sony develops an energy harvesting module that uses electromagnetic wave noise to efficiently generate electricity.
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-09-18 17:45:081081browse
Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation (hereinafter referred to as "SSS") announced on September 8 that it has successfully developed an energy harvesting module that utilizes electromagnetic wave noise energy
The new module applies the technology accumulated by SSS in the tuner development process and can efficiently utilize electromagnetic wave noise to generate electricity. For example, this technology can use the continuous electromagnetic wave noise generated by robots in factories, monitors and lighting equipment in offices, monitors and TVs in stores and homes to operate low-power IoT sensors and communication devices. Stable power required.
With the popularity and complexity of IoT devices, powering more and more IoT devices has become a challenge. However, this highly efficient energy harvesting technology is expected to be widely used. SSS aims to use this new technology as part of building a power cycle model to promote the development of a sustainable IoT society
1: A technology that can harvest trace amounts of energy from the environment and living things and convert it into electrical energy
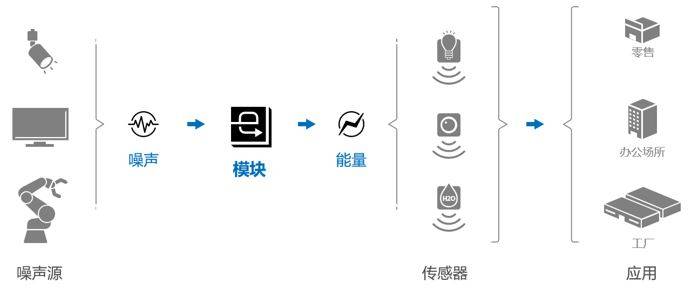 Energy harvesting framework using electromagnetic wave noise
Energy harvesting framework using electromagnetic wave noise
 Usage scenarios: factory (left), office (middle), retail (right)
Usage scenarios: factory (left), office (middle), retail (right)
Energy harvesting technology is a technology that is expected to contribute to the development of the Internet of Things and the sustainable development of the earth's environment. This technology currently has related research in the fields of radio waves, light, heat and vibration. SSS's energy harvesting technology uses the electromagnetic wave noise generated by all electronic devices to generate electricity, which is more efficient.
The new module is based on the antenna technology built by SSS during the tuner development process. It uses metal parts of electronic equipment as part of the antenna and adopts a rectifier circuit with enhanced electrical conversion efficiency to achieve a highly original structure. Despite being a small module, it is capable of converting electromagnetic wave noise in the range of a few hertz to 100 megahertz into electrical energy to power low-power IoT sensors and communication devices, or to charge batteries. This is a leading energy harvesting technology that provides stable power for devices by effectively utilizing previously ignored electromagnetic wave noise as a new power source
Control the number of components used in the module, resulting in a compact design and greater freedom in installation settings. In addition, if the electronic device is powered on, it can collect energy even when it is on standby, so this technology is expected to be widely used in various indoor and outdoor use environments such as factories, offices, shops, and homes.
Generally speaking, we need a circuit that converts alternating current into direct current. Alternating current is usually used to transmit electrical energy, while rectifier circuits are used to provide power to devices that require direct current.
 Developed module (size: 7 mm square)
Developed module (size: 7 mm square)
The main characteristics refer to the main features or characteristics of a thing or concept. It describes the most important attribute, characteristic, or characteristic of the thing or concept. By emphasizing the main features, we can understand more clearly the nature and importance of the thing or concept. Main features are usually key features closely related to the thing or concept that can help us better understand and analyze. By understanding the main characteristics, we can better evaluate and compare the differences and similarities between different things or concepts
The content that needs to be rewritten is: ■High power generation level
This module uses electronic equipment that generates a large amount of electromagnetic wave noise, such as household appliances, computers, lighting equipment, vending machines, elevators, automobiles, and industrial equipment, as energy source, and can obtain power from tens of microwatts to tens of milliwatts. This can power low-power IoT sensors and communication devices
■Wide range of applications
· If the electronic device is powered on, it can also collect power when in standby. Therefore, this method is different from other energy harvesting methods that use sunlight, radio waves, and temperature differences, which are all susceptible to environmental factors such as lighting brightness and indoor environment. The new module therefore enables continuous energy harvesting.
· Controls the number of components used in the module, resulting in a compact design and greater freedom of installation and setup.
■Identifiable device status
This technology can continuously acquire the electromagnetic wave noise generated by electronic equipment and identify the internal status of the equipment by detecting changes in voltage. Therefore, it can be used to detect whether lighting is working properly or to predict equipment failures, such as the failure of robots’ built-in motors.
This technology is expected to empower a wide range of application fields. SSS looks forward to cooperating with partners from all walks of life to jointly develop products based on this technology.
The above is the detailed content of To help the Internet of Things, Sony develops an energy harvesting module that uses electromagnetic wave noise to efficiently generate electricity.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- What links can the IoT industry chain be broken down into?
- What does IoT mean?
- Sony considers splitting financial sector to go public to enhance investment strength
- Make clear calls and enjoy your music! Sony WF-1000XM5 headset three-microphone design provides excellent call quality
- Sony camera update plan exposed: multiple new cameras will be released next year

