Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Python basics and data types
Python basics and data types
- Go语言进阶学习forward
- 2023-07-25 16:21:151082browse
1. Base system
1. What is base system?
The base system is also the carry counting system, which is an artificially defined counting method with carry (there are counting methods without carry, such as the original knot counting method, when counting votes Commonly used "positive" word counting, and similar tally mark counting). For any base system - the X base system, it means that the number operation at each position is carried out by one digit every time X is reached. The decimal system carries one after every tenth, the hexadecimal system carries forward every sixteenth, the binary system carries through every two, and so on, the x-based system carries forward every x. (From Baidu)
Popular explanation, the so-called base system is a method of counting. The base system means that when the base system is satisfied, one digit will be advanced to the high order. .
2. Base conversion.
In Python, you can use the built-in function int() function to convert binary to decimal; the int() function can convert a numeric string or decimal number in a specified base into an integer.
Syntax:
int(object,base)
Return value: Return the integer type data.
Convert binary number to decimal number
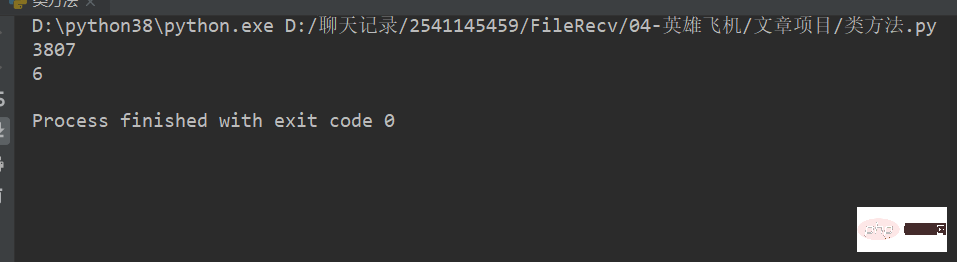
test = ['111011011111', '0b110']
for number in test:
print(int(number, 2))Run result:
将八进制数转化为十进制数。
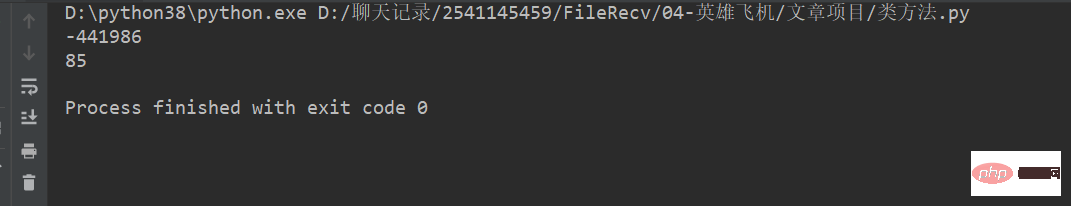
test = ['-1537202', '125']
for number in test:
print(int(number, 8))运行 结果 :
二、数值类型
1. 布尔型
布尔型其实是整型的子类型,布尔型数据只有两个取值:True和False,分别对应整型的1和0。
每一个Python对象都天生具有布尔值(True或False),进而可用于布尔测试(如用在if、while中)。
以下对象的布尔值都是False:
| Return value | ##Type |
|---|---|
| ##False | ##(Boolean)|
| ##(integer 0) | |
| ##(long integer 0) | 0.0 |
| ##(floating point 0) | |
| 0.0 0.0j | (plural 0) |
| "" | (empty string) |
| [] | (empty list) |
| () | (empty tuple) |
| {} | (empty dictionary) |
-
用户自定义的 类实例,该类定义了方法 nonzero() 或 len(),并且这些方法返回0或False。
除上述对象之外的所有其他对象的布尔值都为True。
# 1. Python对象的布尔值
>>> bool(None)
False
>>> bool(False), bool(0), bool(0L), bool(0.0), bool(0.0+0.0j)
(False, False, False, False, False)
>>> bool(''), bool([]), bool(()), bool({})
(False, False, False, False)
# 2. 数值运算中,布尔值True和False分别对应整型的1和0
>>> int(True), int(2 < 1)
(1, 0)
>>> False + 100
100 #输出结果
>>> True + 100
101 #输出结果
2. 整型
整型等价于C语言中的有符号长整型(long),与系统的最大整型一致(如32位机器上的整型是32位,64位机器上的整型是64位),可以表示的范围有限。整型字面值的表示方法有3种:十进制(常用)、二进制(以“0b”开头)、八进制(以数字“0”开头)和十六进制(以“0x”或“0X”开头)。
>>> a = 0b10100 >>> type(a) int #输出结果 >>> a 20 #输出结果 >>> bin(20), oct(20), hex(20) ('0b10100', '024', '0x14') # 输出结果
3. 长整型
长整型是整型的超集,可以表示无限大的整数。长整型字面值的后面带有字母“L”或“l”(使用大写的“L”)。
>>> a = 999 ** 8 # 整型自动转换为长整型 >>> a 8920457944069944027201L >>> type(a) long
4. 浮点型
浮点型类似于C中的双精度浮点型(double)。浮点型字面值可以用十进制或科学计数法表示,在科学计数法中,e或E代表10,+(可以省略)或 - 表示指数的正负。
>>> type(1) int #输出结果 >>> type(1.0) float #输出结果 >>> 1 + 1.0 2.0 #输出结果 >>> a = 1e-2 >>> a #输出结果 0.01 >>> type(a) float #输出结果 >>> pi = 3.1415926 >>> round(pi) 3.0 #输出结果 >>> round(pi, 4) 3.1416 #输出结果
5. 复数
复数与数学中的复数概念完全相同。Python中的复数有以下几个特性:
复数由实数部分和虚数部分构成,表示为:real+imagj 或 real+imagJ。
复数的实部real和虚部imag都是浮点型。
>>> a = 1+2j >>> a (1+2j) #输出结果 >>> a.real # 实部 1.0 #输出结果 >>> type(a.real) float #输出结果 >>> a.imag # 虚部 2.0 #输出结果 >>> type(a.imag) float #输出结果
三、总结
本文基于Python基础,主要讲解了进制和数值类型。通过一个个小项目详细的讲解和图片的效果展示,以期让读者更好的了解Python中进制转换和数值类型,希望能够帮助大家更好的学习。
The above is the detailed content of Python basics and data types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An article to guide you through Python anonymous functions
- An article to help you understand Python's distributed process interface
- An article teaches you how to use three simple functions in Python
- Things to take stock of the list of Python basics
- An article to help you understand Python's higher-order functions

