Home >Backend Development >Golang >Analyzing issues related to computer bits from the perspective of Go language
Analyzing issues related to computer bits from the perspective of Go language
- Go语言进阶学习forward
- 2023-07-21 11:52:271302browse
A piece of code
This time I will take the Go language as an example. The Go language is a C-like language, and some of the underlying layers are very similar!
Code
package main
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
//定义一个 字符a
var a = 'a'
//定义一个 正 整数3
var b uint8 = 3
var c uint8 = 98
fmt.Printf("值:%c,十进制:%d,类型:%T,二进制:%b,大小%v字节\n", a, a, a, a, unsafe.Sizeof(a)) // 4个字节
fmt.Printf("值%d,十进制:%d,类型:%T,二进制%b,大小%v字节\n", b, b, b, b, unsafe.Sizeof(b)) //一个字节
fmt.Printf("值%c,十进制,%d,类型:%T,二进制%b,大小%v字节\n", c, c, c, c,unsafe.Sizeof(c)) //一个字节
}Execution Result

There are several questions
When I name a variable Character a, why is it 97 in decimal and 1100001 in binary?
Why is variable c named 98, but b can be output?
Bits and bytes
To understand the above issues, we still need to understand the essential issues.
Our program runs in memory after all.
And our memory module is probably like this.
The essence of a memory stick is each electronic component,After all, there are only two states,Power on (1), No power on (0).
bit
aelectronic component, It’s a bit.
byte
anda word Section , equal to 8 bits,1 byte=8 bits.
One bit is a 0 or 1 is Binary, is either 0 or 1.
A byte is 8 0s or 1s, like this,00000000,If you see less than 8 0s or 1s, fill in all the leading 0s with 0s to make up for 8 digits.
Normally, the language generally only operates on the bytes , and rarely operates in place.
Why a is 97
Although we know the above, a bit means a powered or not powered Electronic component.
One byte represents 8 powered or is a combination of electronic components that are not powered on .
But this does not solve the actual problem. I want to save a 10, add a 20, and perform addition calculations. What should I do? ? ?
So at this time, there must be a rule, whichever is lit or which is not lit, means what it is.
So there is ASCII This specification, the smallest unit of this specification is bytes, that is, Manage 8 0s or 1s at the same time.
For example, the first byte is the first eight digits. If all are 0, it means the decimal number 0.
8 binary representation is 00000000.
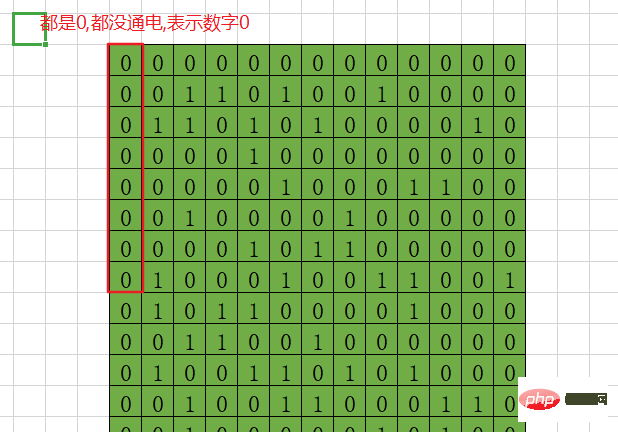
also stipulates that counting from the end, if the end is lit and the other 7 are not lit, it means decimal 1.
00000001
## and so on, the bits are organized by bytes, and each 8 bits are different A combination of symbols, numbers, letters, etc.
Specific binary corresponding symbols or numbers:https://baike.baidu.com/item/ASCII/309296?fromtitle=ASCII encoding&fromid =3712529&fr=aladdin
It can be known by querying ASCII.
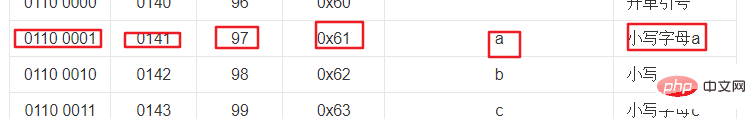
The binary version of the letter a is 0110 0001, and the decimal version is 97 , the symbol represented is a.
So let’s face it at the beginning!
Why can 98 output b? It’s because ASCII, because 98 represents the letter b , which is binary 0110 0010.
It’s just that the output method is different.
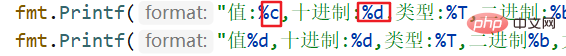
Current encoding direction
In fact, one byte, 8 bits, if all Turn on the light, it is 11111111, its decimal value is 255, theoretically It is said that it can support 255 symbols.
It should be sufficient for English-speaking countries. Each letter has 8 bits and one byte. To store a hello is 5 bytes. A total of 40 bits is enough.
But nowadays, computers have become a towering tree. China uses them, Japan uses them, and sticks are used. The total number of characters in each country is no longer as simple as 255.
So some codes like China’s GBK are derived, and various codes are based on ASCIIExtended.
ASCII occupies one byte, 8 bits, then IGBK It’s not enough. There are tens of thousands of Chinese characters. So I have two bytes, 16 bits, 16 0s or 1s. I should make do. If not, three bytes, 24 0s or 1s, three bytes. The decimal system has reached 16777215, which is tens of millions, enough to preserve the symbols and characters of various countries.
But GBK is not compatible with other encodings, so now it is derived from Codes such as utf-8 include codes from various countries.
Currentlyutf-8 is the best encoding and is basically supported by all computers.
Summary
This article is mainly about understanding the nature of computer memory. 1 byte=8 bits,1 bit=a powered or unpowered electronic component, different symbols are represented by different 00101010.
The above is the detailed content of Analyzing issues related to computer bits from the perspective of Go language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- http.Transport optimization skills and practice sharing in Go language
- Request flow control configuration and practice of http.Transport in Go language
- Object-oriented design principles and best practices in Go language
- Concurrency and WorkerPool in Go language - Part 2
- Several common ways to copy files in Go language

