Why are so many people angry about New York's AI hiring law?
An overwhelming number of people were outraged by the artificial intelligence and hiring laws that took effect in New York City last week. This law is the first AI law in the United States, so the way it is implemented will provide lessons and guidance for other cities developing AI policy and debate. Like New York, other U.S. states are also considering incorporating AI hiring provisions into the European Artificial Intelligence Act.
The use of artificial intelligence in recruiting has sparked criticism due to the presence of automation and the way it can reinforce existing racial and gender biases. AI systems have been shown to favor white, male, and able-bodied candidates when evaluating their facial expressions and language.
This issue deserves attention because most companies have used artificial intelligence at least once in the recruitment process. Charlotte Burrows, chairwoman of the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, said at a January 2023 meeting that as many as 80% of companies use some form of automated tools to make hiring decisions.
New York City’s Automated Employment Decision Tool Act, which took effect on July 5, stipulates that employers who use artificial intelligence in recruitment must truthfully inform candidates that they are doing so. To prove that their systems are not racist or sexist, they need annual independent audits. Job seekers can ask potential employers for information about the collection and analysis of data involved in this technology. Violations are subject to fines of up to $1,500.
 (Source: STEPHANIE ARNETT/MITTR | GETTY)
(Source: STEPHANIE ARNETT/MITTR | GETTY)
Supporters of the law say it's a good start, even if it's not perfect, for regulating artificial intelligence and mitigating some of the harms and risks that come with its use. Companies are being asked to take a deeper look at the algorithms they use to determine whether the technology is inadvertently unfairly discriminating against women or people of color.
This is a rare but successful case, and from the perspective of U.S. artificial intelligence regulatory policy, we may see more relevant local regulations. Sounds promising, right?
But this law has been hugely controversial. Public interest groups and civil rights advocates say the bill is neither enforceable nor broad enough, while businesses that must comply argue it is impractical and burdensome.
Organizations such as the Center for Democracy & Technology and the Surveillance Technology Oversight Project (S.T.O.P.) argue that the law is “inadequately inclusive” and risks missing the use of many automated systems in recruitment. Including systems that use artificial intelligence to screen thousands of candidates.
Given that the relevant audit industry is currently immature, the more important aspects of the results of independent audits that are uncertain are its more important aspects. The BSA - an influential tech trade group whose members include Adobe, Microsoft and IBM - submitted comments to New York City in January 2023 criticizing the law, arguing that third-party audits were "unfeasible."
S.T.O.P. Executive Director Albert Fox Cahn said: "The key question is how auditors will obtain company information and to what extent they can actually interrogate the company's operations way. Although we employ financial auditors, we lack a set of universally accepted accounting principles, let alone tax laws and auditing rules."
According to Kahn, the law could lead to a false sense of security about artificial intelligence and the hiring process. He said: "This is a fig leaf used only to demonstrate that protections exist, and in practice I don't think any company will be held accountable as a result of this being enshrined in law."
Importantly, mandatory audits must assess whether the output of an AI system is biased against specific groups of people, using a metric known as an "impact ratio" to determine whether the technology's "selection rate" is due to It varies from group to group.Audits do not need to try to determine how an algorithm makes a decision, and the law sidesteps the issue of “explainability” in complex forms of machine learning such as deep learning. As you can imagine, these omissions have become a hot topic of debate among AI experts.
In the United States, pending federal legislation, we may see more local laws regulating artificial intelligence of this kind, most of which target one specific application of the technology. By engaging with these local legal controversies, we can shed light on how definitions of AI tools, security mechanisms, and enforcement will evolve in the coming decades. New Jersey and California are already considering similar laws.
Support: Ren
The above is the detailed content of Why are so many people angry about New York's AI hiring law?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 5 Statistical Tests Every Data Scientist Should Know - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 10:27 AM
5 Statistical Tests Every Data Scientist Should Know - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 10:27 AMData Science's Essential Statistical Tests: A Comprehensive Guide Unlocking valuable insights from data is paramount in data science. Mastering statistical tests is fundamental to achieving this. These tests empower data scientists to rigorously val
 How to Perform Computer Vision Tasks with Florence-2 - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 10:21 AM
How to Perform Computer Vision Tasks with Florence-2 - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 10:21 AMIntroduction The introduction of the original transformers paved the way for the current Large Language Models. Similarly, after the introduction of the transformer model, the vision transformer (ViT) was introduced. Like the
 7 Ways to Split Data Using LangChain Text Splitters - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 10:11 AM
7 Ways to Split Data Using LangChain Text Splitters - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 10:11 AMLangChain Text Splitters: Optimizing LLM Input for Efficiency and Accuracy Our previous article covered LangChain's document loaders. However, LLMs have context window size limitations (measured in tokens). Exceeding this limit truncates data, comp
 Free Generative AI Course: Pioneering the Future of InnovationApr 19, 2025 am 10:01 AM
Free Generative AI Course: Pioneering the Future of InnovationApr 19, 2025 am 10:01 AMGenerative AI: Revolutionizing Creativity and Innovation Generative AI is transforming industries by creating text, images, music, and virtual worlds at the touch of a button. Its impact spans video editing, music production, art, entertainment, hea
 Creating a QA Model with Universal Sentence Encoder and WikiQAApr 19, 2025 am 10:00 AM
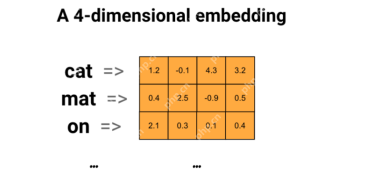
Creating a QA Model with Universal Sentence Encoder and WikiQAApr 19, 2025 am 10:00 AMHarnessing the Power of Embedding Models for Advanced Question Answering In today's information-rich world, the ability to obtain precise answers instantly is paramount. This article demonstrates building a robust question-answering (QA) model using
 Top 10 Must Read Machine Learning Research PapersApr 19, 2025 am 09:53 AM
Top 10 Must Read Machine Learning Research PapersApr 19, 2025 am 09:53 AMThis article explores ten seminal publications that have revolutionized artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). We'll examine recent breakthroughs in neural networks and algorithms, explaining the core concepts driving modern AI. Th
 Top 11 AI Tools to Replace SEO Agencies - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 09:49 AM
Top 11 AI Tools to Replace SEO Agencies - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 09:49 AMAI's Rise in SEO: Top 11 Tools to Outperform SEO Agencies The rapid advancement of AI has profoundly reshaped the SEO landscape. Businesses aiming for top search engine rankings are leveraging AI's power to optimize their online strategies. From au
 Top 10 Free AI Playgrounds For You to Try in 2025 - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 09:45 AM
Top 10 Free AI Playgrounds For You to Try in 2025 - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 09:45 AMExploring the Best Free AI Playgrounds in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide Access to the right tools and platforms is key to learning and innovating in the ever-evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI). AI playgrounds offer a fantastic opportunity


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.





