 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Google DeepMind, OpenAI and others jointly issued an article: How to evaluate the extreme risks of large AI models?
Google DeepMind, OpenAI and others jointly issued an article: How to evaluate the extreme risks of large AI models?Currently, the methods of building general artificial intelligence (AGI) systems, while helping people better solve real-world problems, also bring some unexpected risks.
Therefore, In the future, the further development of artificial intelligence may lead to many extreme risks, such as offensive network capabilities or powerful manipulation skills, etc.
Today, Google DeepMind, in collaboration with universities such as the University of Cambridge and Oxford University, companies such as OpenAI and Anthropic, as well as institutions such as the Alignment Research Center, published an article titled "Model evaluation for extreme risks" on the preprint website arXiv.Proposes a framework for a common model for novel threat assessments and explains why model assessment is critical to dealing with extreme risks.
They argue that developers must have the ability to identify hazards (via the "Hazard Capability Assessment"), and the model's propensity to cause harm by applying its capabilities (via the "Alignment Assessment" "). These assessments will be critical to keeping policymakers and other stakeholders informed and making responsible decisions about model training, deployment, and security.

Academic Toutiao (ID: SciTouTiao) has made a simple compilation without changing the main idea of the original text. The content is as follows:
In order to responsibly promote the further development of cutting-edge research in artificial intelligence, we must identify new capabilities and new risks in artificial intelligence systems as early as possible.
AI researchers have used a series of evaluation benchmarks to identify undesirable behavior in AI systems, such as AI systems making misleading claims, biased decisions, or duplicating copyrighted content. Now, as the AI community builds and deploys increasingly powerful AI, we must broaden our assessments to include the possible extremes of general AI models with the ability to manipulate, deceive, cyberattack, or otherwise be dangerous. Risk considerations.
In collaboration with the Universities of Cambridge, Oxford, Toronto, Montreal, OpenAI, Anthropic, the Alignment Research Center, the Center for Long-Term Resilience and the Center for the Governance of AI, we introduce a framework for assessing these new threats.
Model safety assessment, including assessing extreme risks, will become an important component of safe AI development and deployment.

To assess the extreme risks of new general artificial intelligence systems, developers need to assess their dangerous capabilities and alignment levels. Identifying risks early can lead to greater accountability in training new AI systems, deploying these AI systems, transparently describing their risks, and applying appropriate cybersecurity standards.
Assess extreme risks
Generic models typically learn their capabilities and behaviors during training. However, existing methods for guiding the learning process are imperfect. Previous research from Google DeepMind, for example, has explored how AI systems can learn to pursue goals that humans don’t want, even when we correctly reward them for good behavior.
Responsible AI developers must go further and anticipate possible future developments and new risks. As progress continues, future universal models may learn various dangerous abilities by default. For example, future artificial intelligence systems will be able to conduct offensive network activities, cleverly deceive humans in conversations, manipulate humans into harmful behaviors, design or acquire weapons (such as biological, chemical weapons), and fine-tune and operate on cloud computing platforms. Other high-stakes AI systems, or assisting humans in any of these tasks, are possible (although not certain).
People with bad intentions may abuse the capabilities of these models. These AI models may act harmful because of differences in values and morals from humans, even if no one intended to do so.
Model evaluation helps us identify these risks in advance. Under our framework, AI developers will use model evaluation to uncover:
- The extent to which a model has certain "dangerous capabilities," threatens security, exerts influence, or evades supervision.
- The extent to which a model is susceptible to using its abilities to cause damage (i.e. the model's alignment level). It is necessary to confirm that the model behaves as expected even under a very wide range of circumstances, and where possible the inner workings of the model should be examined.
Through the results of these assessments, AI developers can understand whether there are factors that may lead to extreme risks. The highest risk situations will involve a combination of hazardous capabilities. As shown below:

图|Elements that pose extreme risks: Sometimes, specific capabilities may be outsourced, either to humans (such as users or crowd workers) or to other AI systems. These abilities must be used to inflict damage, whether from abuse or failure to achieve alignment.
A rule of thumb: If an AI system has characteristics that are capable of causing extreme harm, assuming it is abused or misaligned, then the AI community should consider it "highly dangerous." To deploy such systems in the real world, AI developers will need to demonstrate exceptionally high safety standards.
Model evaluation is critical governance infrastructure
If we have better tools to identify which models are risky, companies and regulators can better ensure that:
- Responsible training: Decide responsibly whether and how to train a new model that shows early signs of risk.
- Responsible Deployment: Make responsible decisions about if, when, and how to deploy potentially risky models.
- Transparency: Reporting useful and actionable information to stakeholders to help them address or reduce potential risks.
- Appropriate Security: Strong information security controls and systems are appropriate for models that may pose extreme risks.
We have developed a blueprint for how model evaluation for extreme risks should support important decisions about training and deploying powerful, general-purpose models. Developers conduct evaluations throughout the process and grant structured access to the model to external security researchers and model reviewers so they can perform additional evaluations. The assessment results can provide a reference for risk assessment before model training and deployment.

Figure | Embed model evaluation for extreme risks into the important decision-making process of the entire model training and deployment.
Looking to the future
At Google DeepMind and elsewhere, important preliminary work on model evaluation for extreme risks has begun. But to build an assessment process that captures all possible risks and helps protect against emerging challenges in the future, we need more technical and institutional efforts. Model assessment is not a panacea; sometimes, some risks may escape our assessment because they rely too much on factors external to the model, such as the complex social, political, and economic forces in society. There is a need to integrate model assessments with broader industry, government and public concerns about safety and other risk assessment tools.
Google recently noted in its blog on responsible AI that “individual practices, shared industry standards, and sound government policies are critical to the proper use of AI.” We hope that the many industries working in AI and affected by this technology can work together to jointly develop methods and standards for the safe development and deployment of AI to the benefit of everyone.
We believe that having procedures in place to track the risk attributes that arise in models, and to respond adequately to related results, is a critical part of working as a responsible developer on the cutting edge of artificial intelligence.
The above is the detailed content of Google DeepMind, OpenAI and others jointly issued an article: How to evaluate the extreme risks of large AI models?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
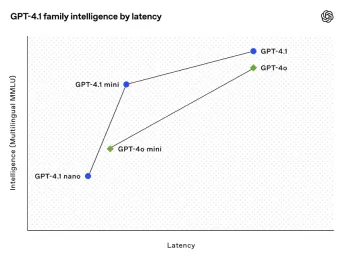 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use






